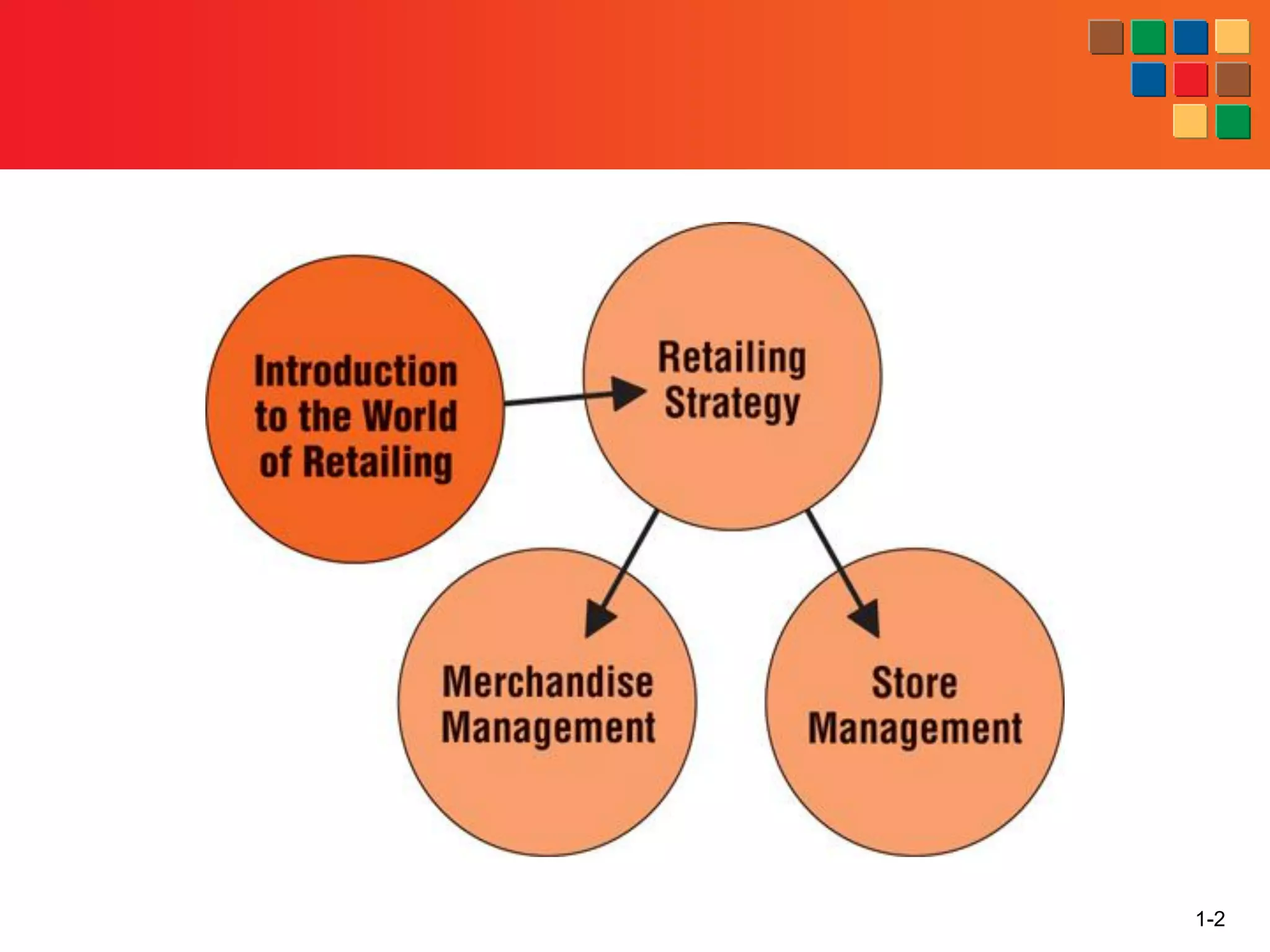
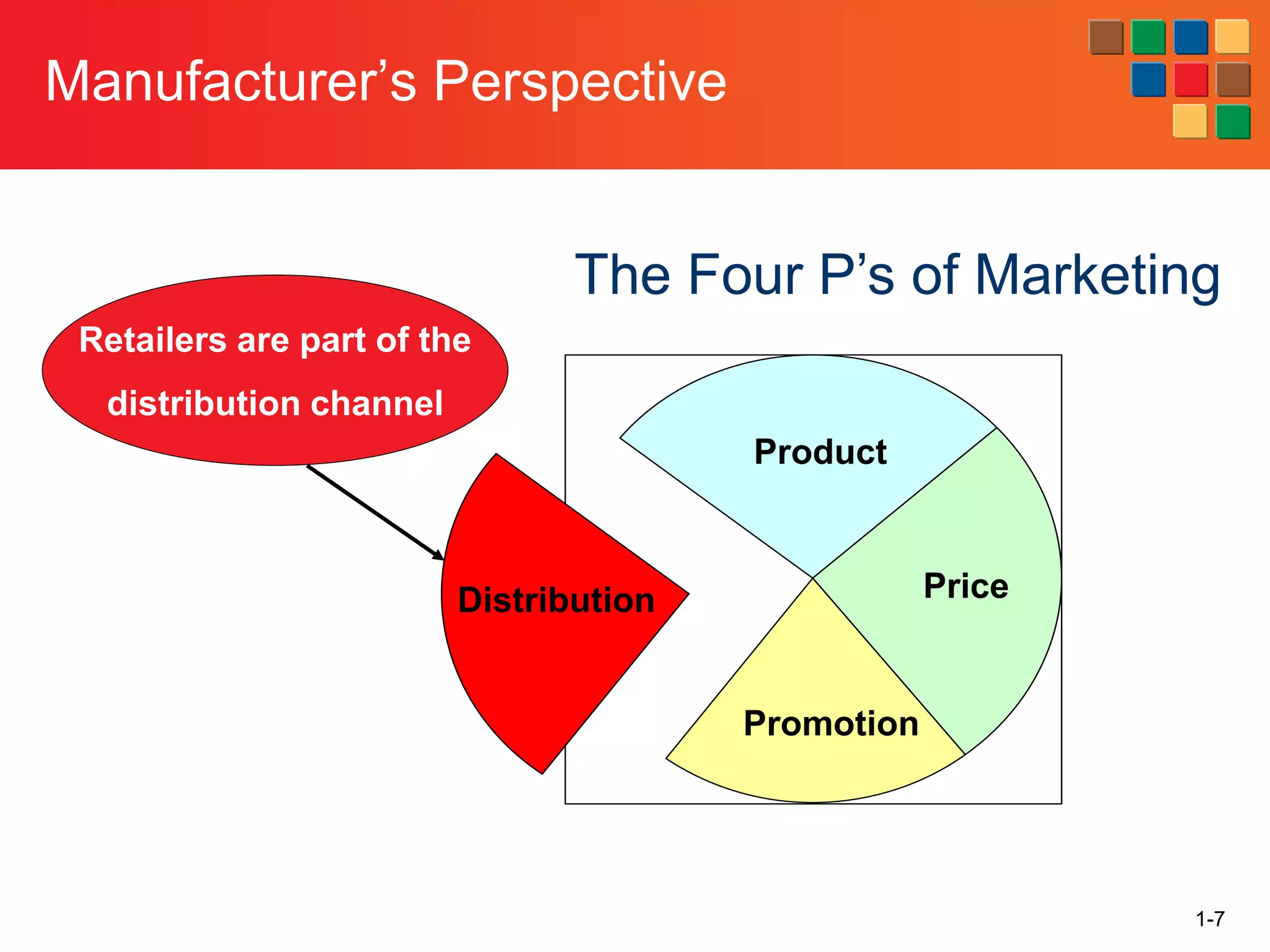
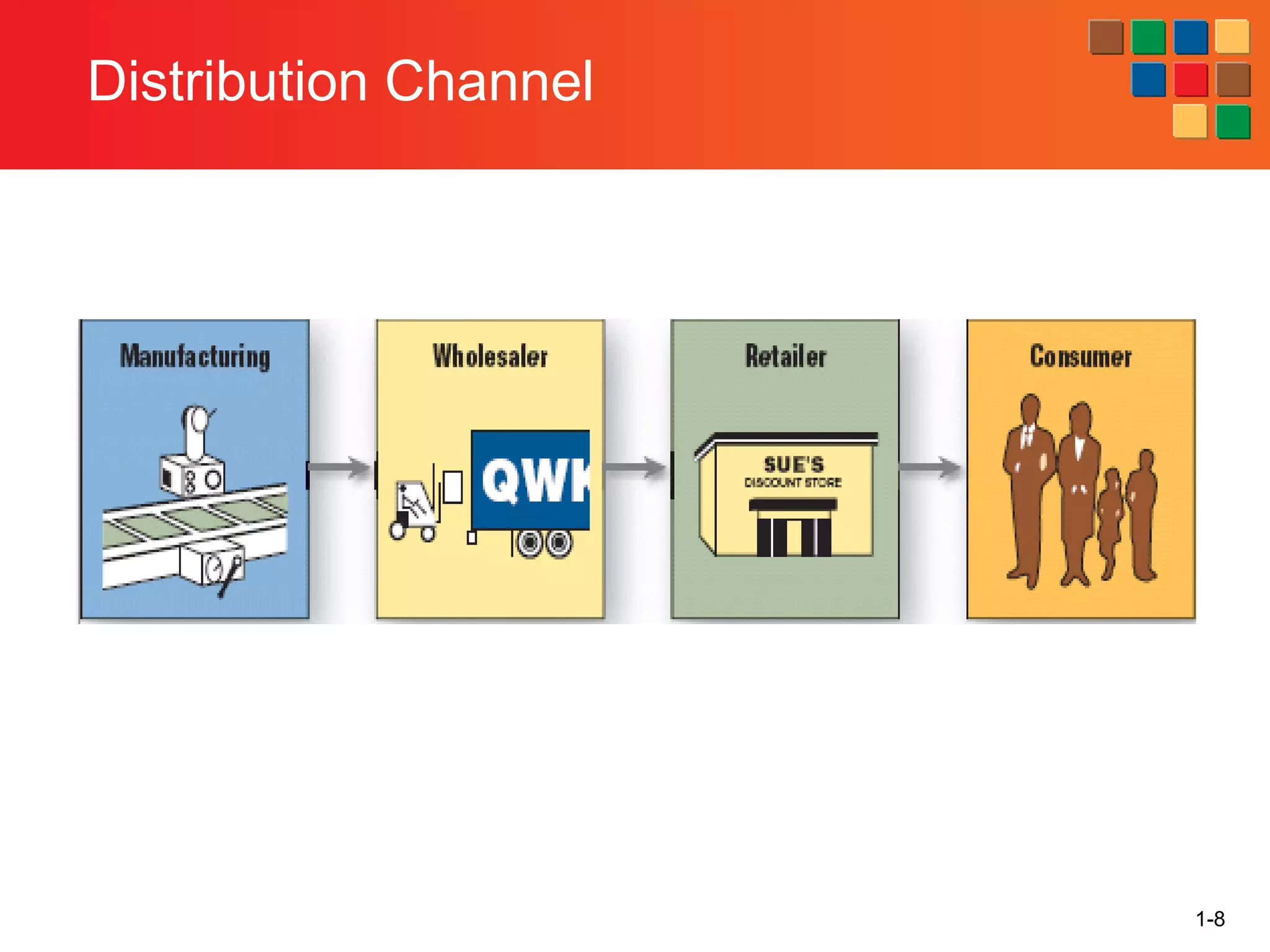
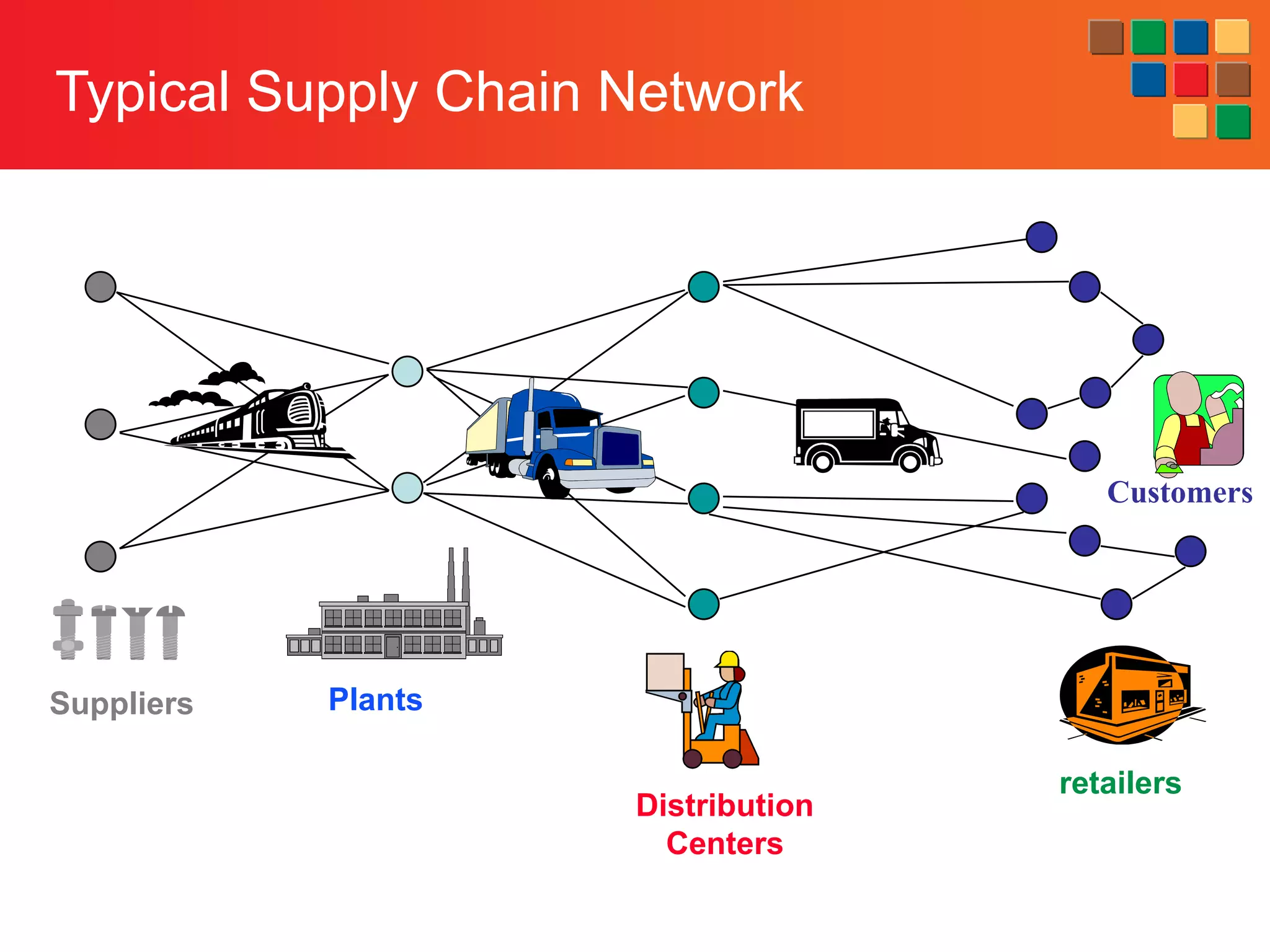
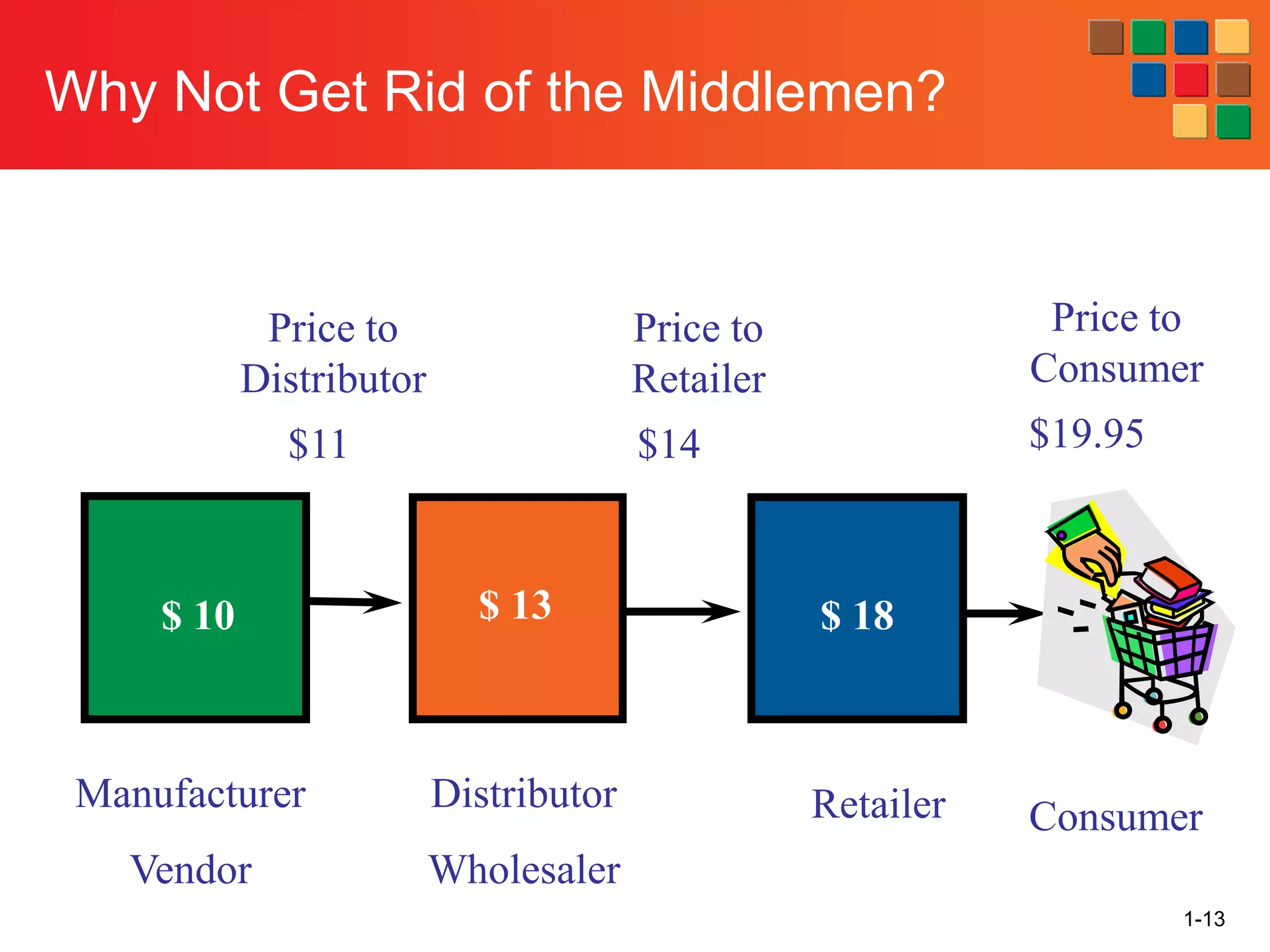
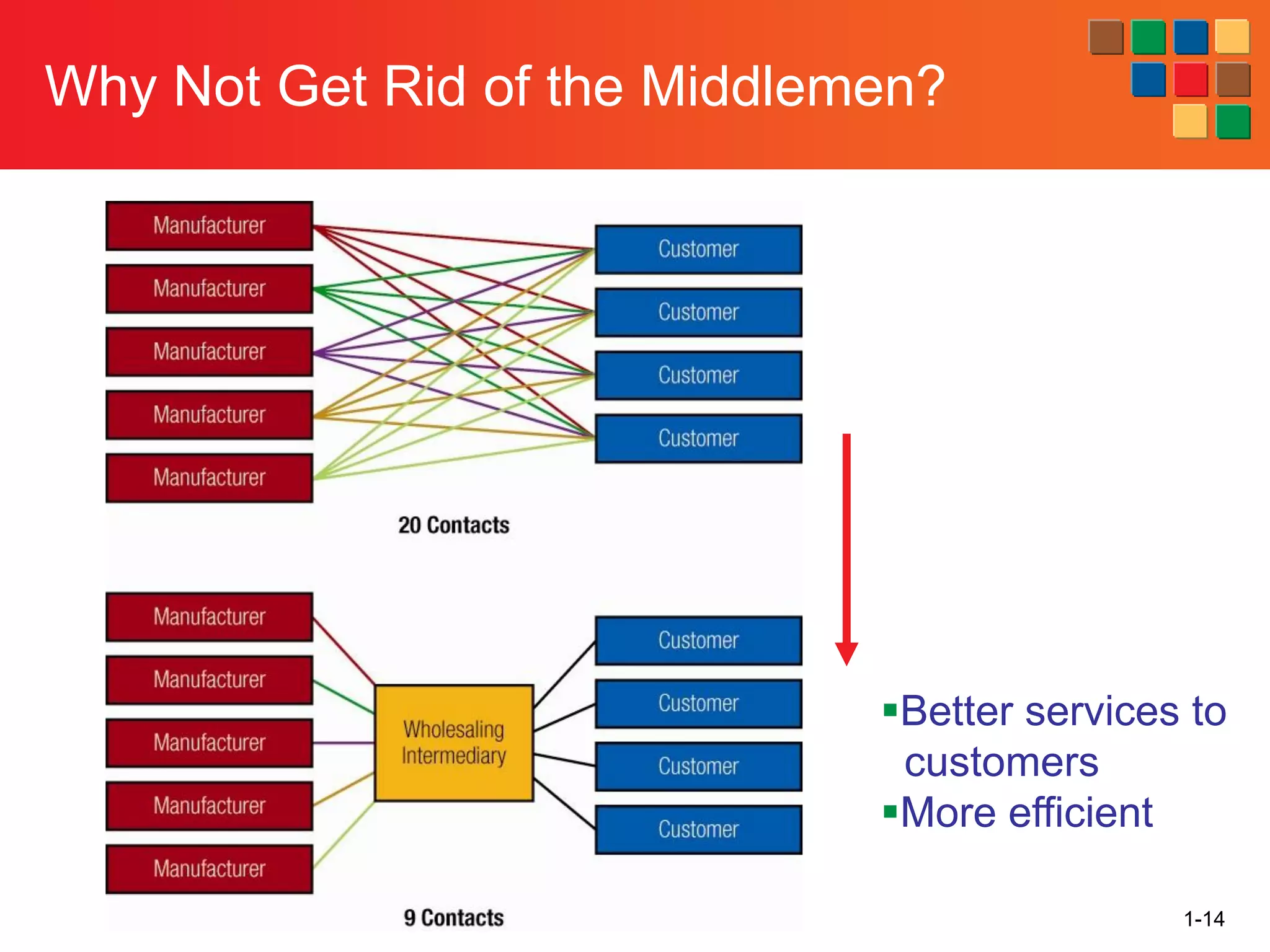
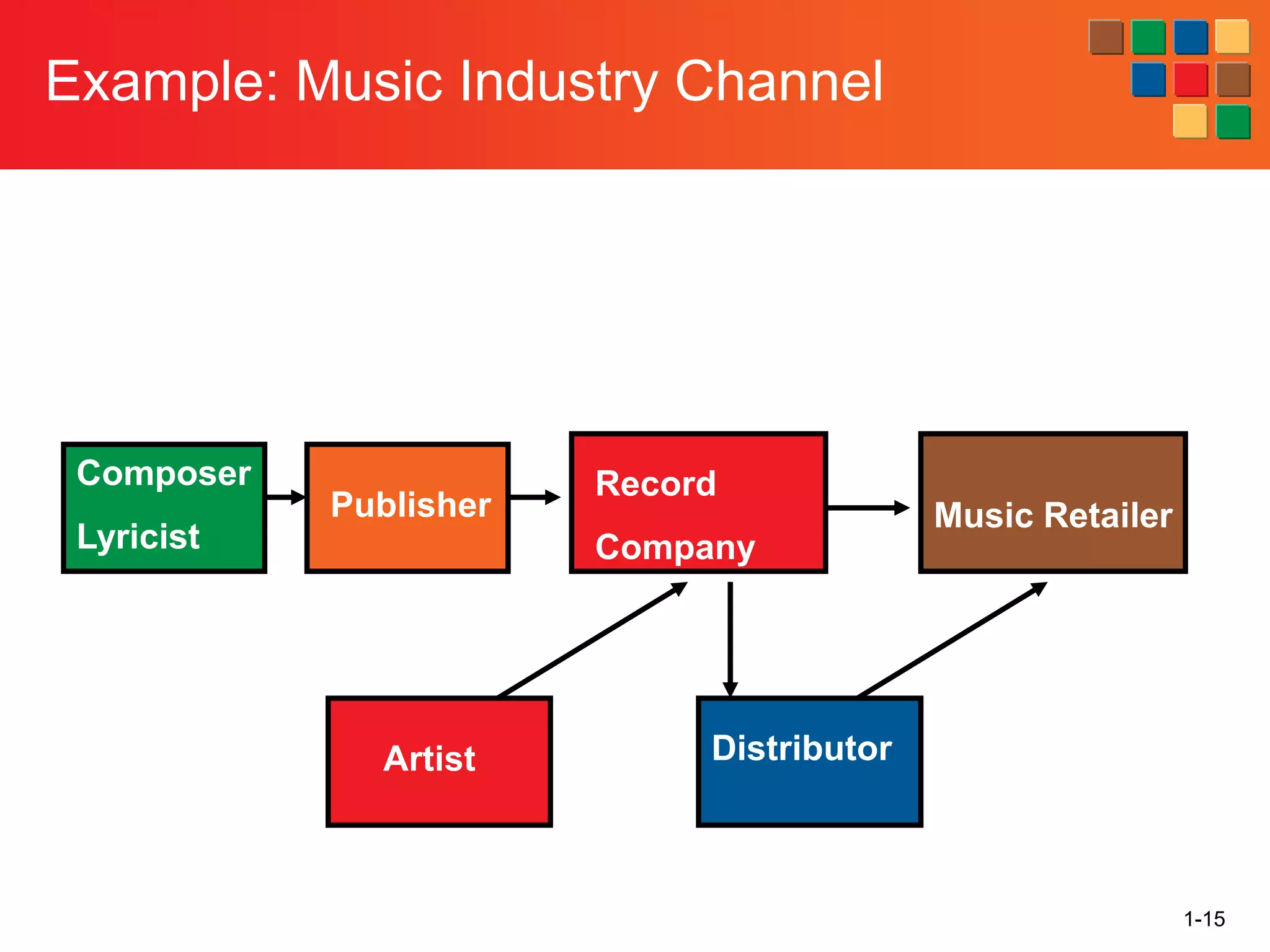
