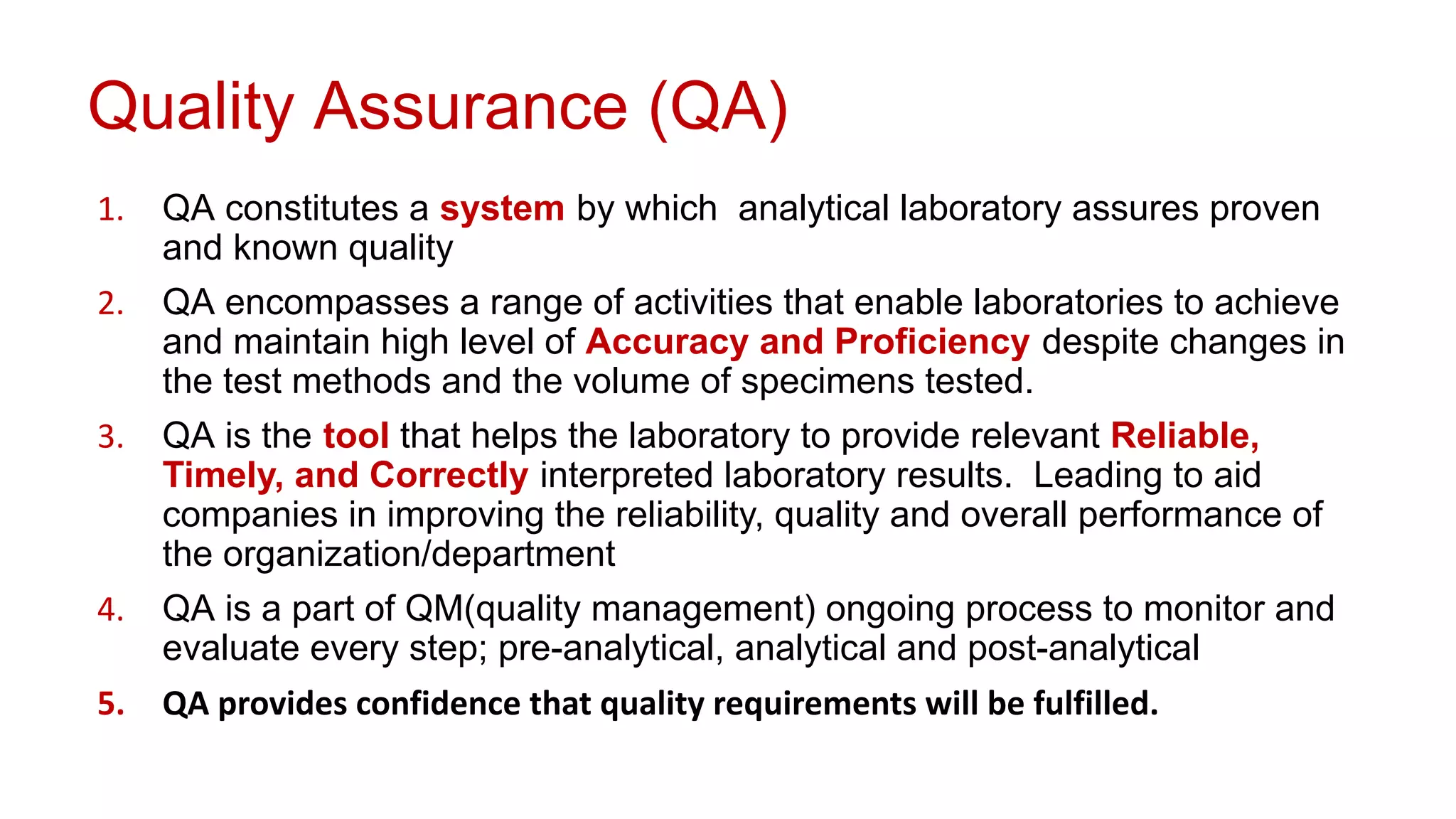
