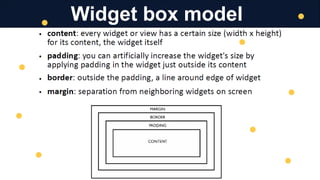
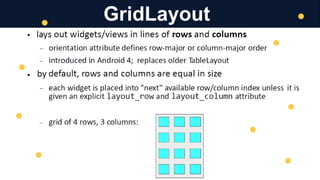
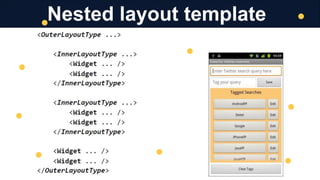
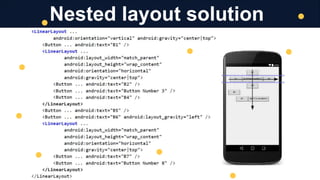
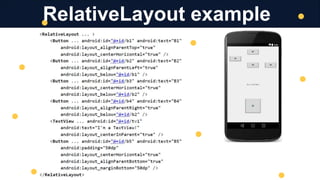
The document discusses mobile application development, focusing on layout, UI, sizing, and positioning techniques. It explains absolute positioning, layout managers, and the ViewGroup superclass, along with XML for describing layouts. Additionally, it covers various layout types such as LinearLayout and RelativeLayout, and their respective use cases in organizing widgets in an app.