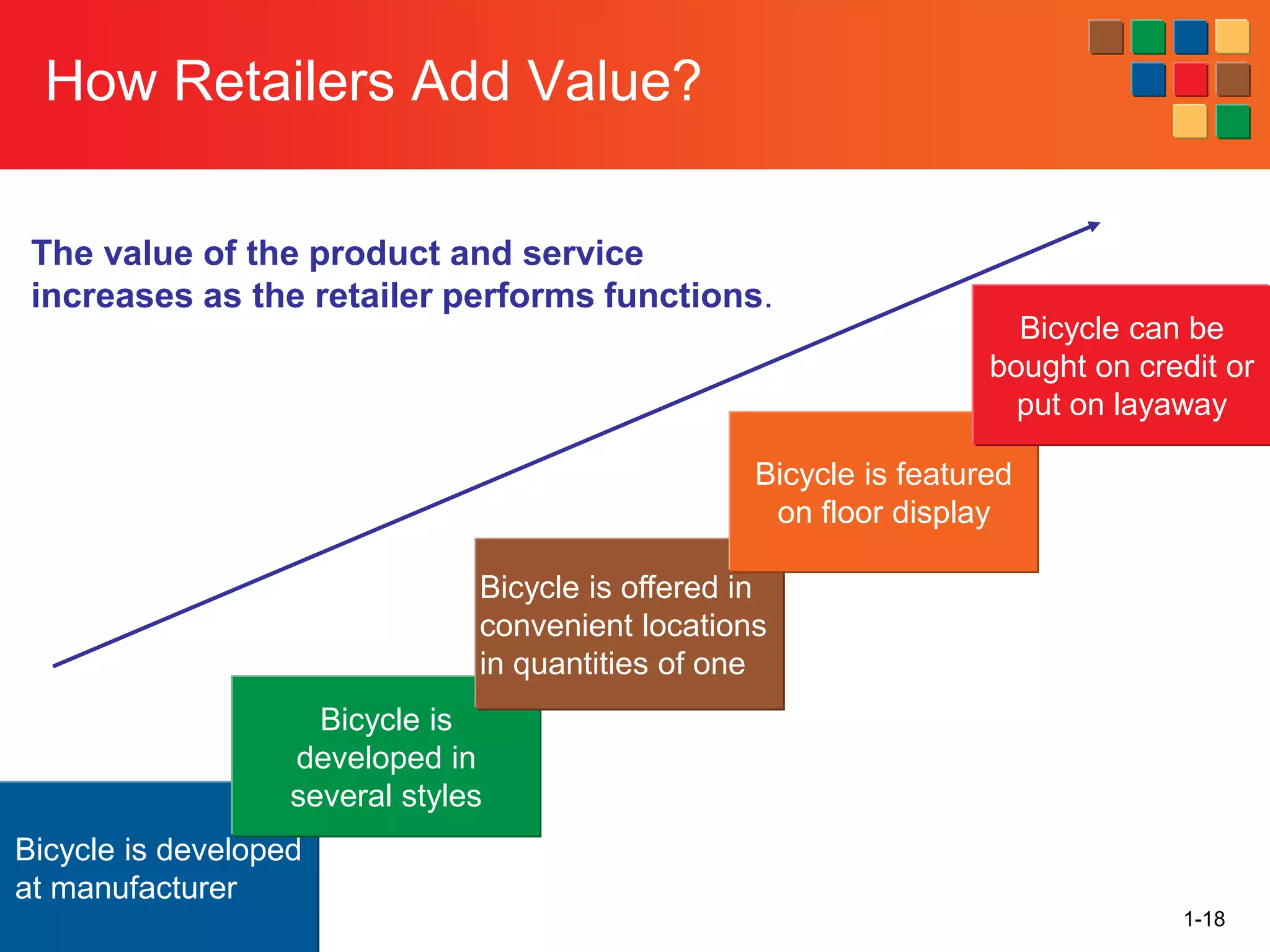
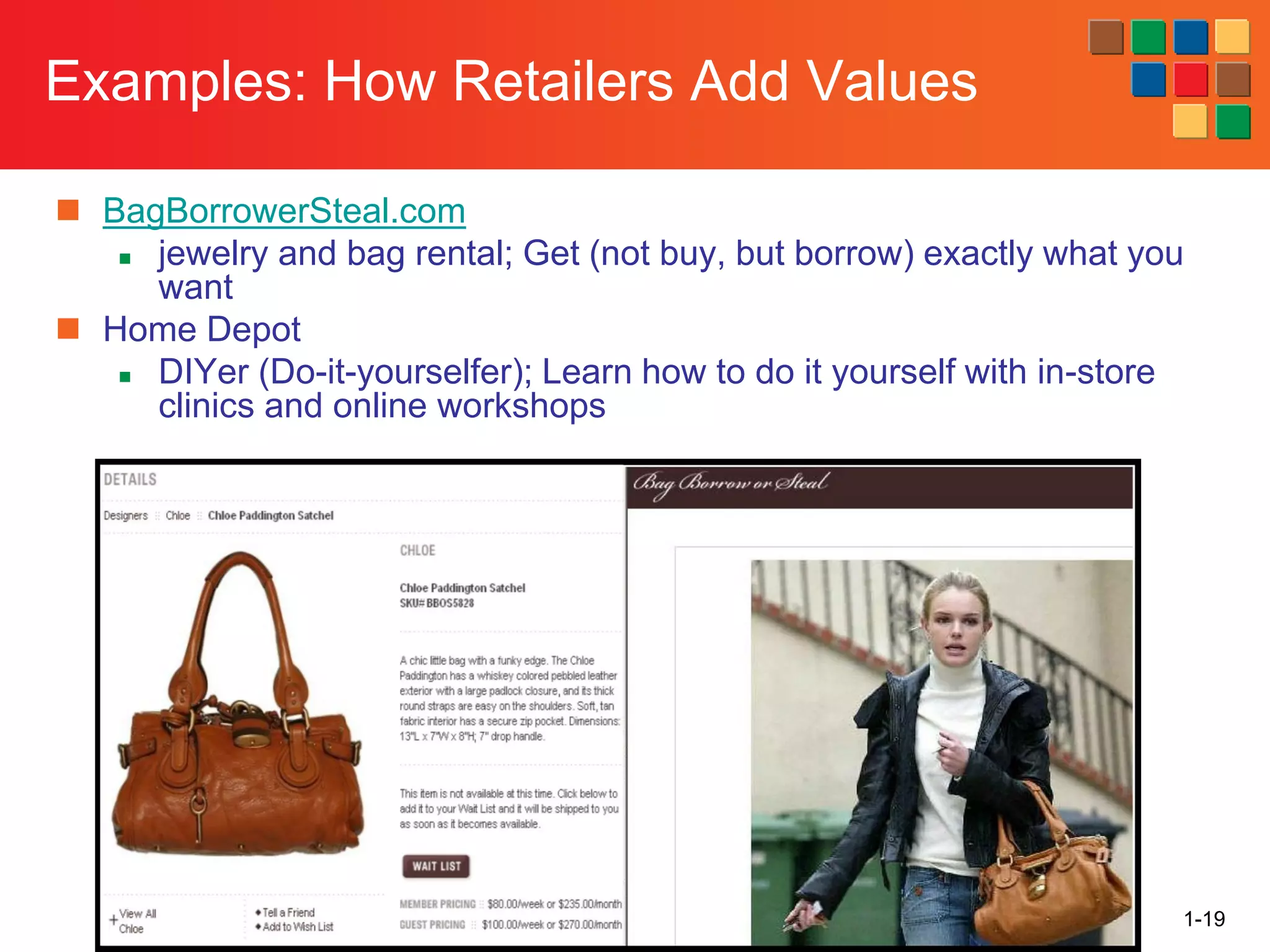
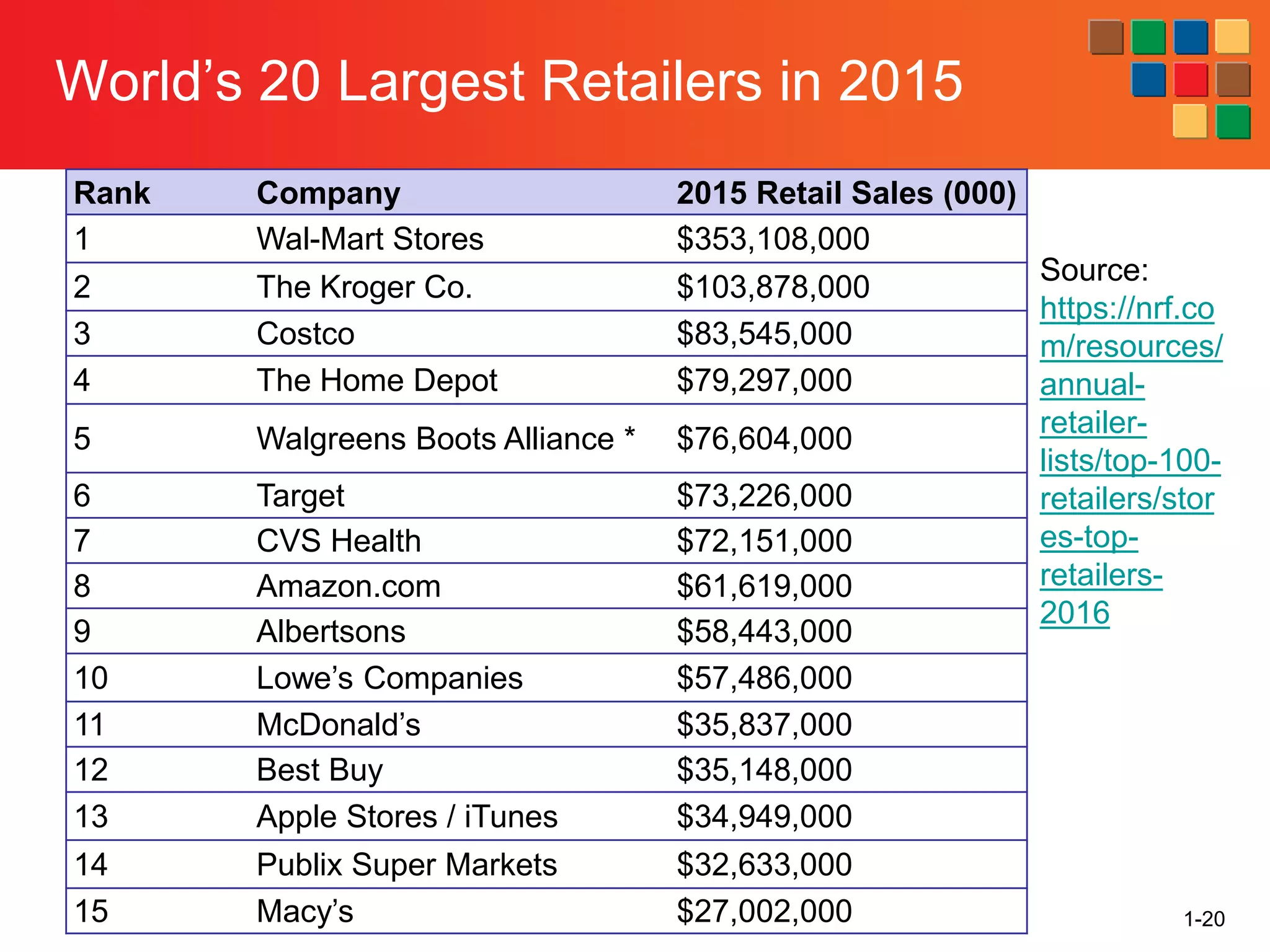
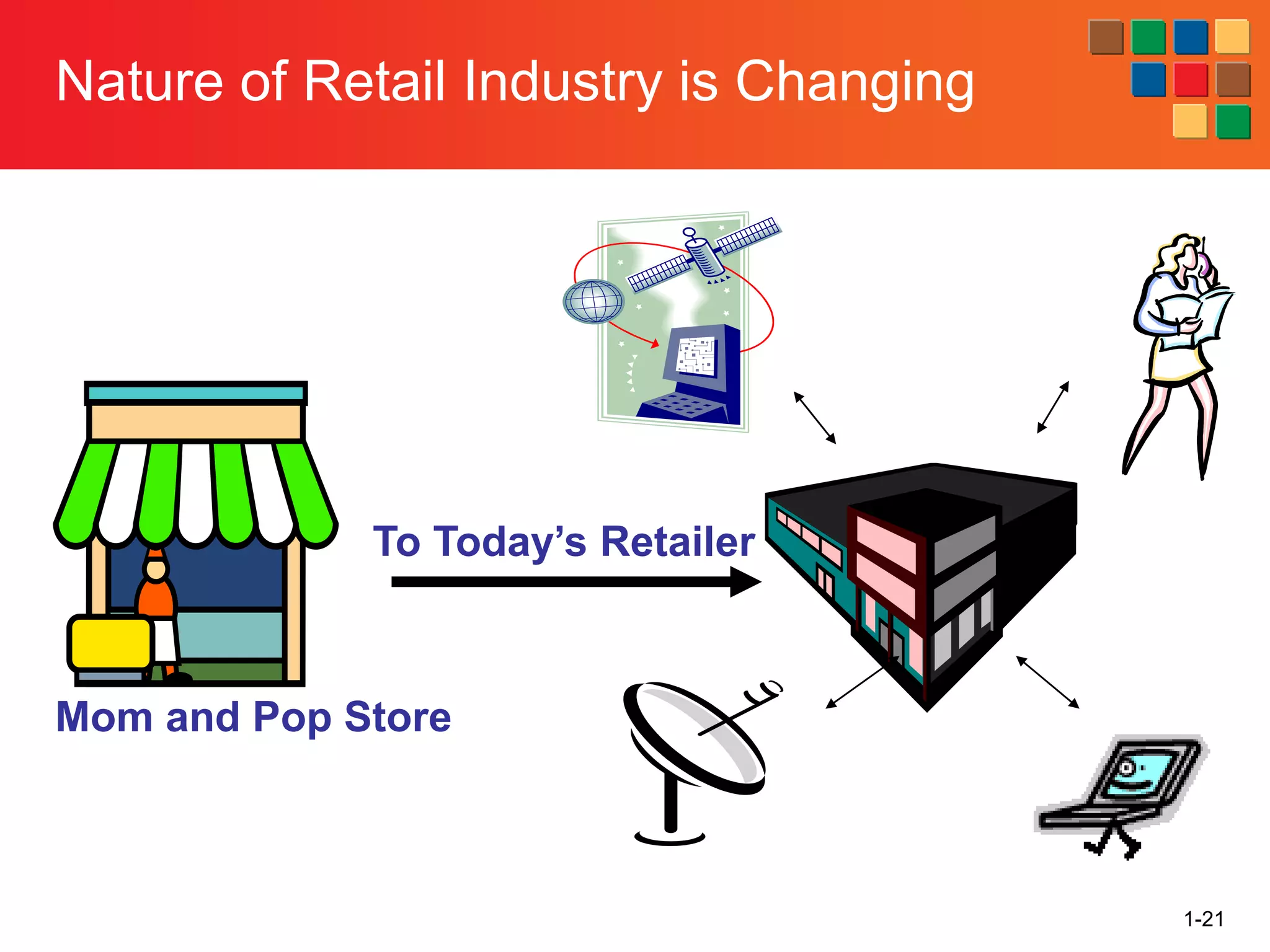
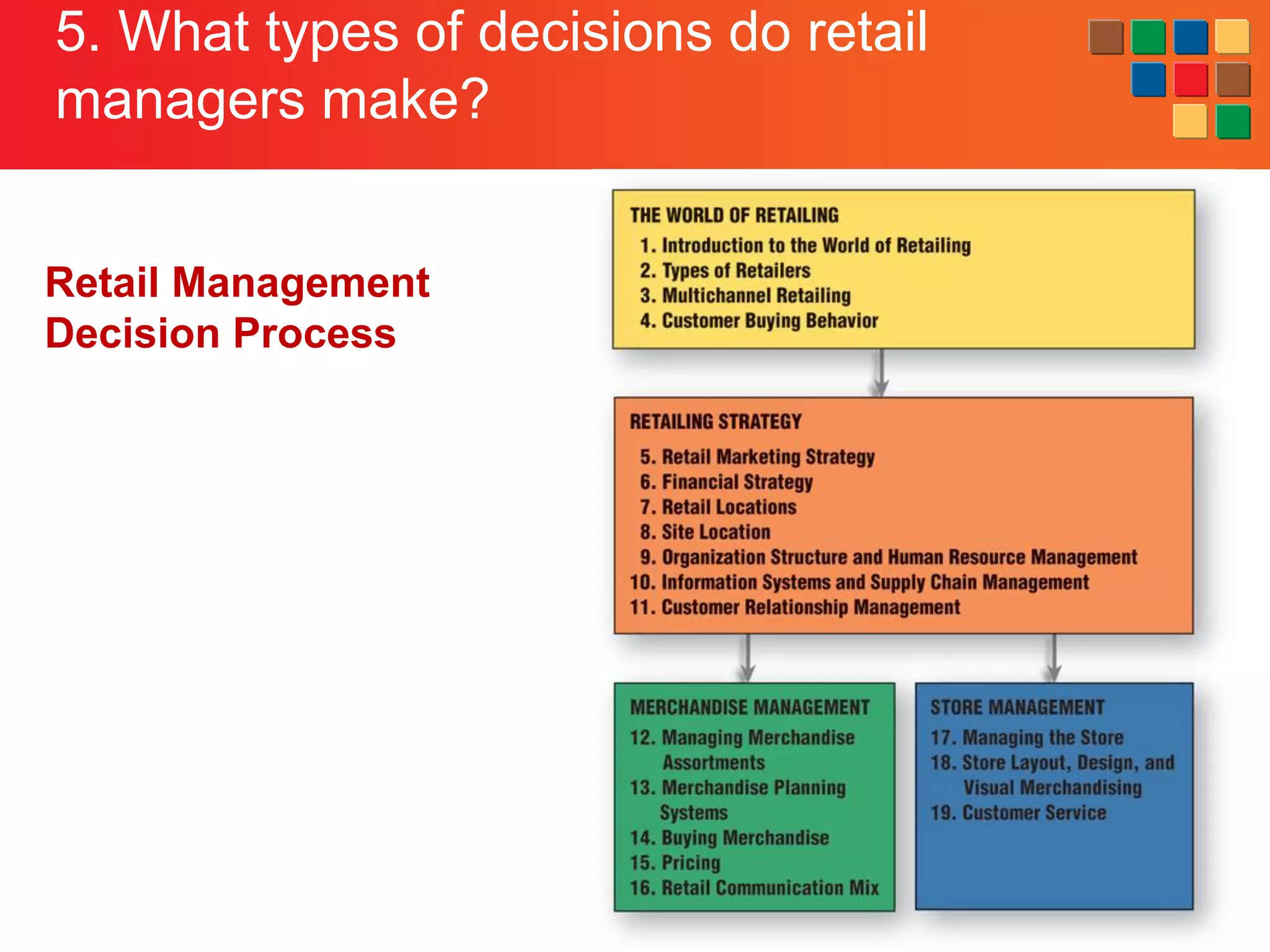
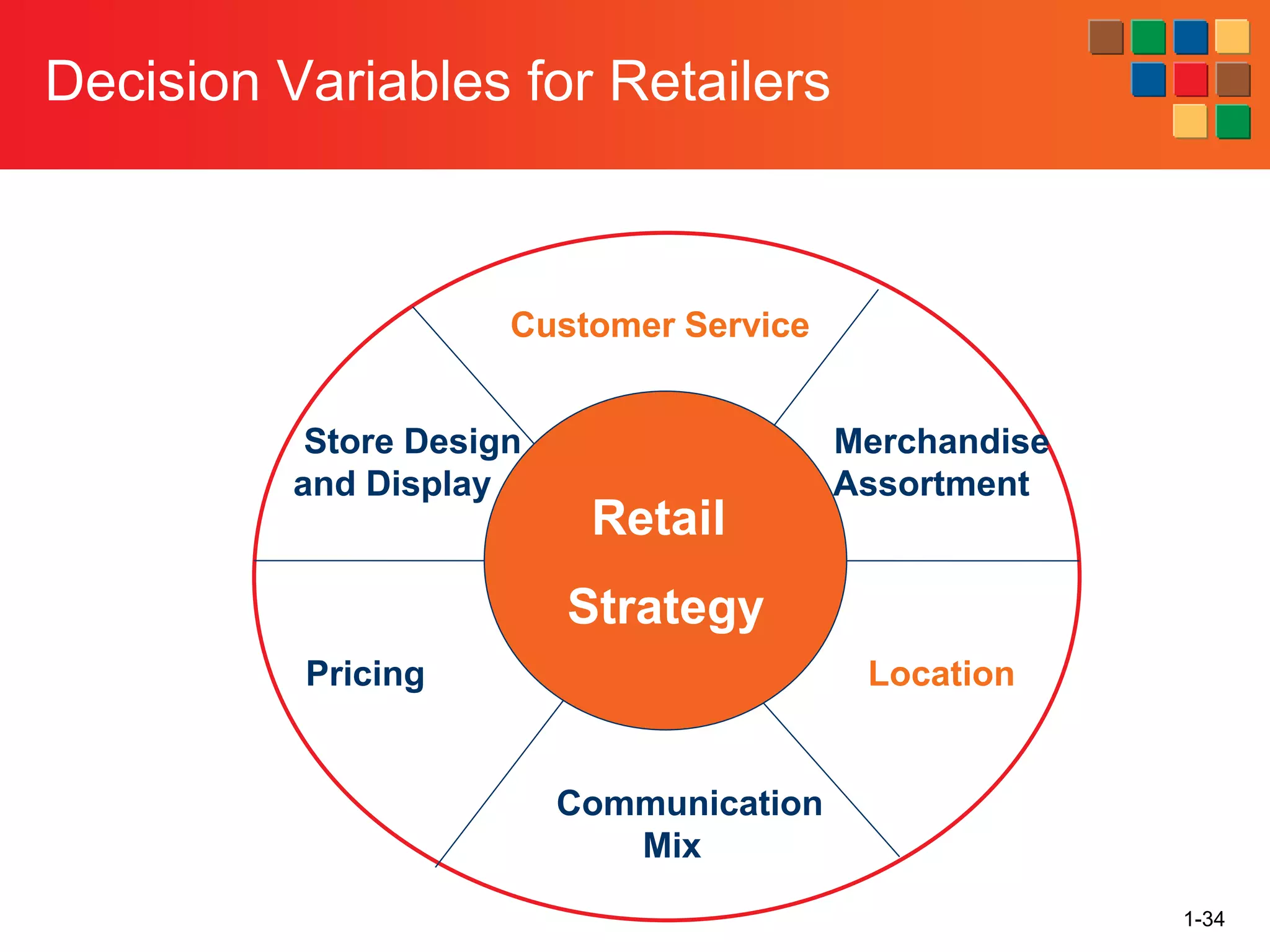
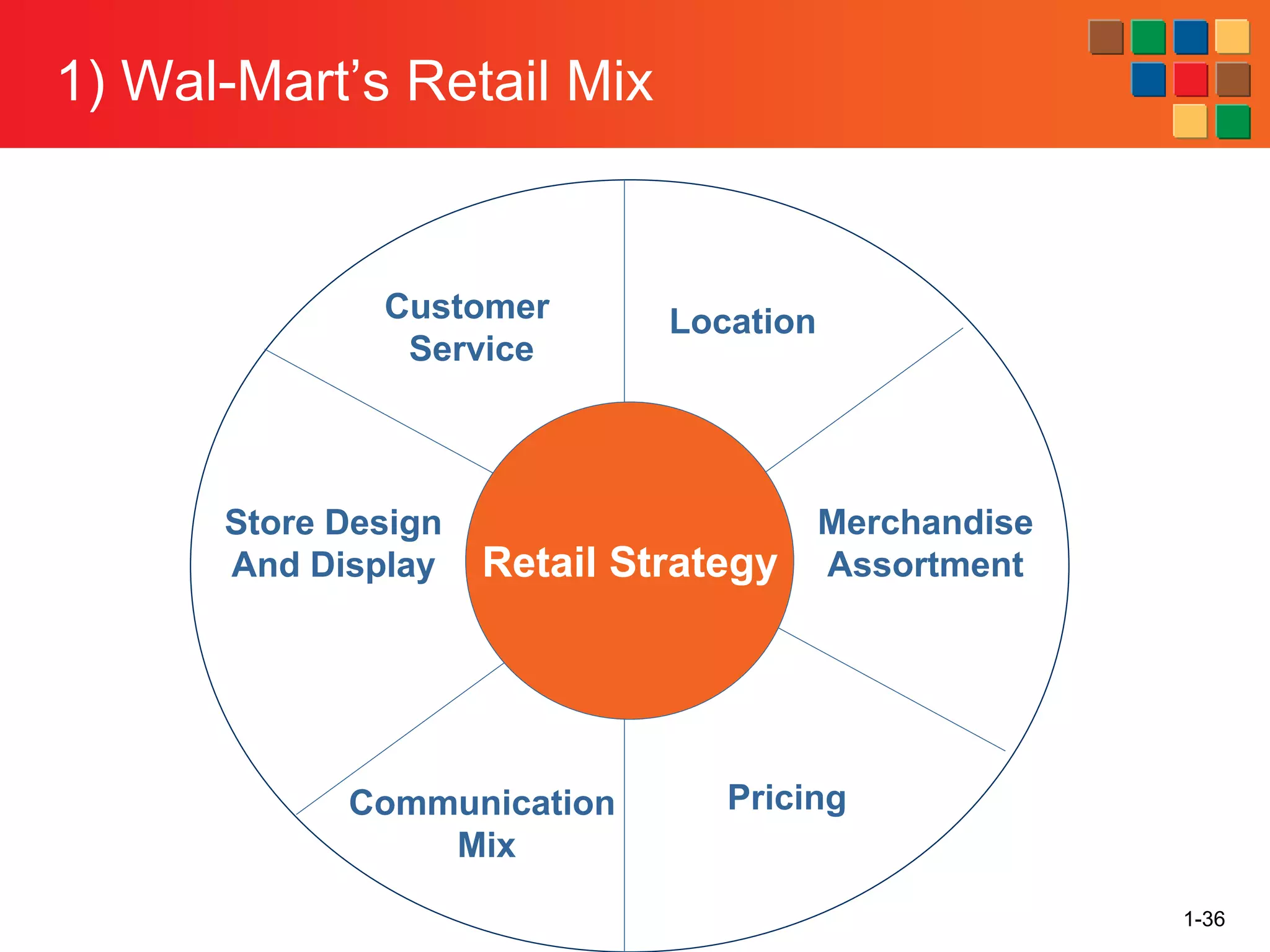
