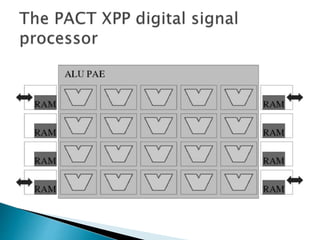
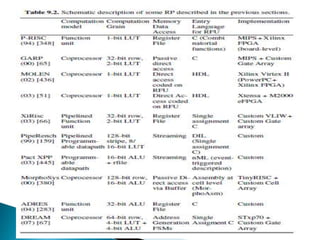
The document discusses coarse-grained reconfigurable architectures and compares them to fine-grained FPGAs. It describes two example coarse-grained architectures: PACT XPP and Morphosys. PACT XPP uses a packet-switched interconnect between its heterogeneous processing elements. Morphosys couples a RISC core to a coarse-grained reconfigurable cell array that operates in SIMD fashion. The document concludes that key parameters for evaluating reconfigurable processors as IP include the reconfigurable fabric design, the application mapping flow, and core-fabric interaction.