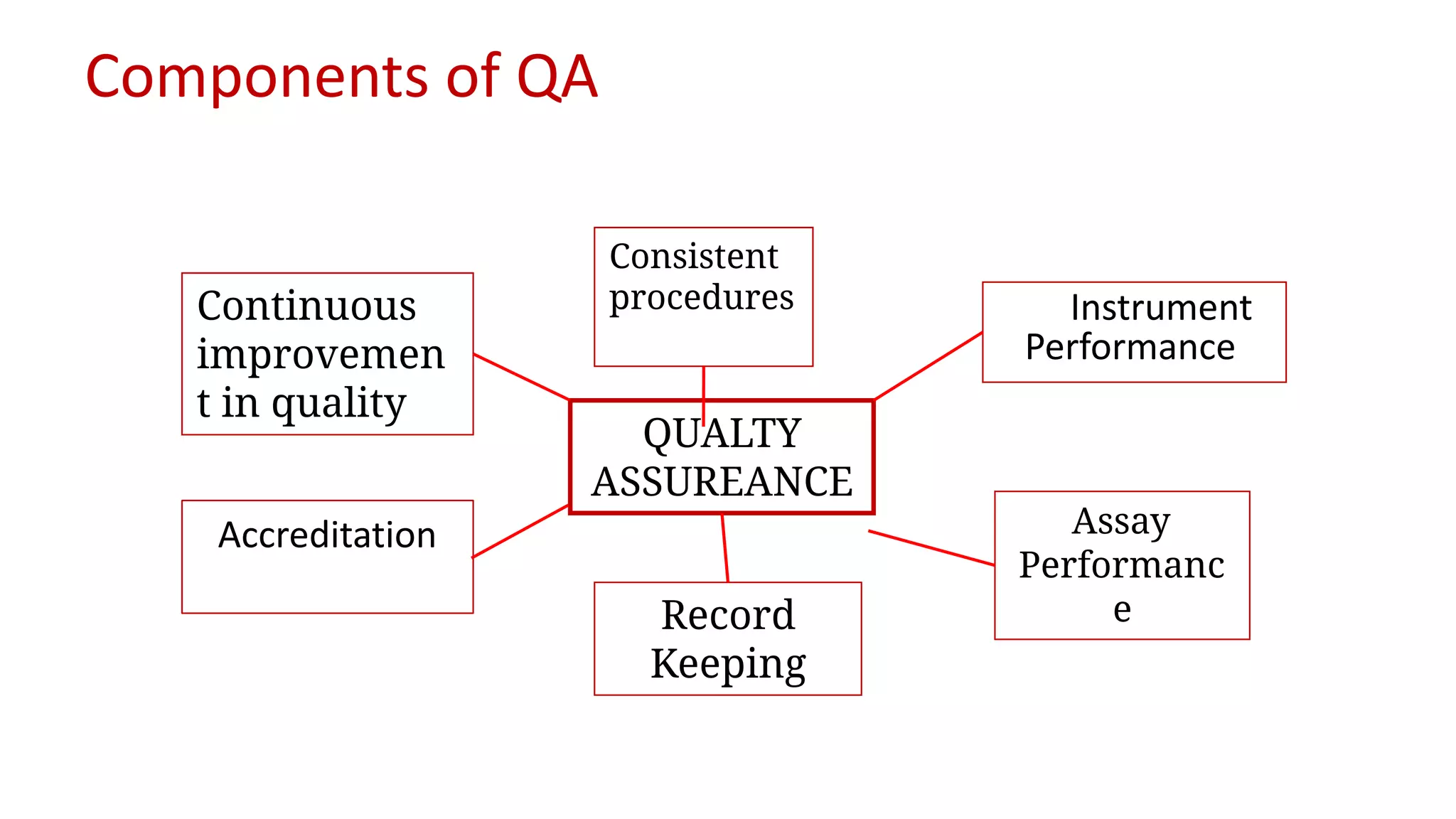