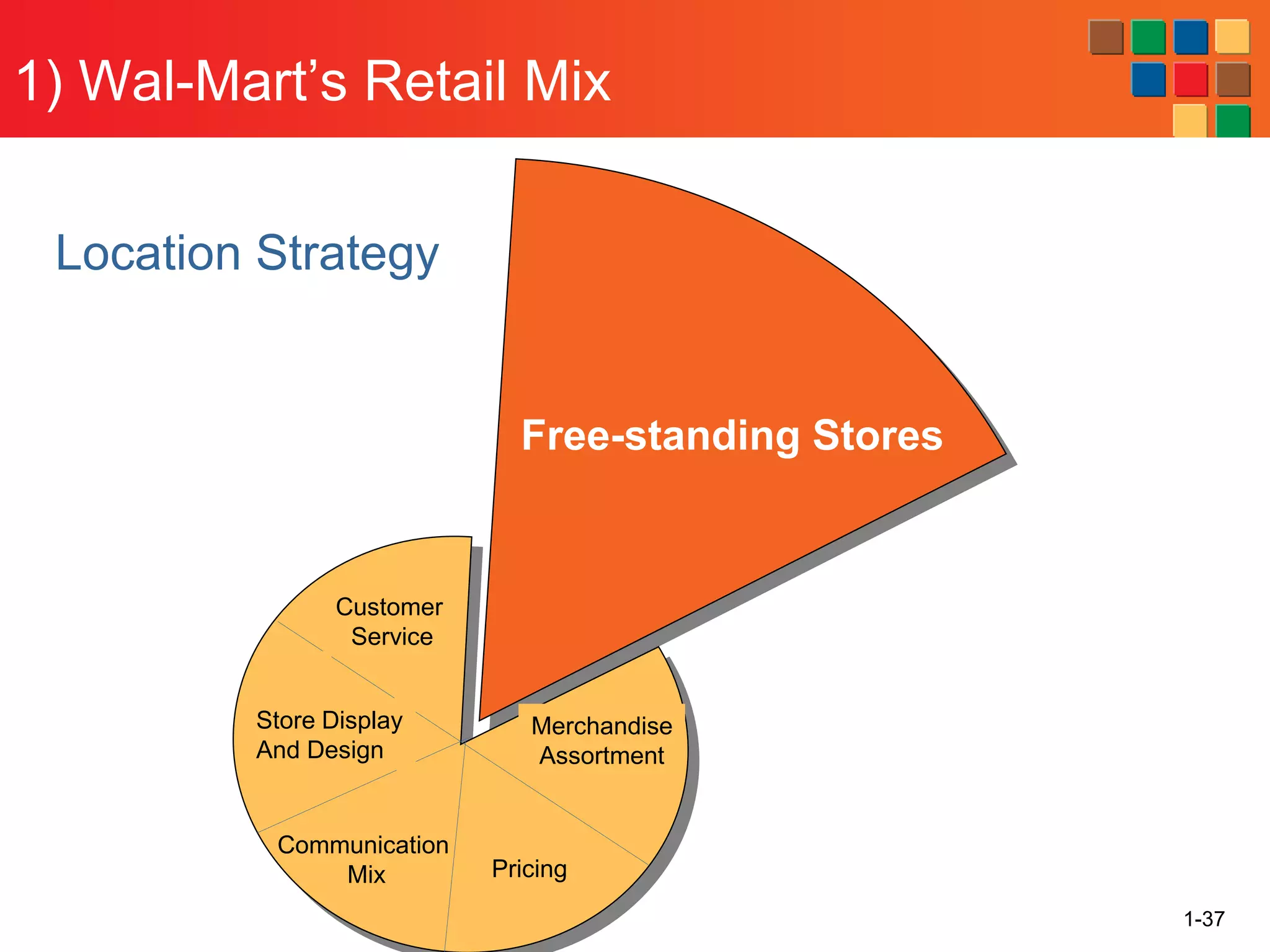
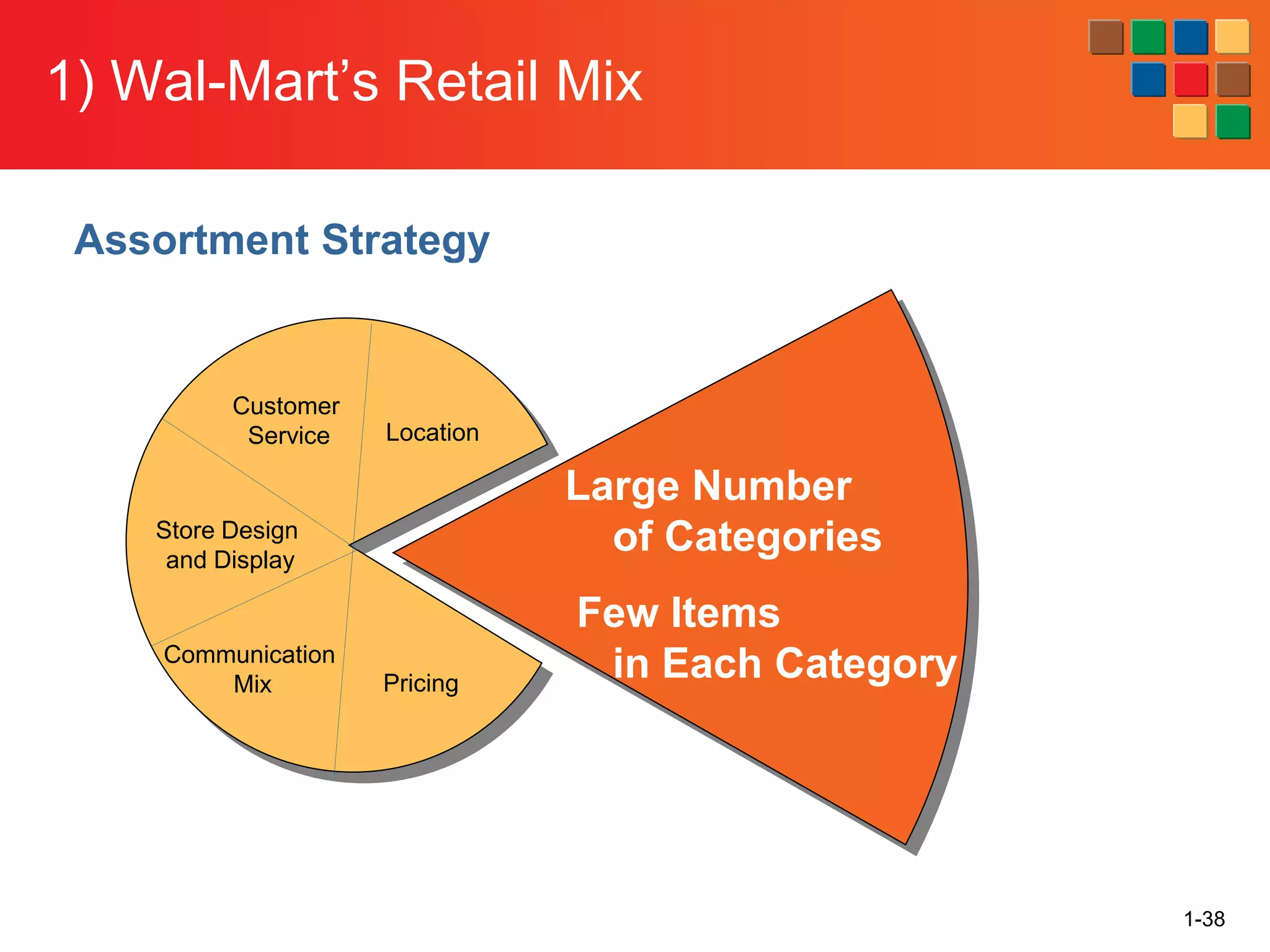
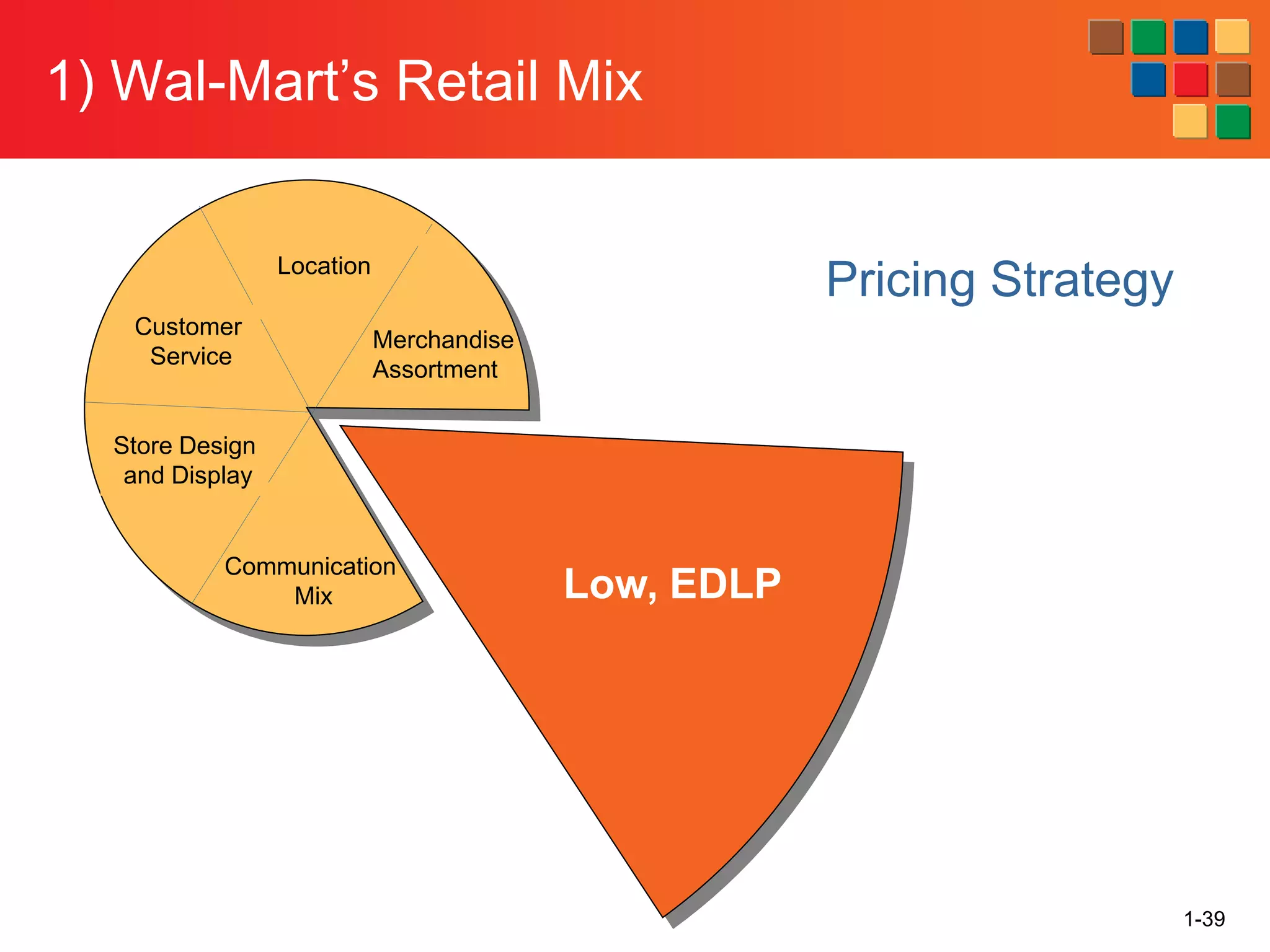
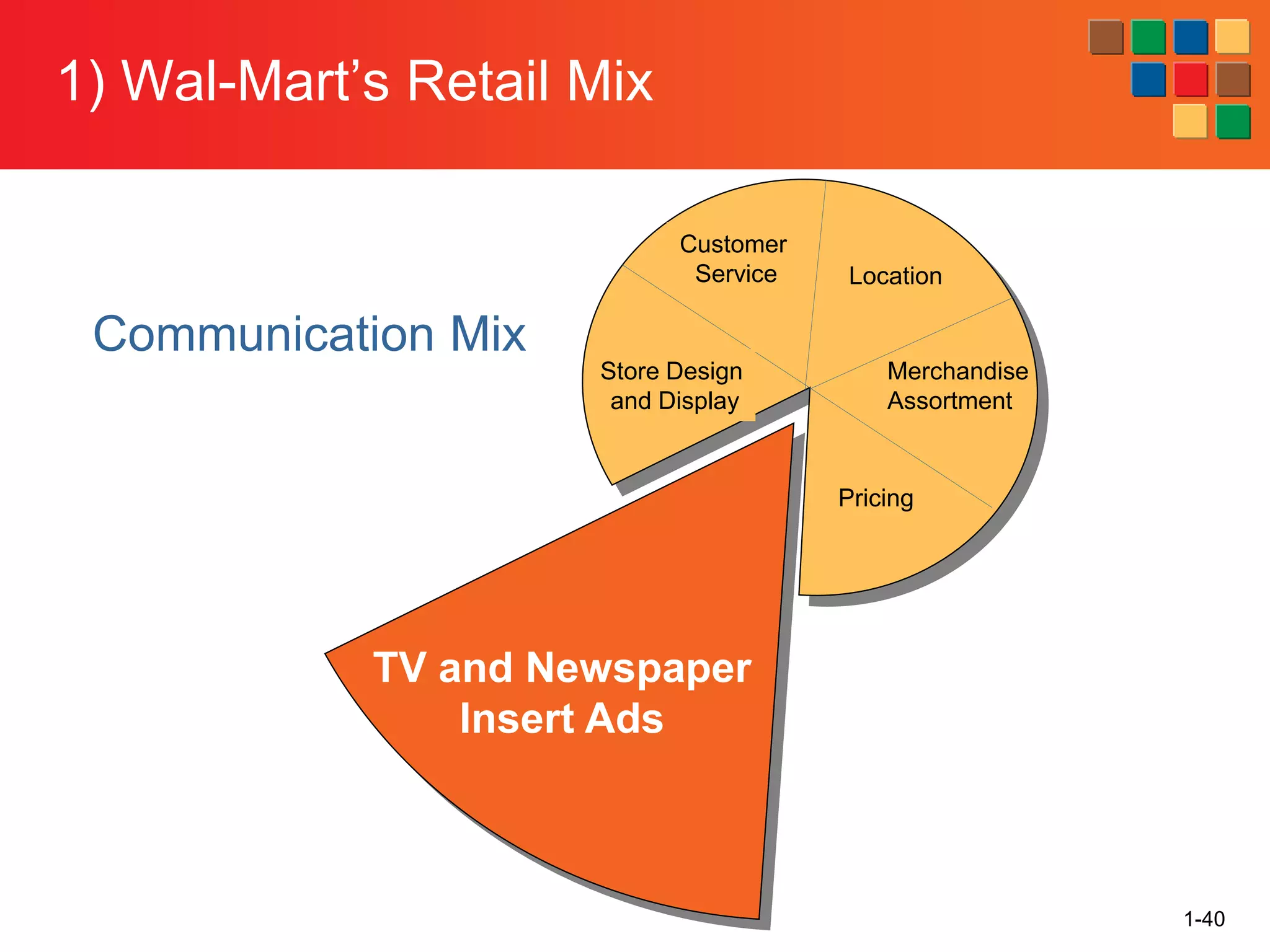
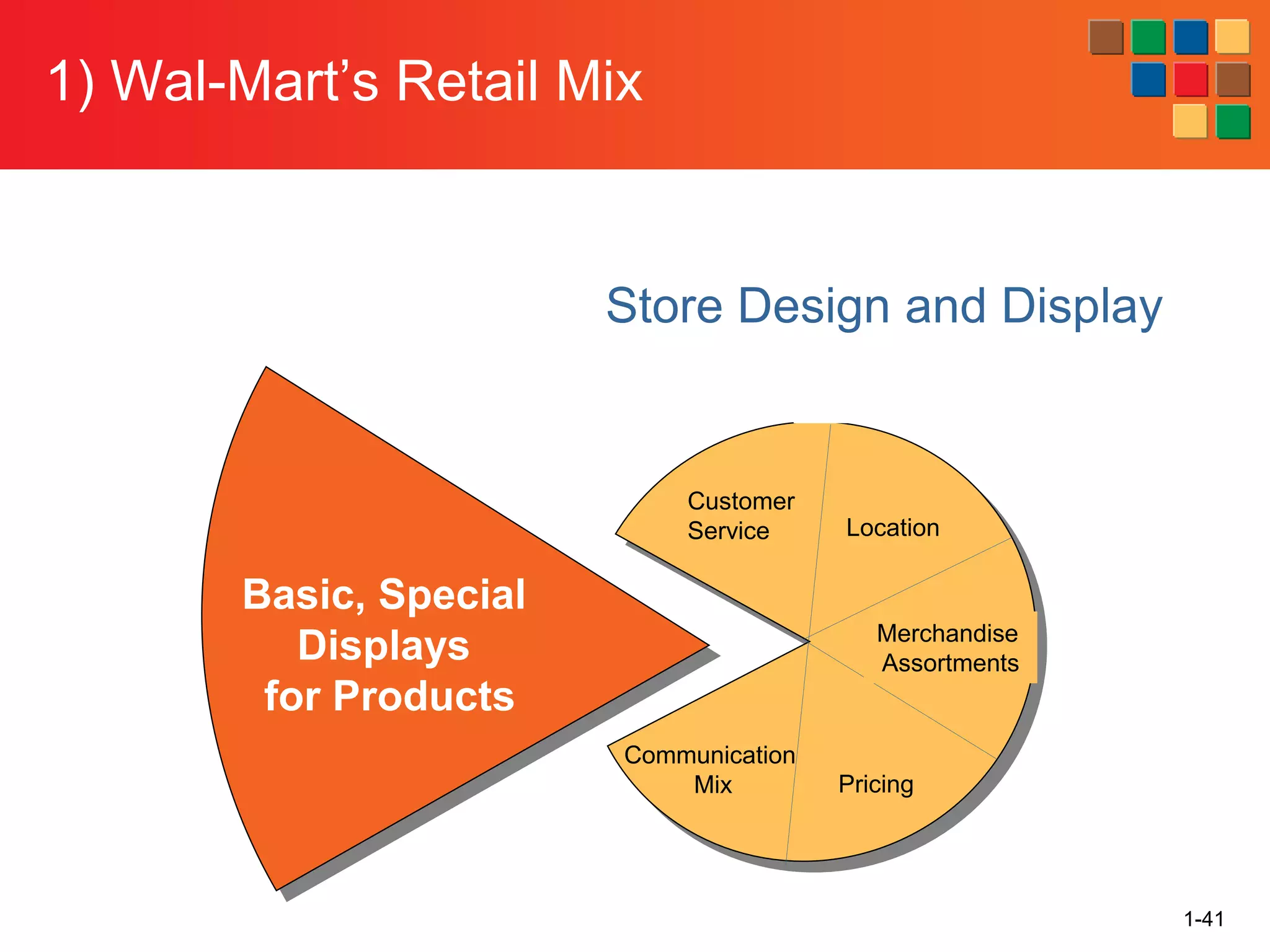
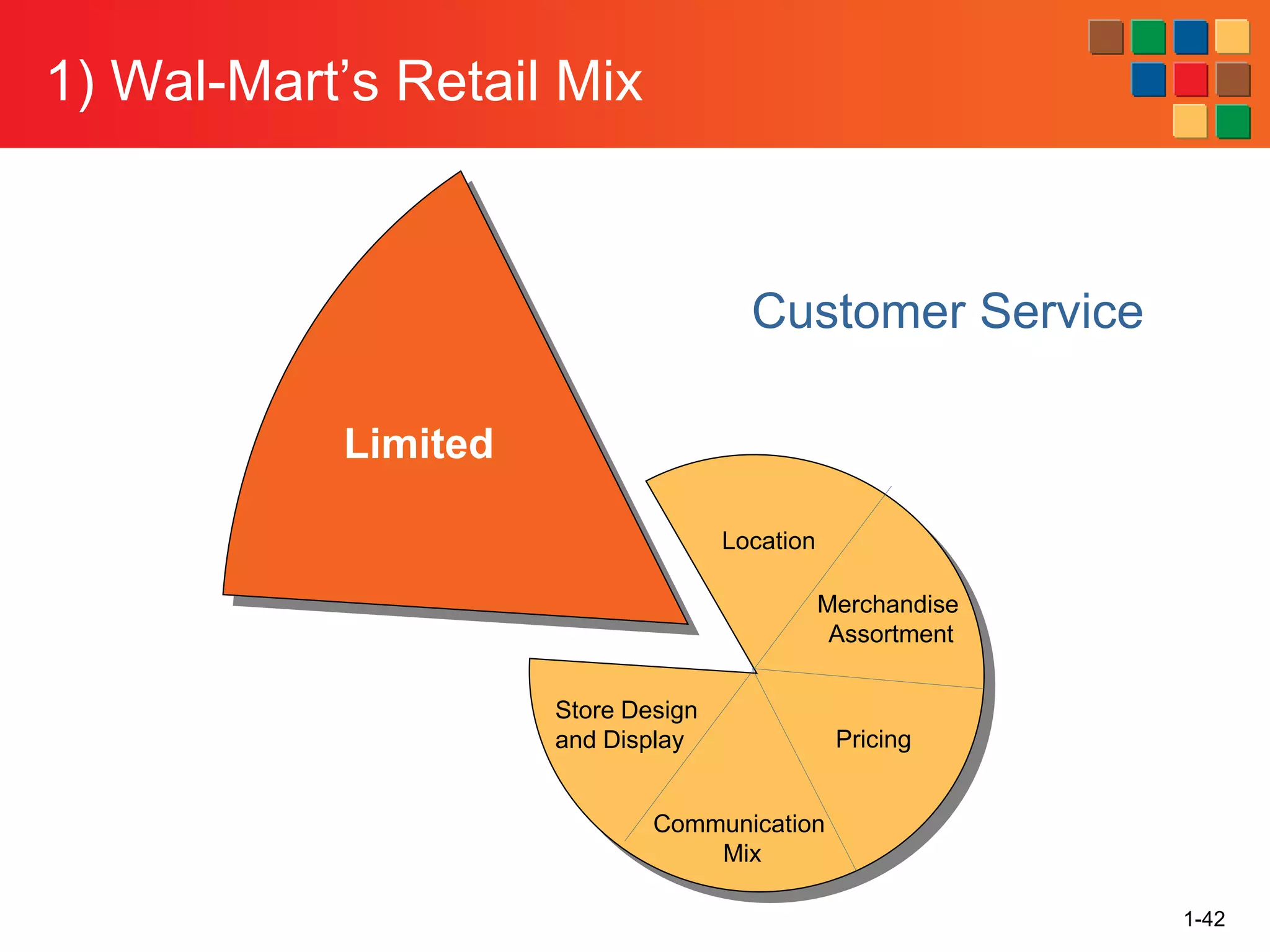
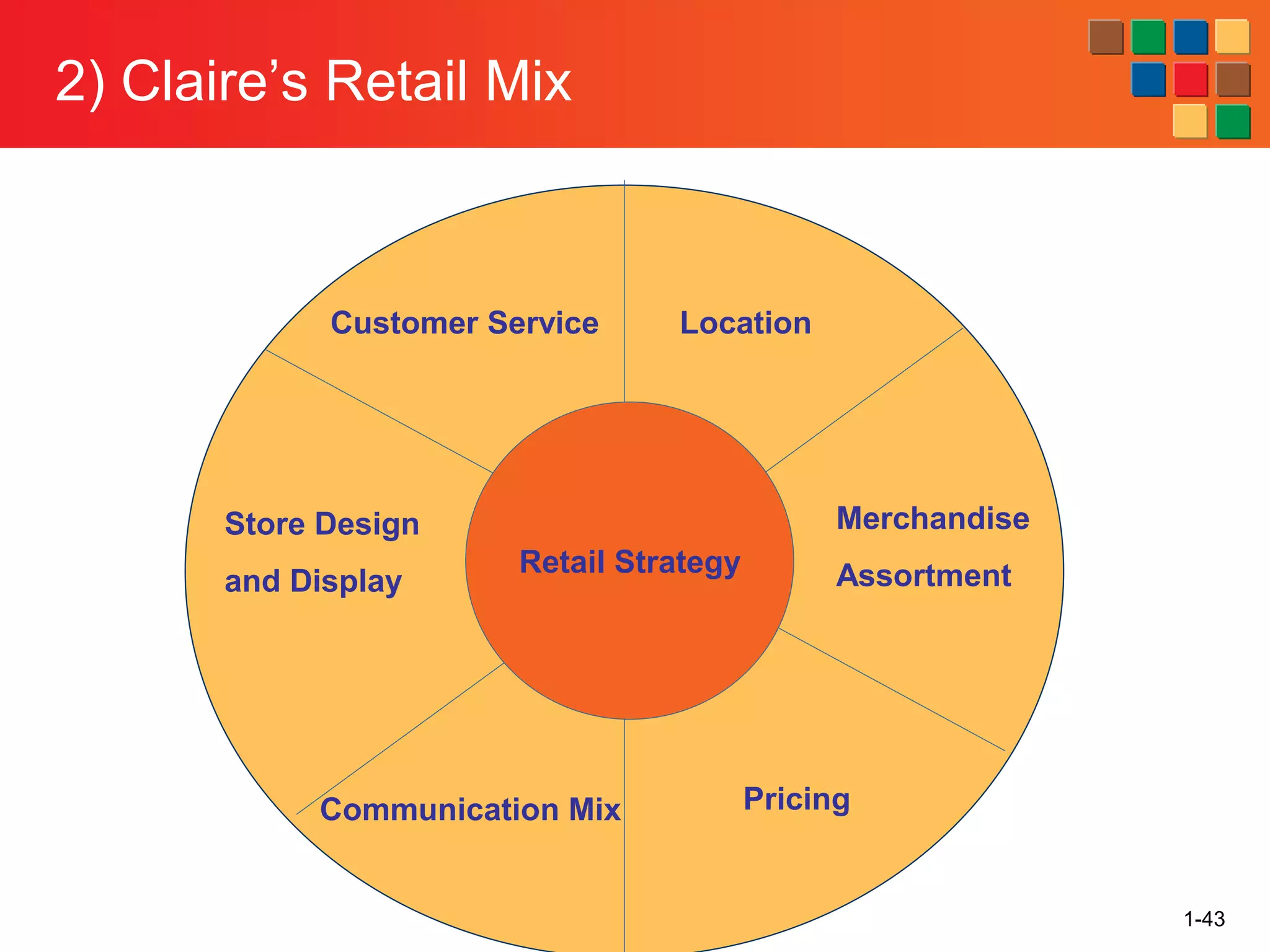