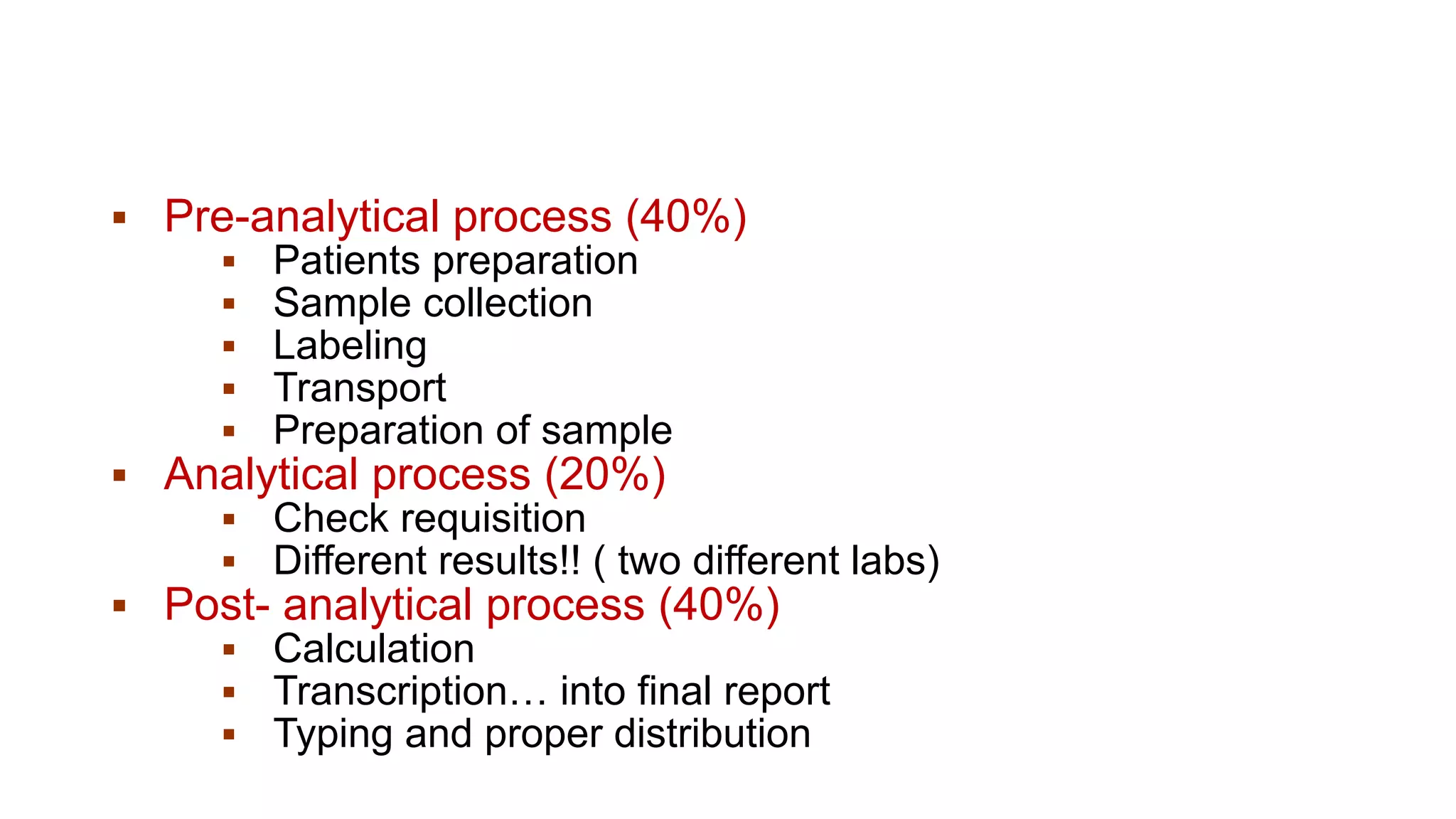
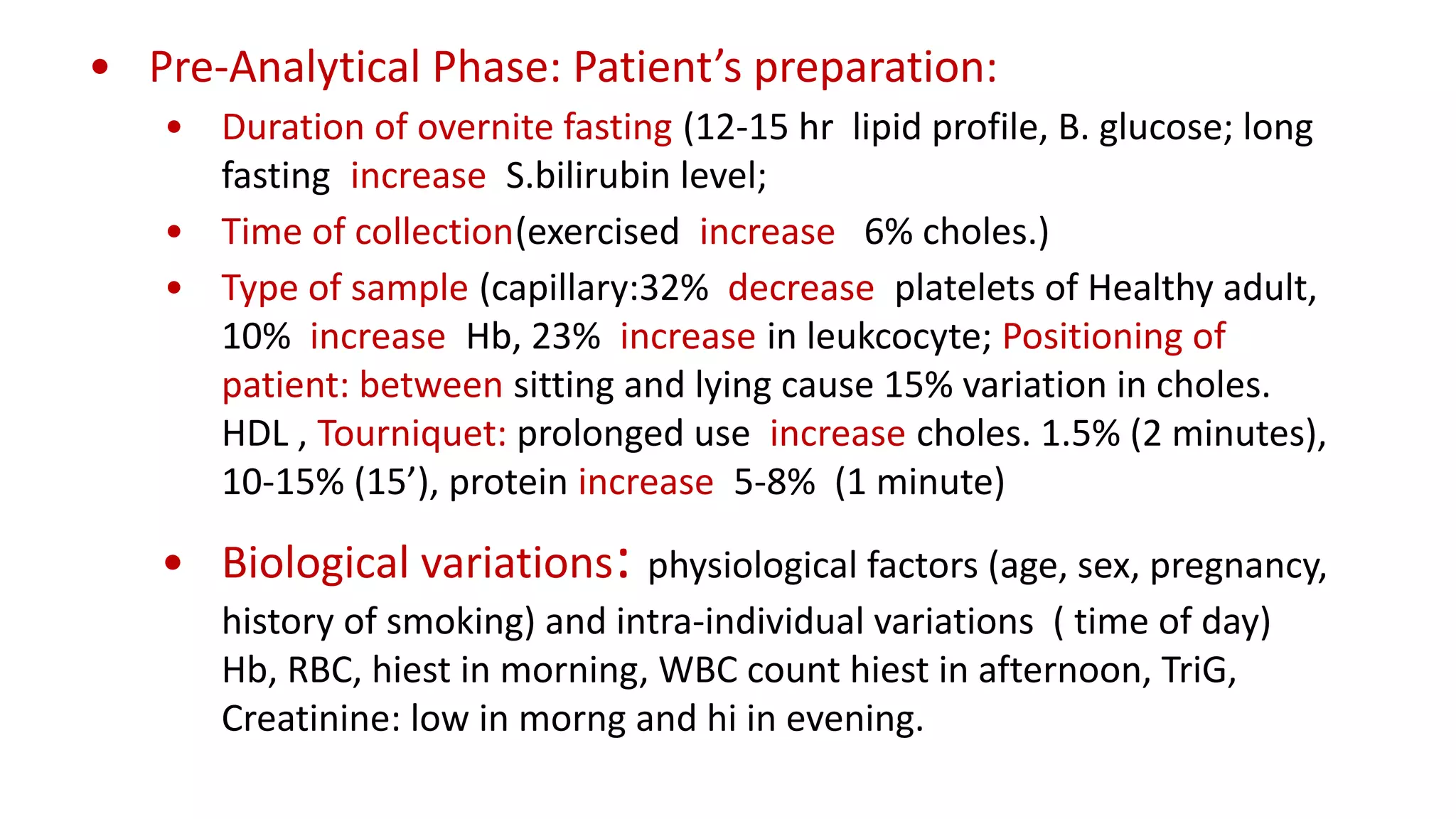