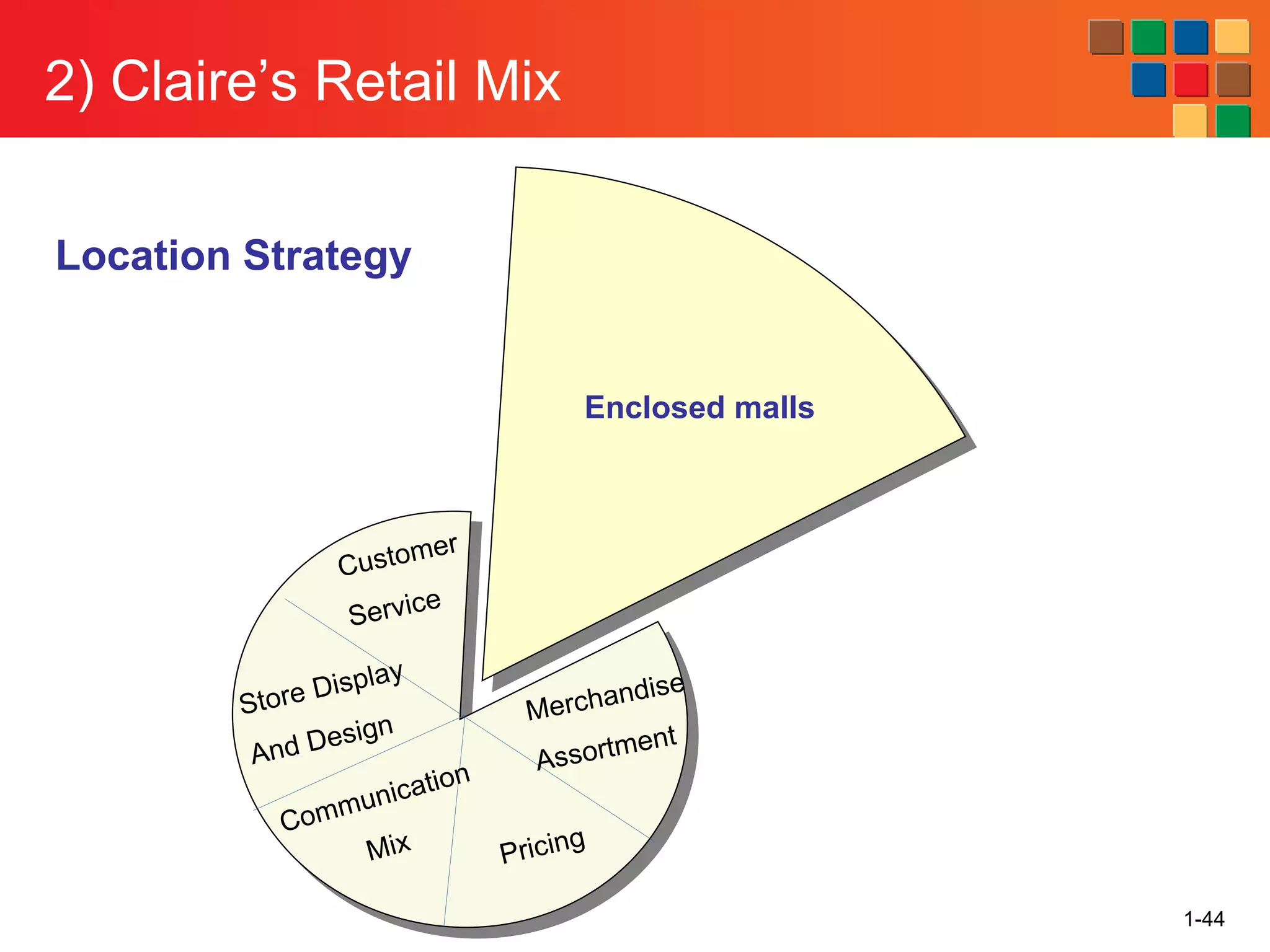
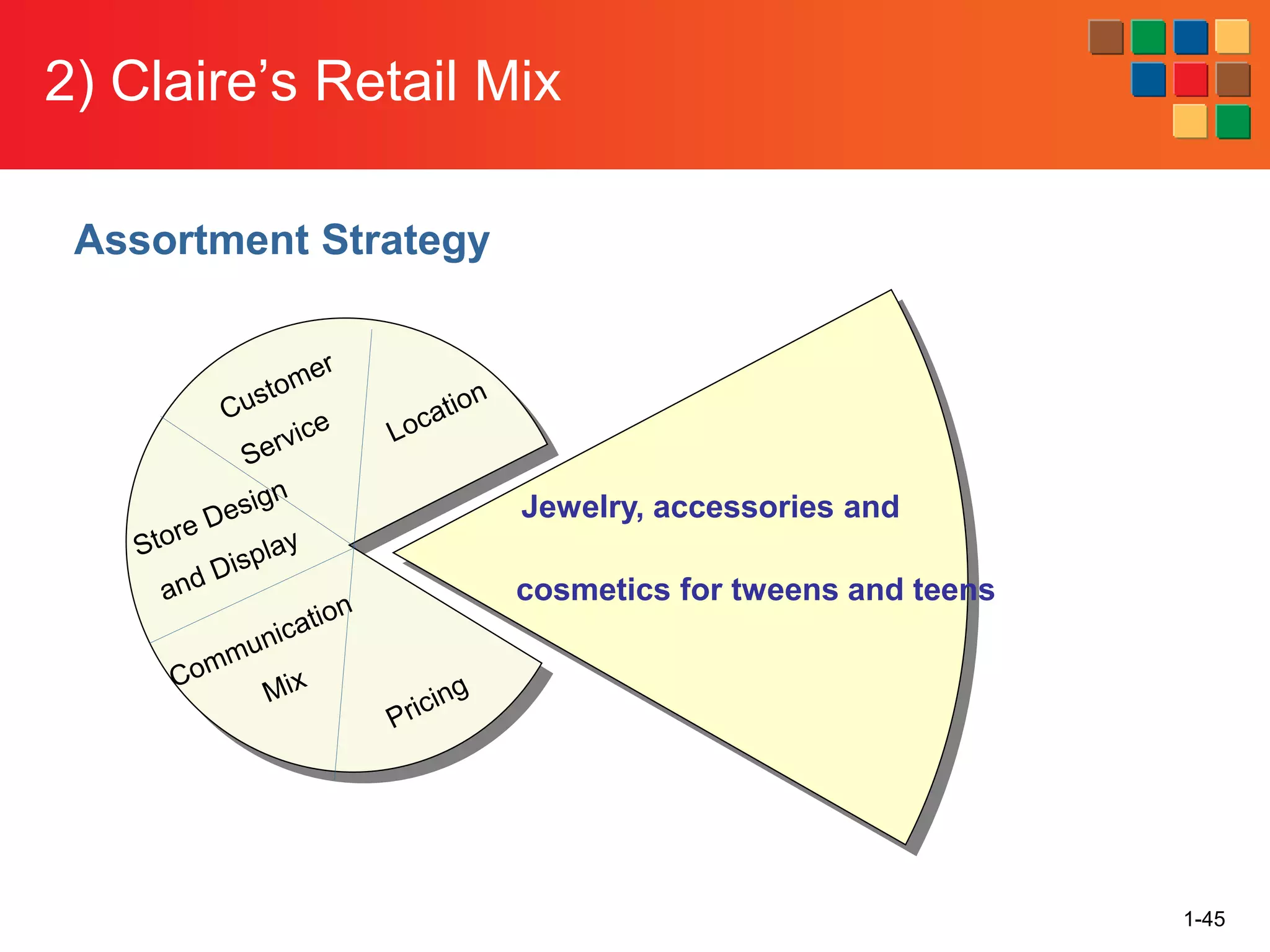
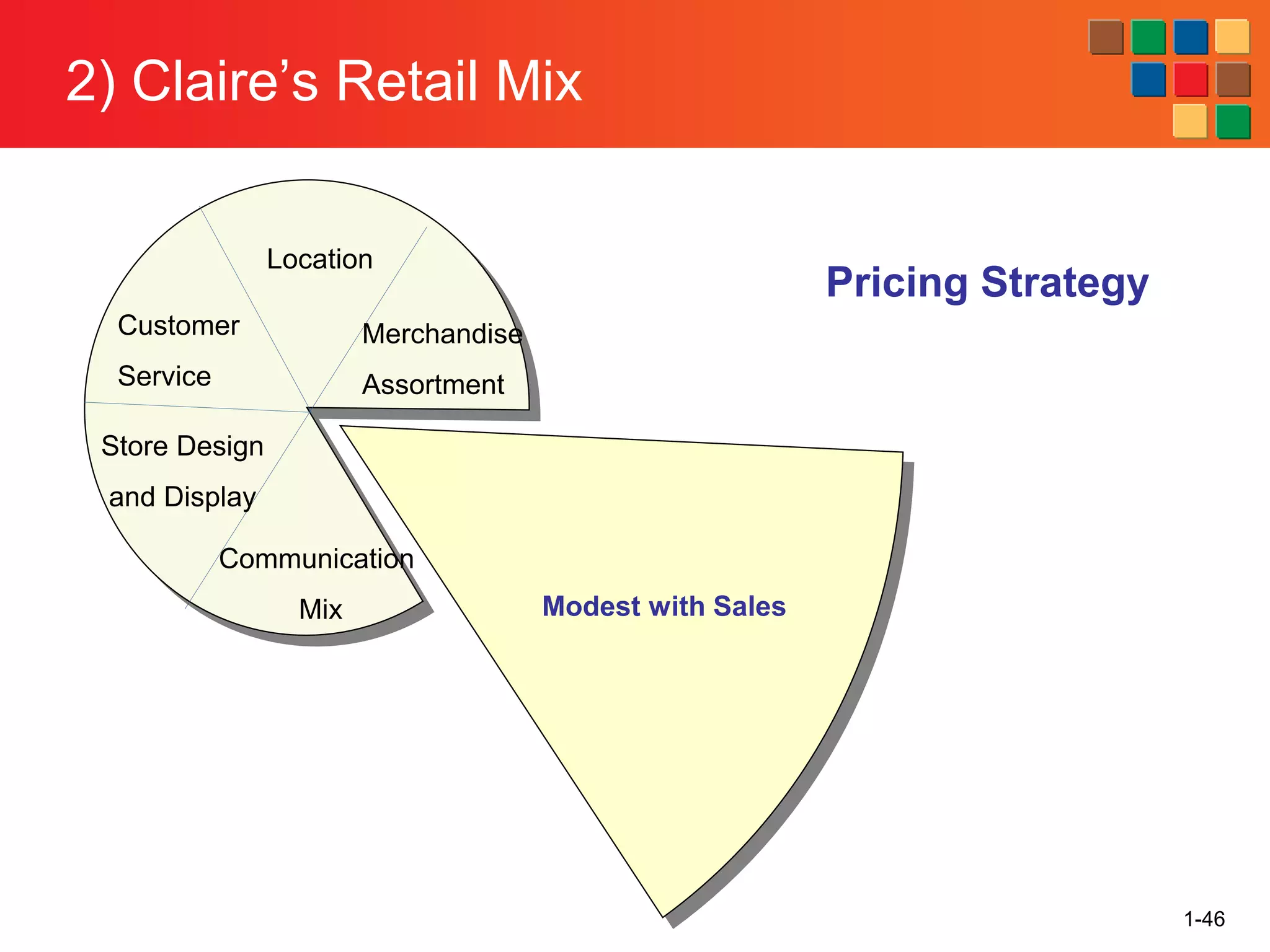
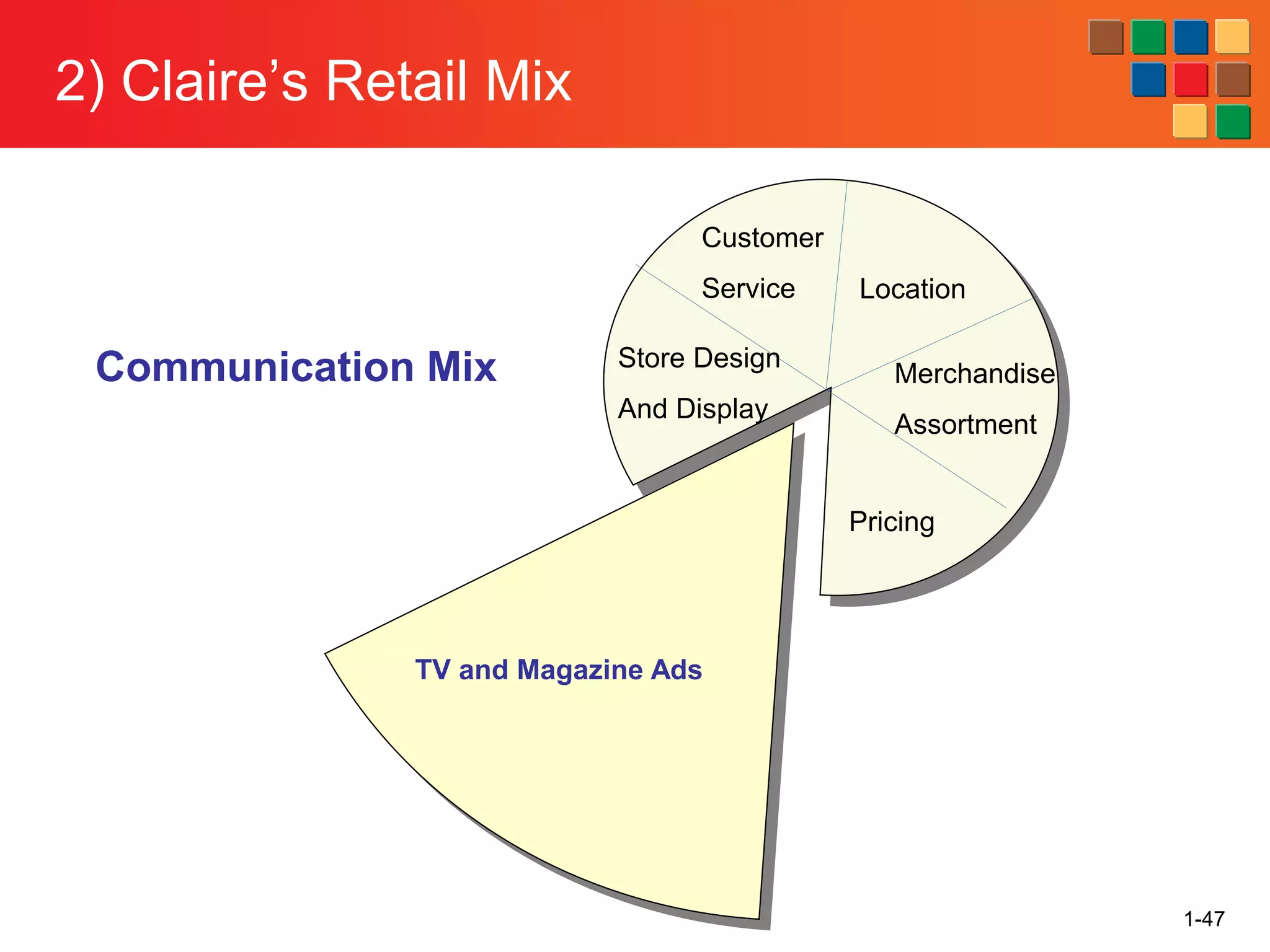
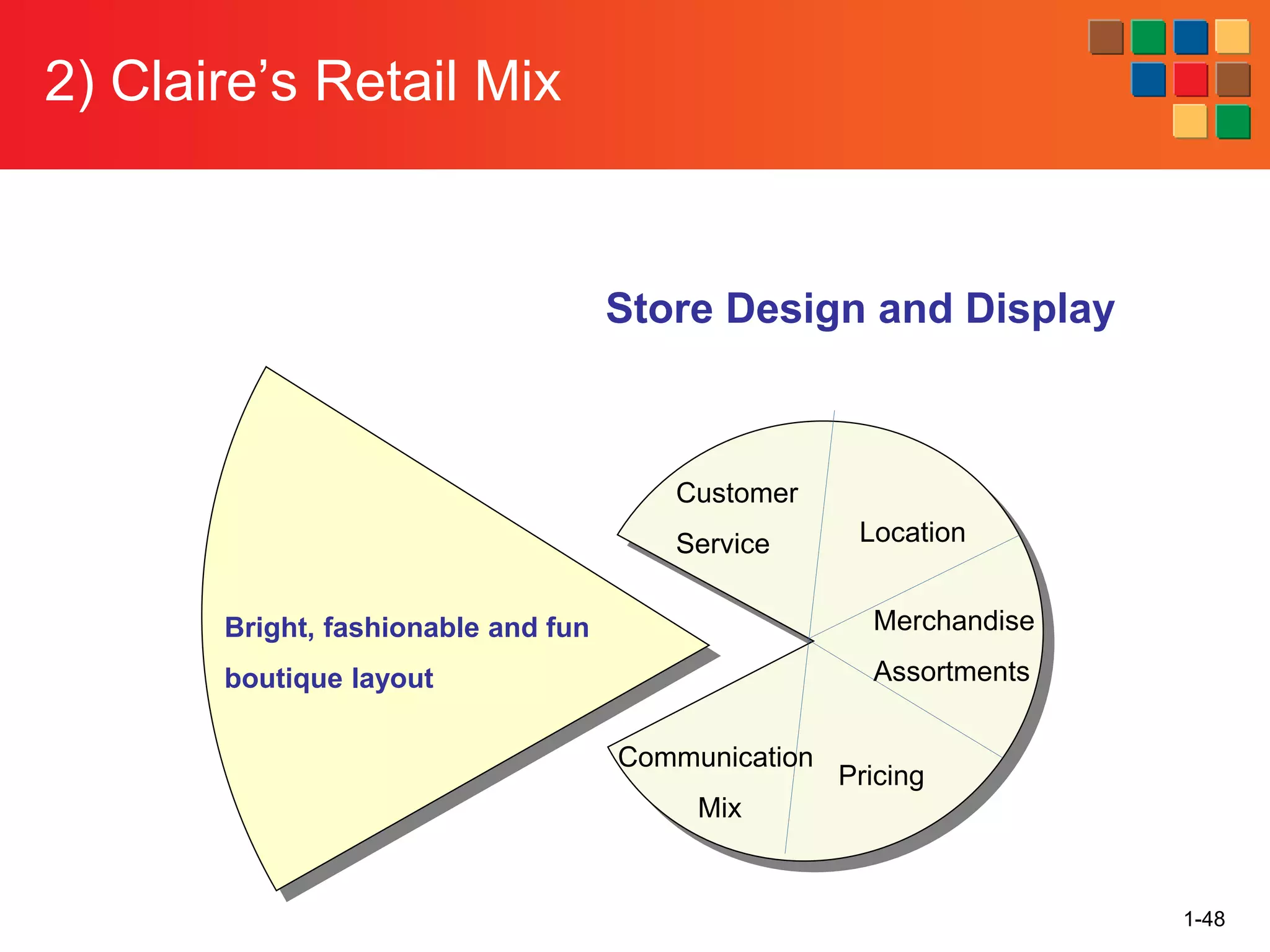
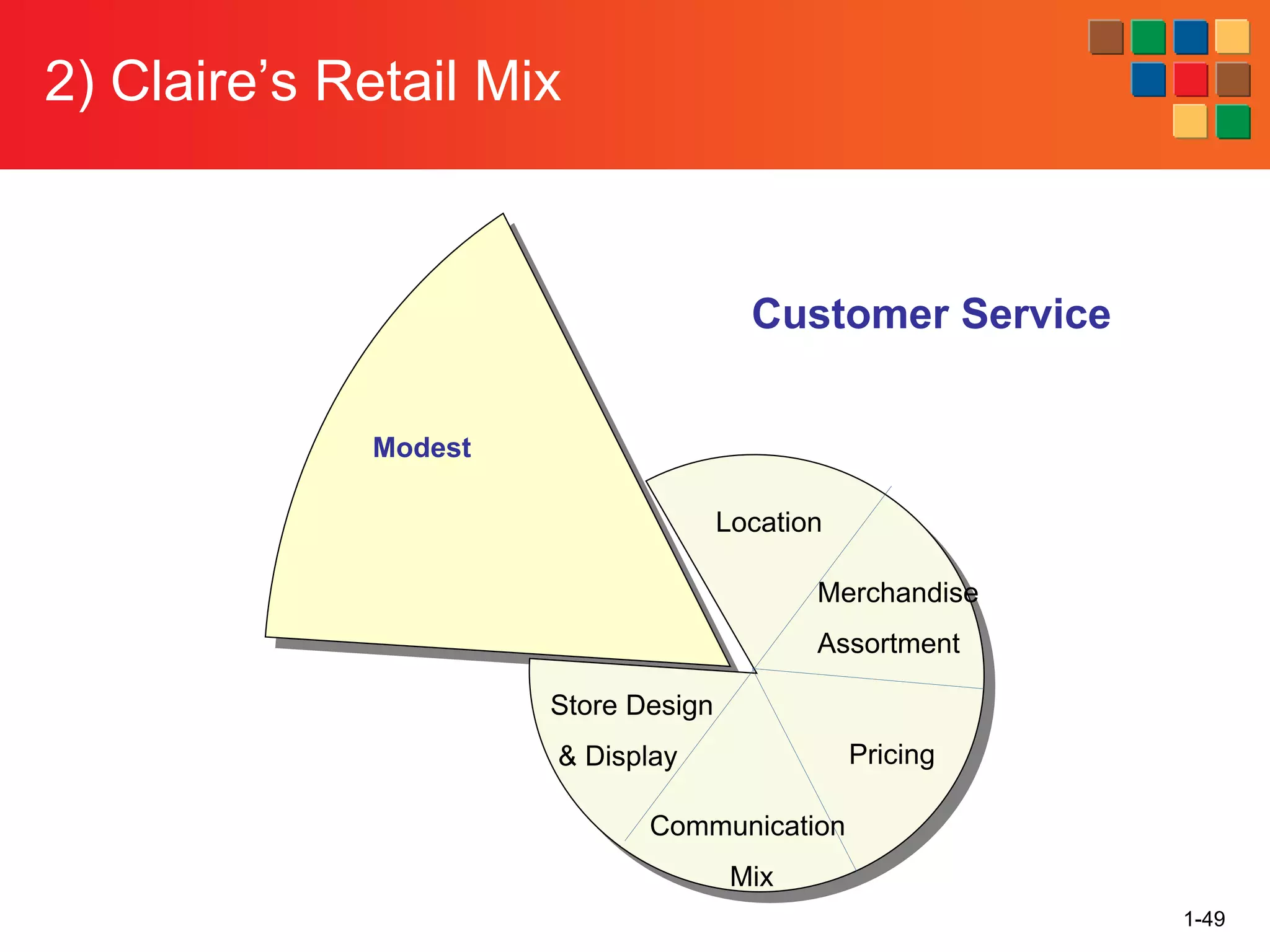
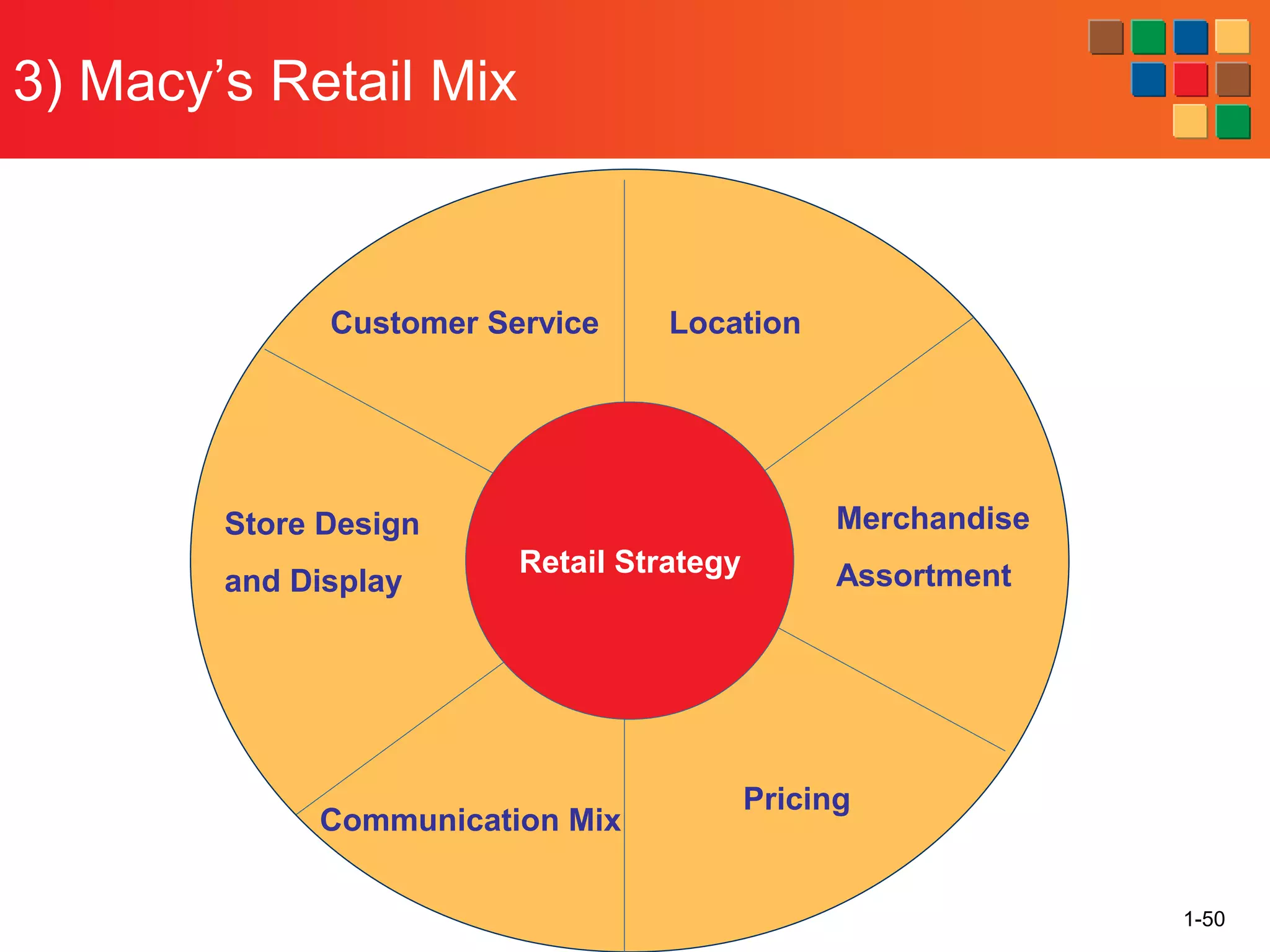