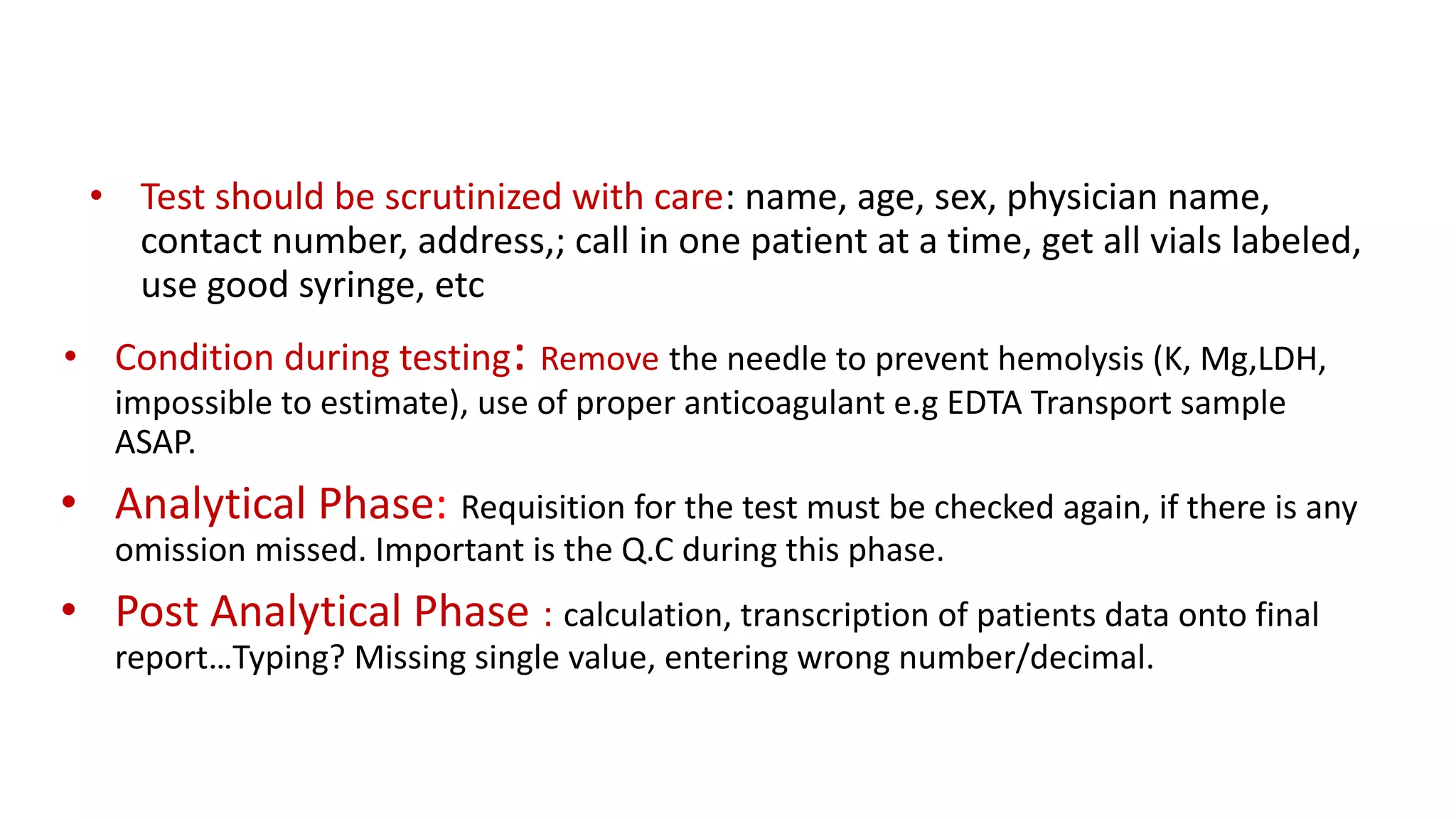