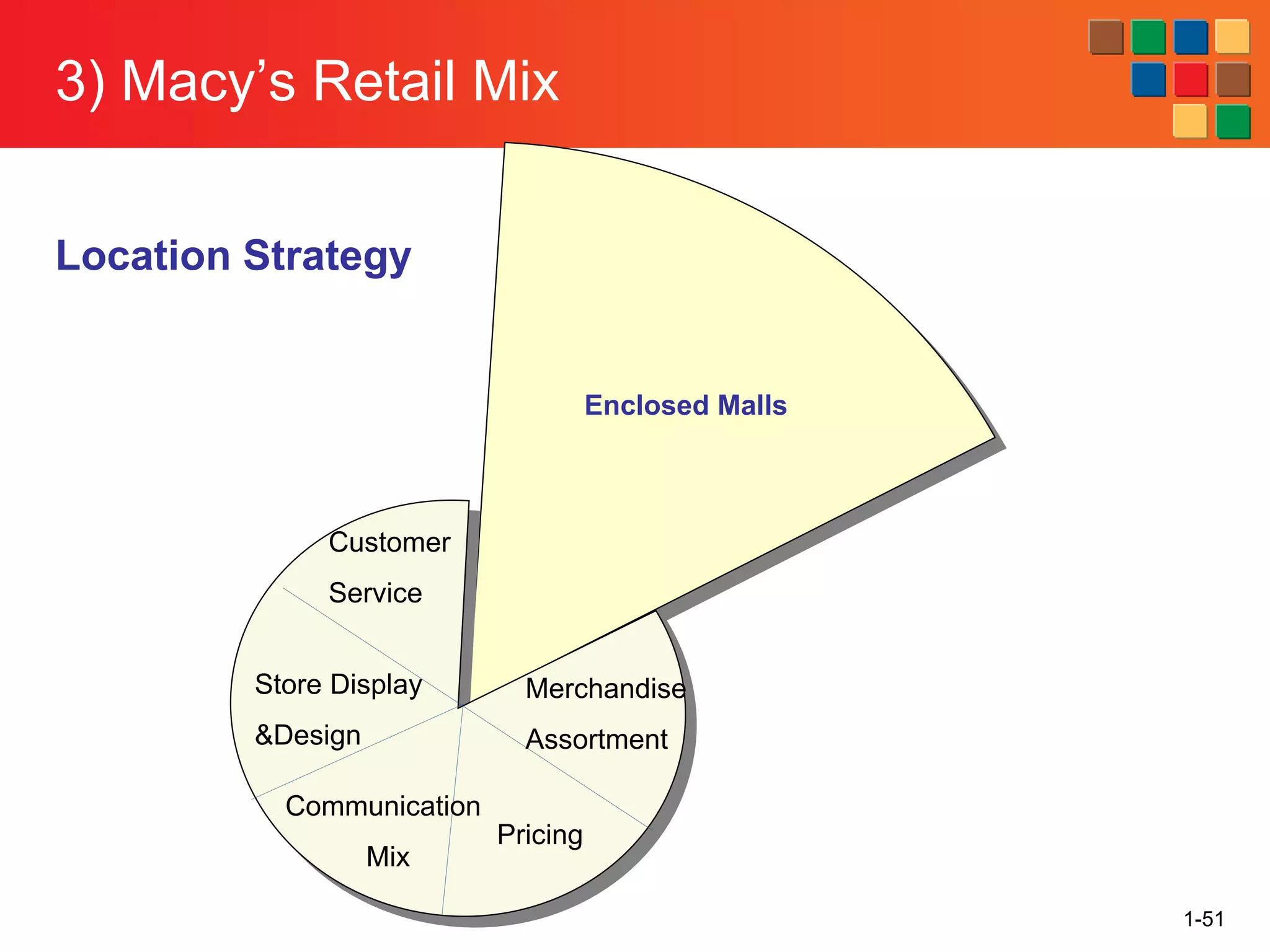
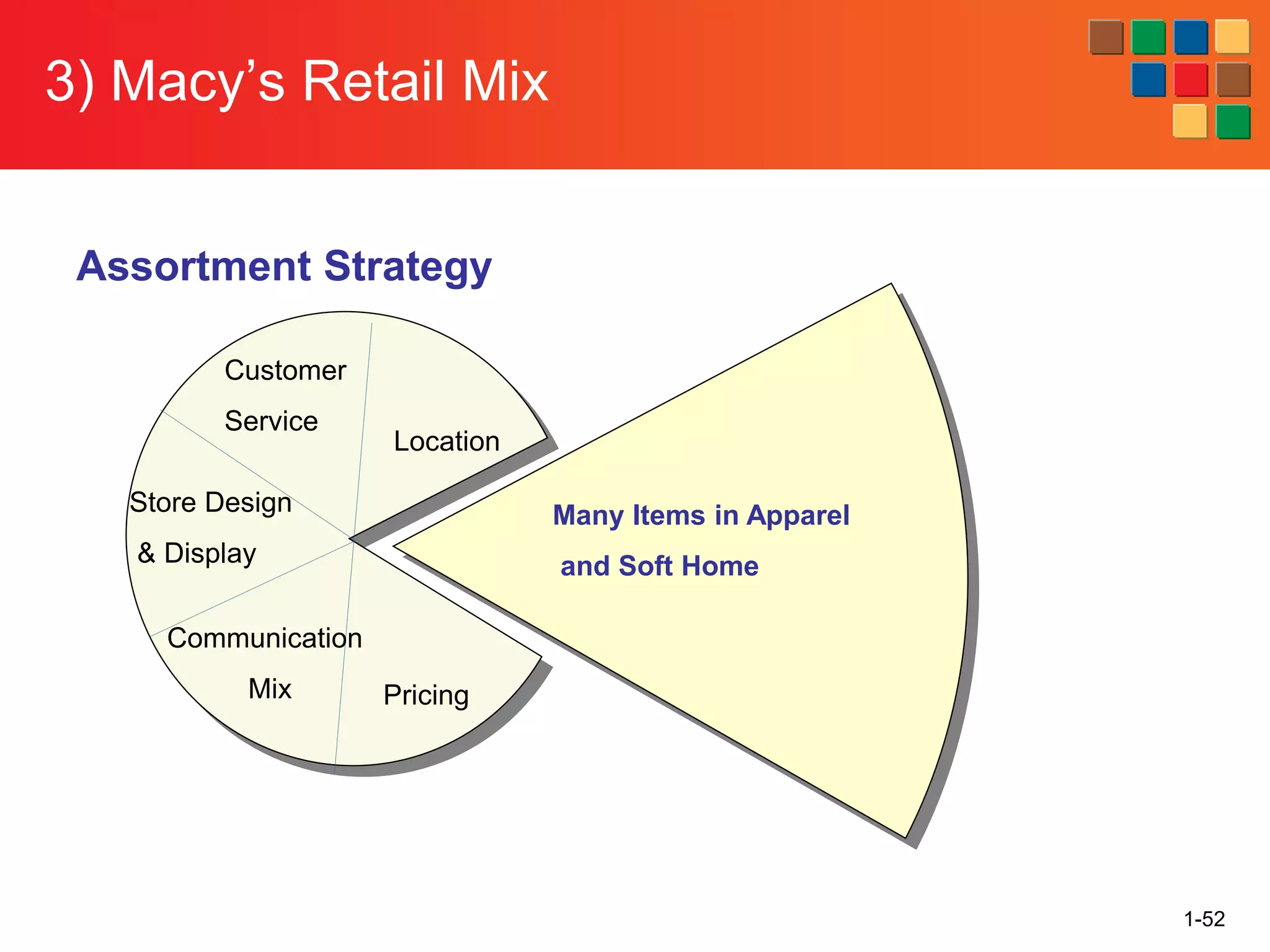
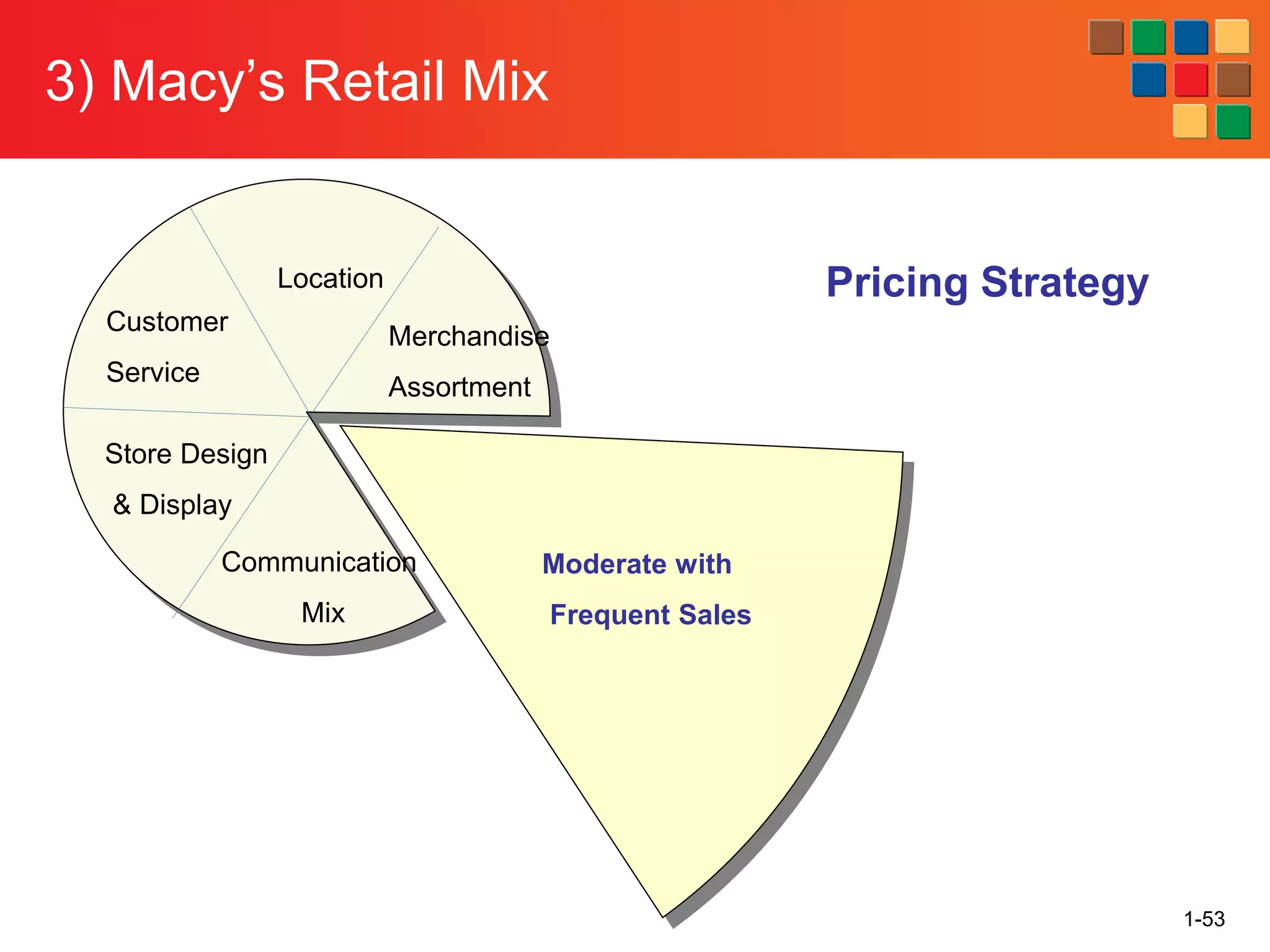
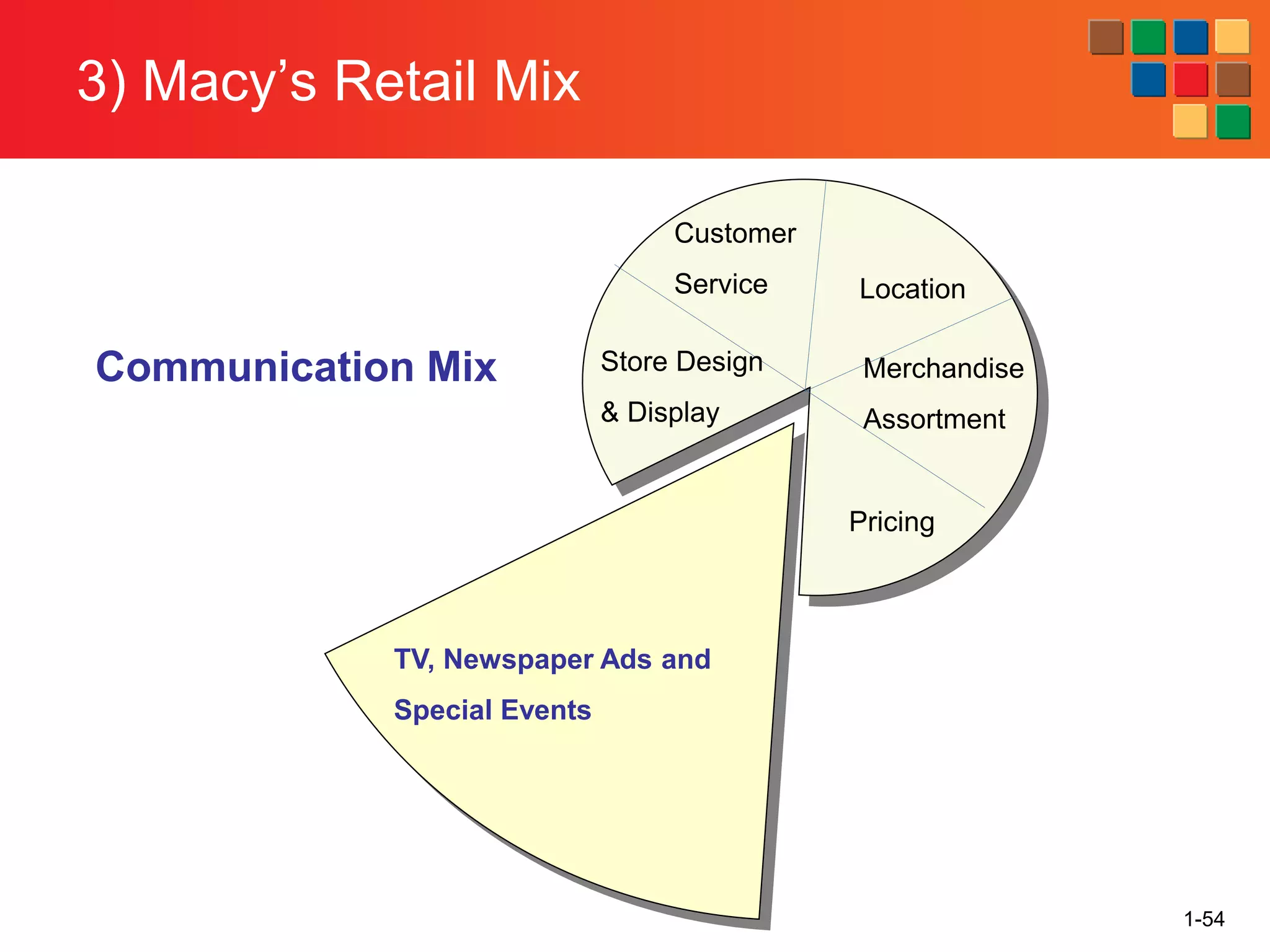
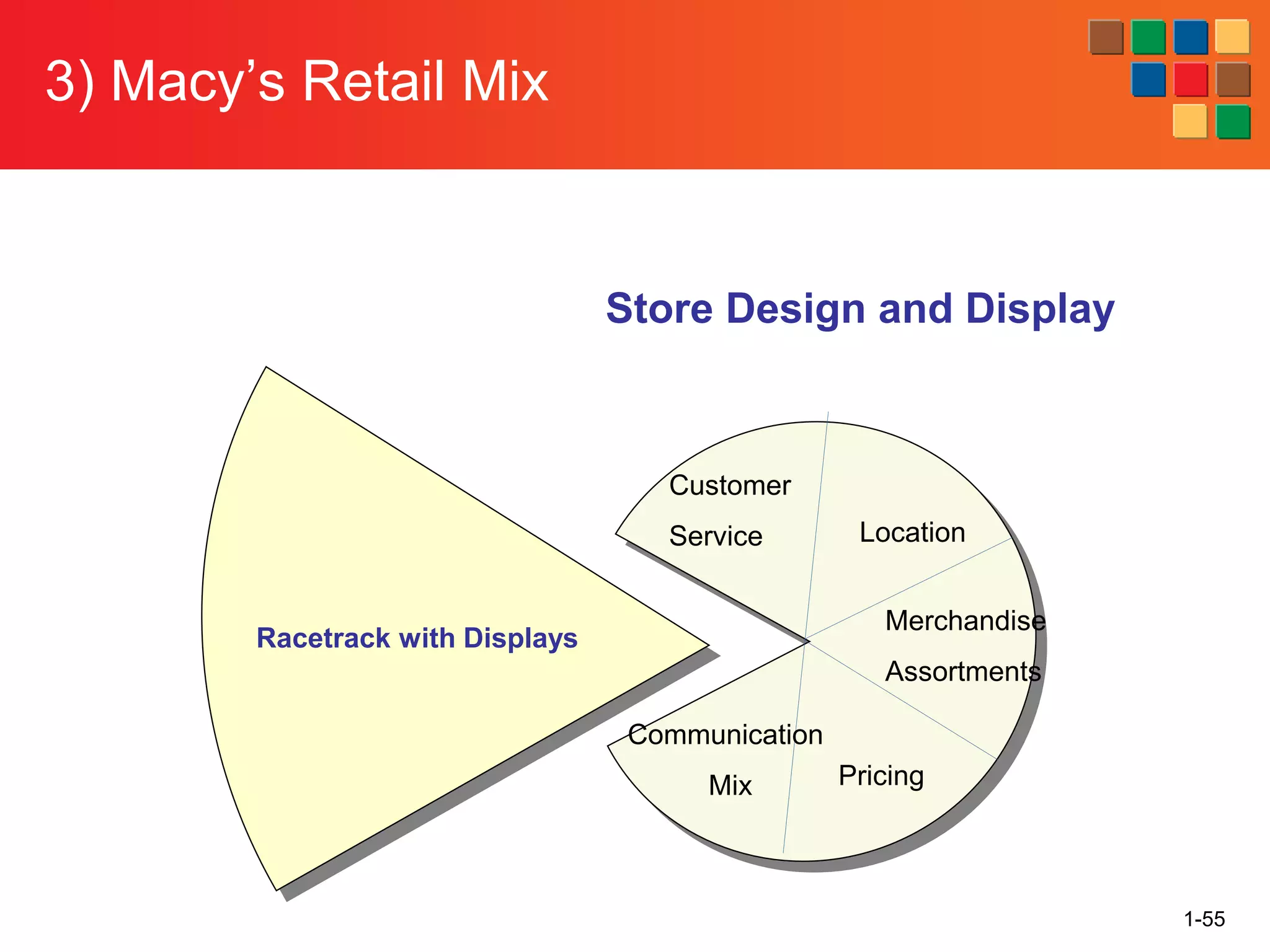
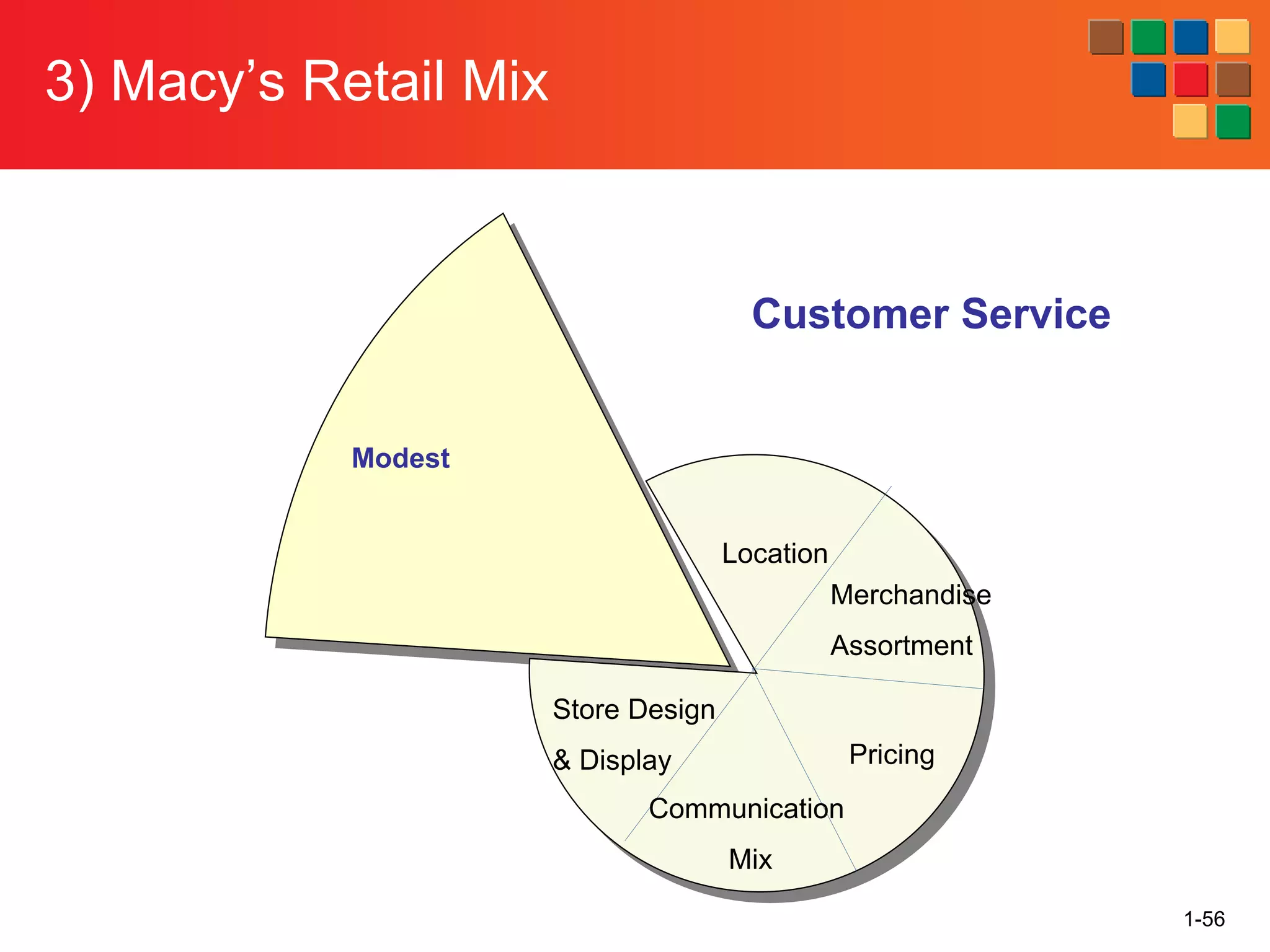
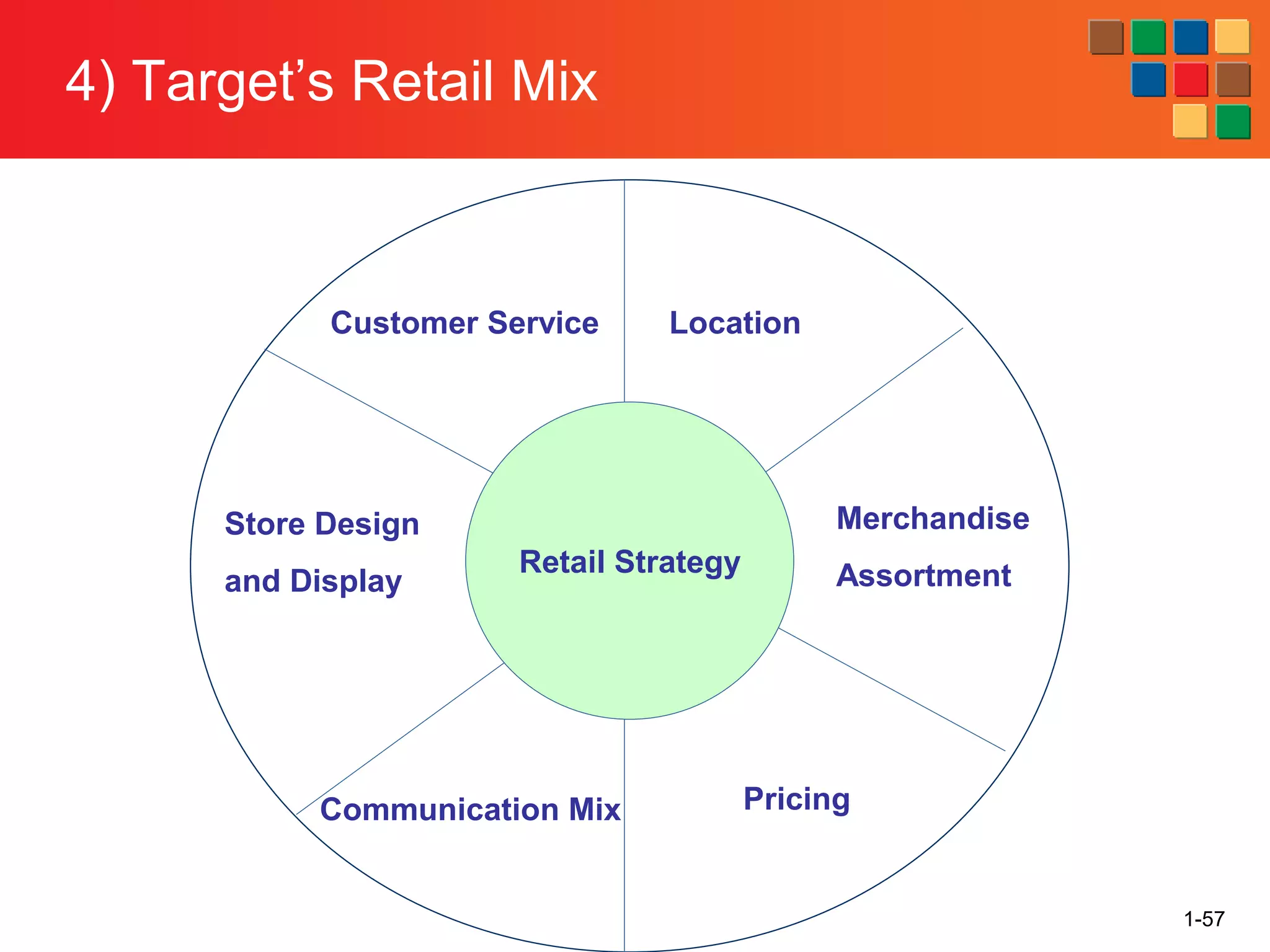
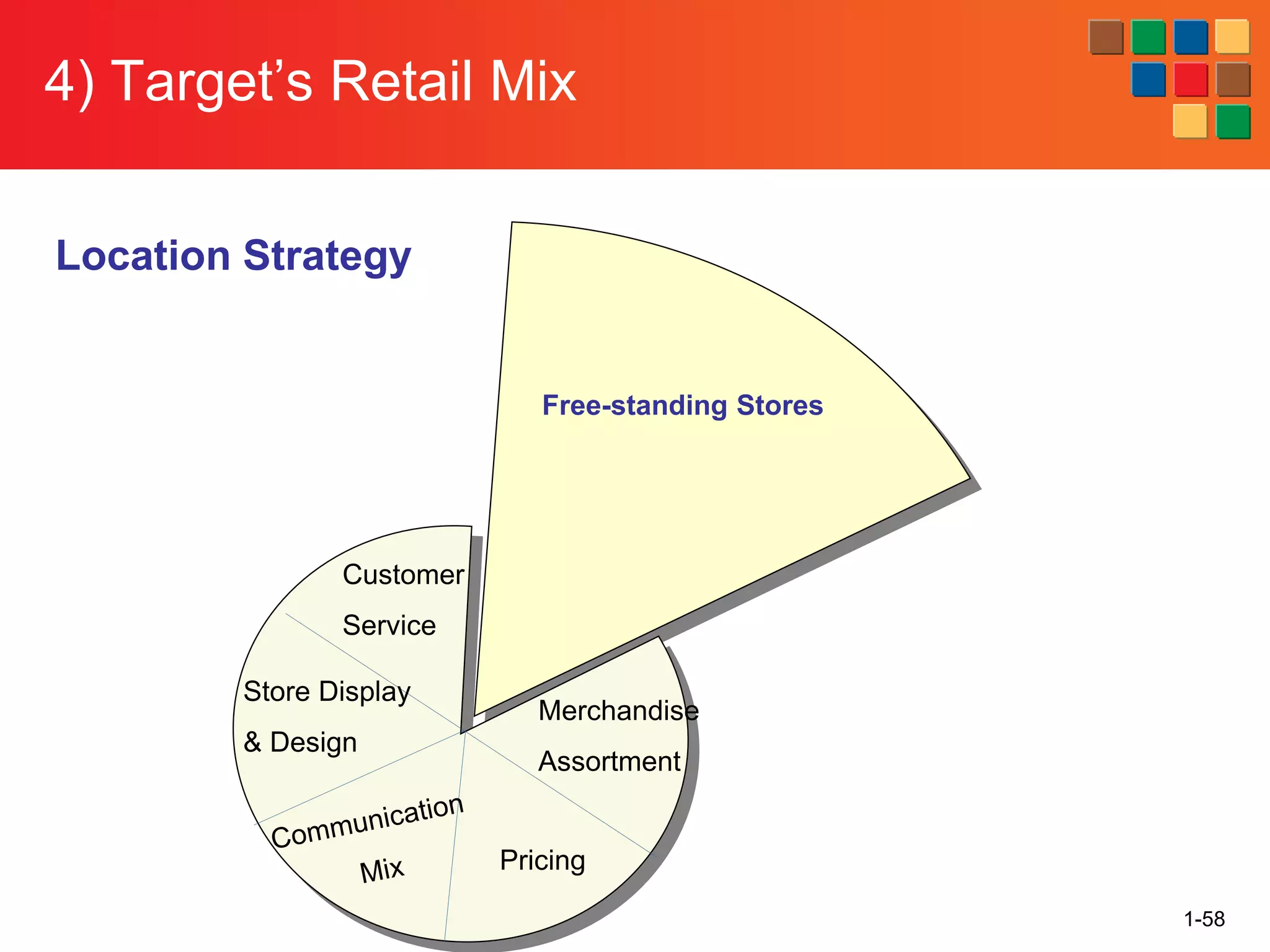
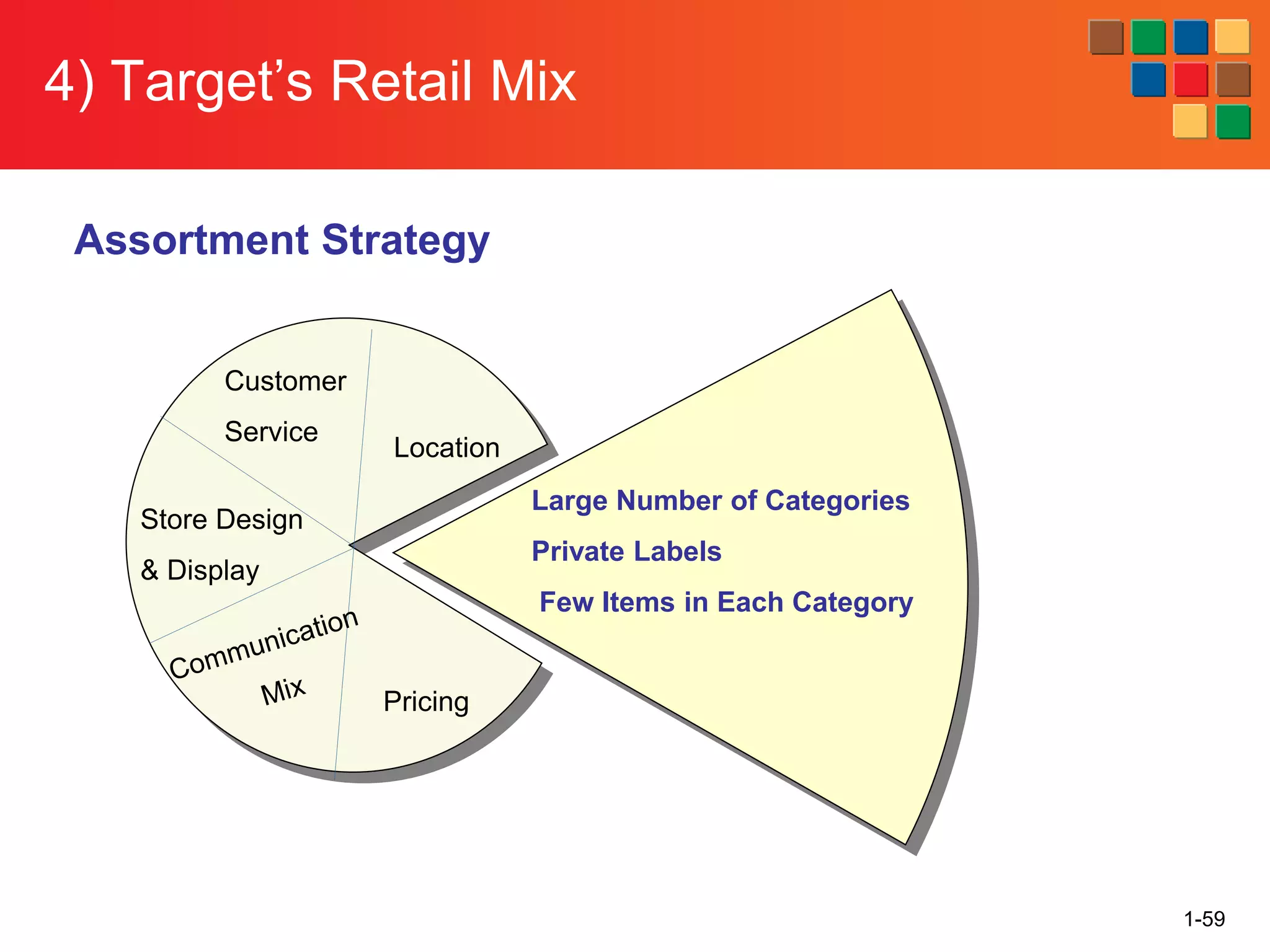
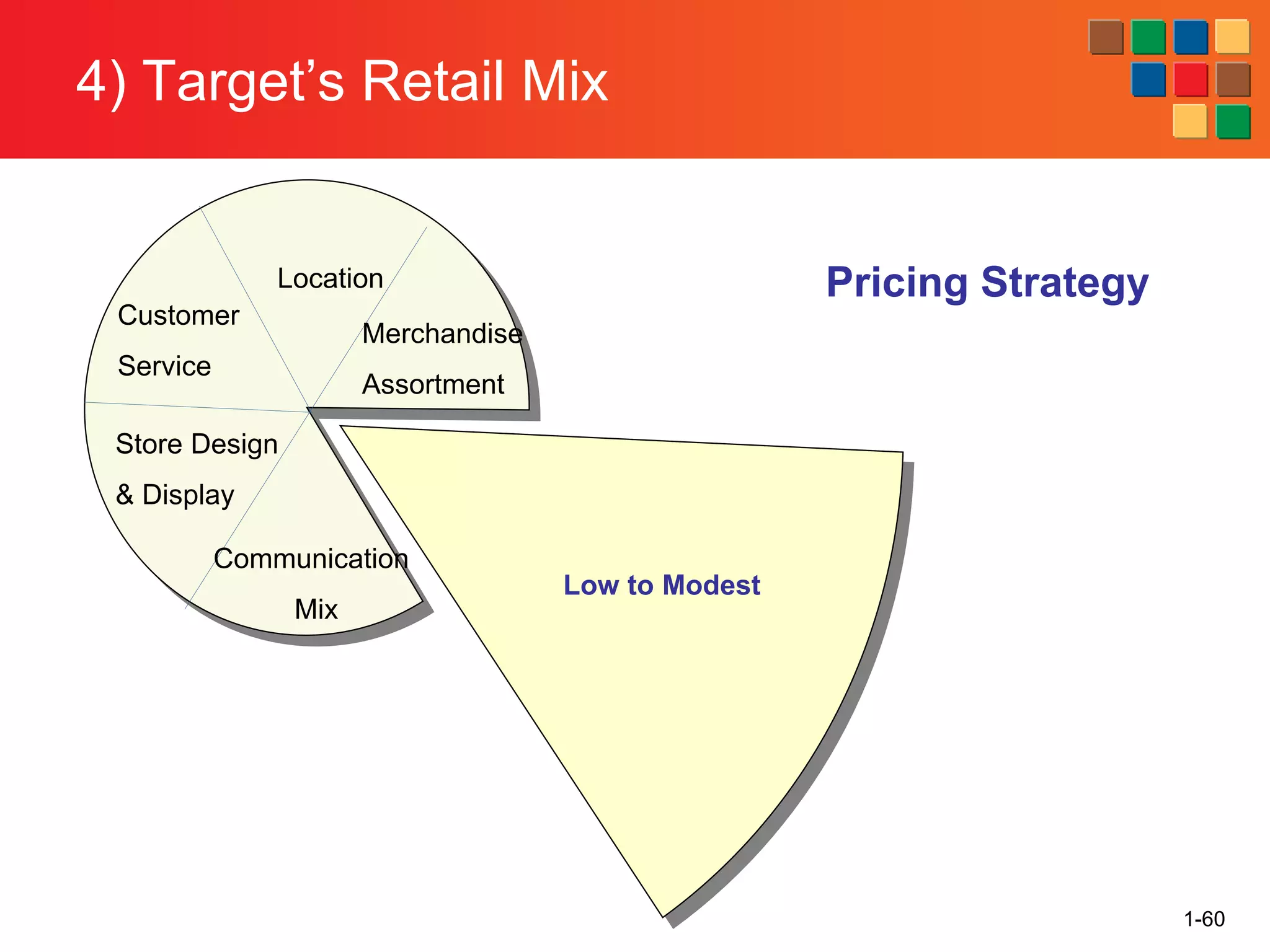
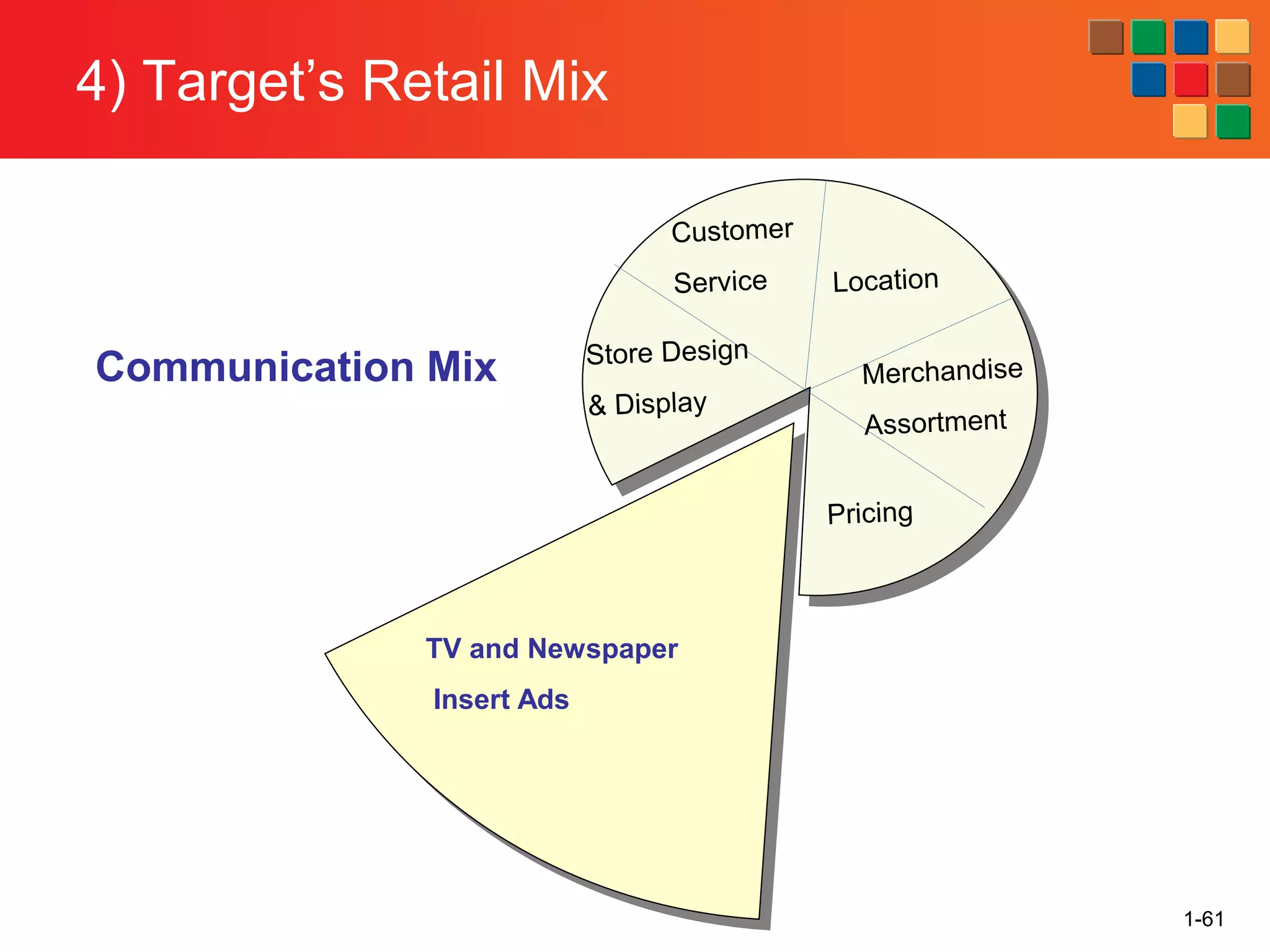
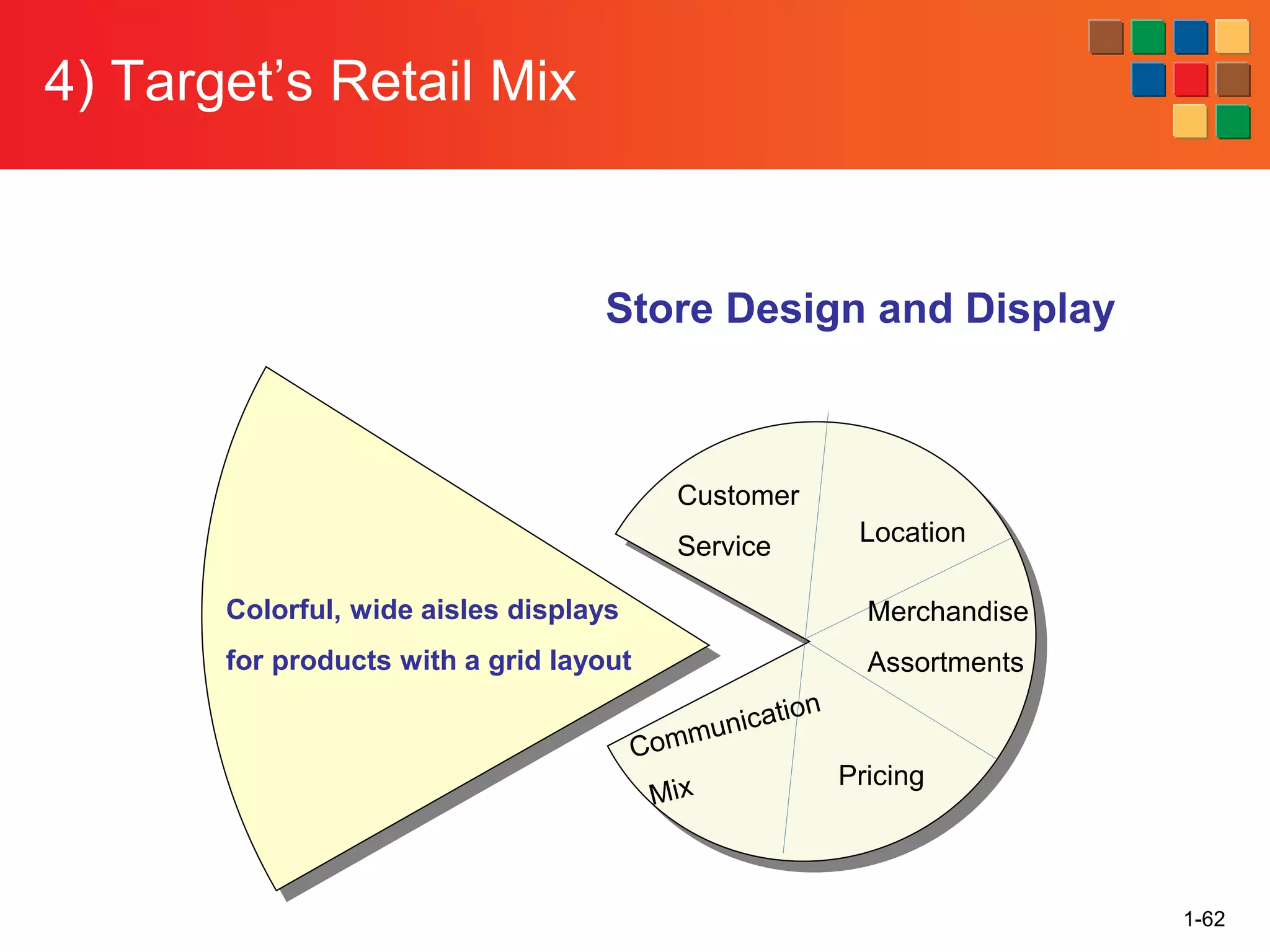
This document provides an overview of retailing as an introduction to the topic. It defines retailing as activities that add value to products and services sold to consumers. Various types of retailers are described, from large chains to those that also participate in wholesaling. The roles of retailers in the supply chain between manufacturers and consumers are explained. Retailers are said to add value through services like breaking bulk, providing assortment and convenience of inventory. Examples are given of how specific retailers have evolved their strategies over time. The document concludes with a discussion of ethical situations retail managers may face.