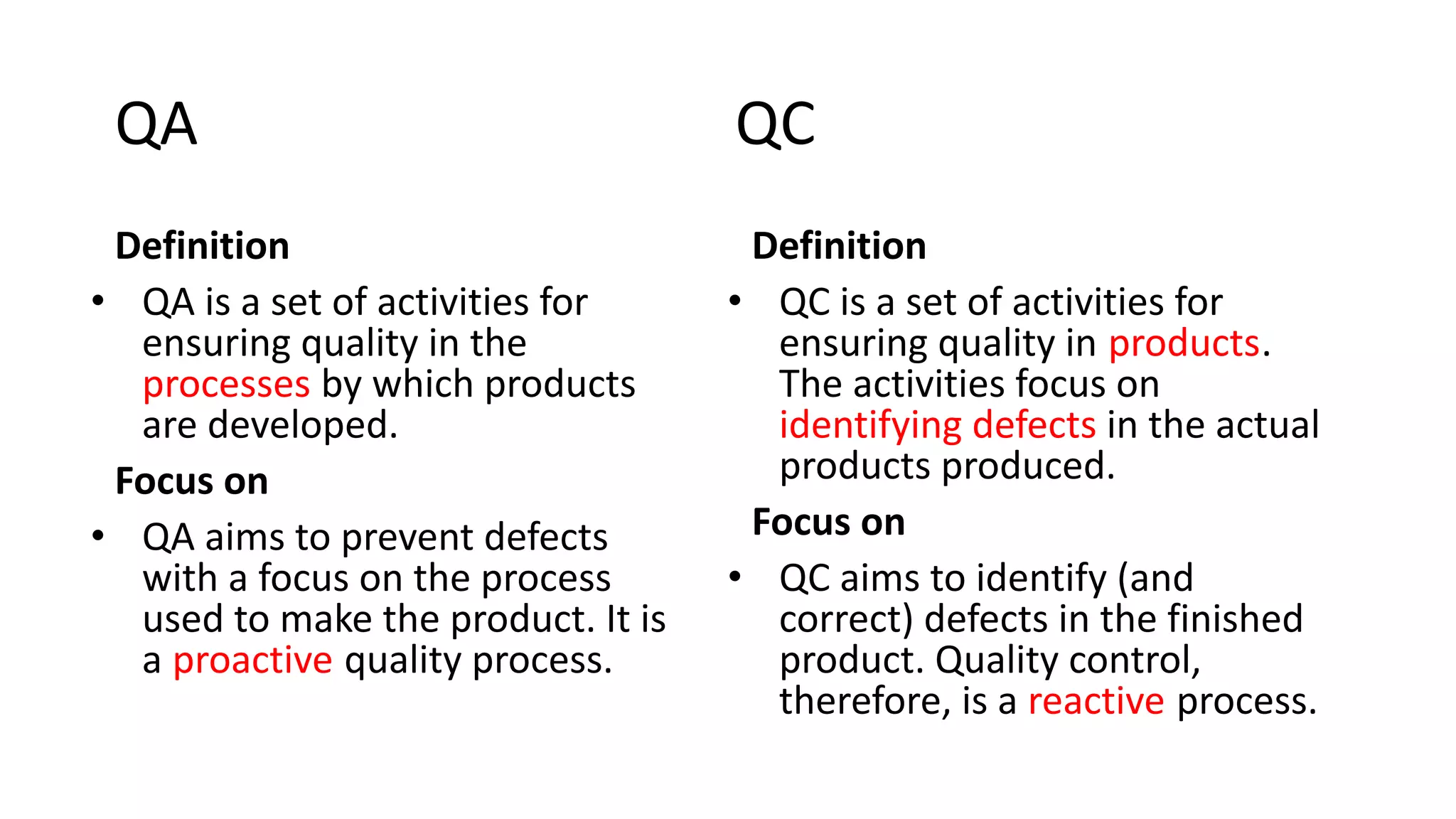
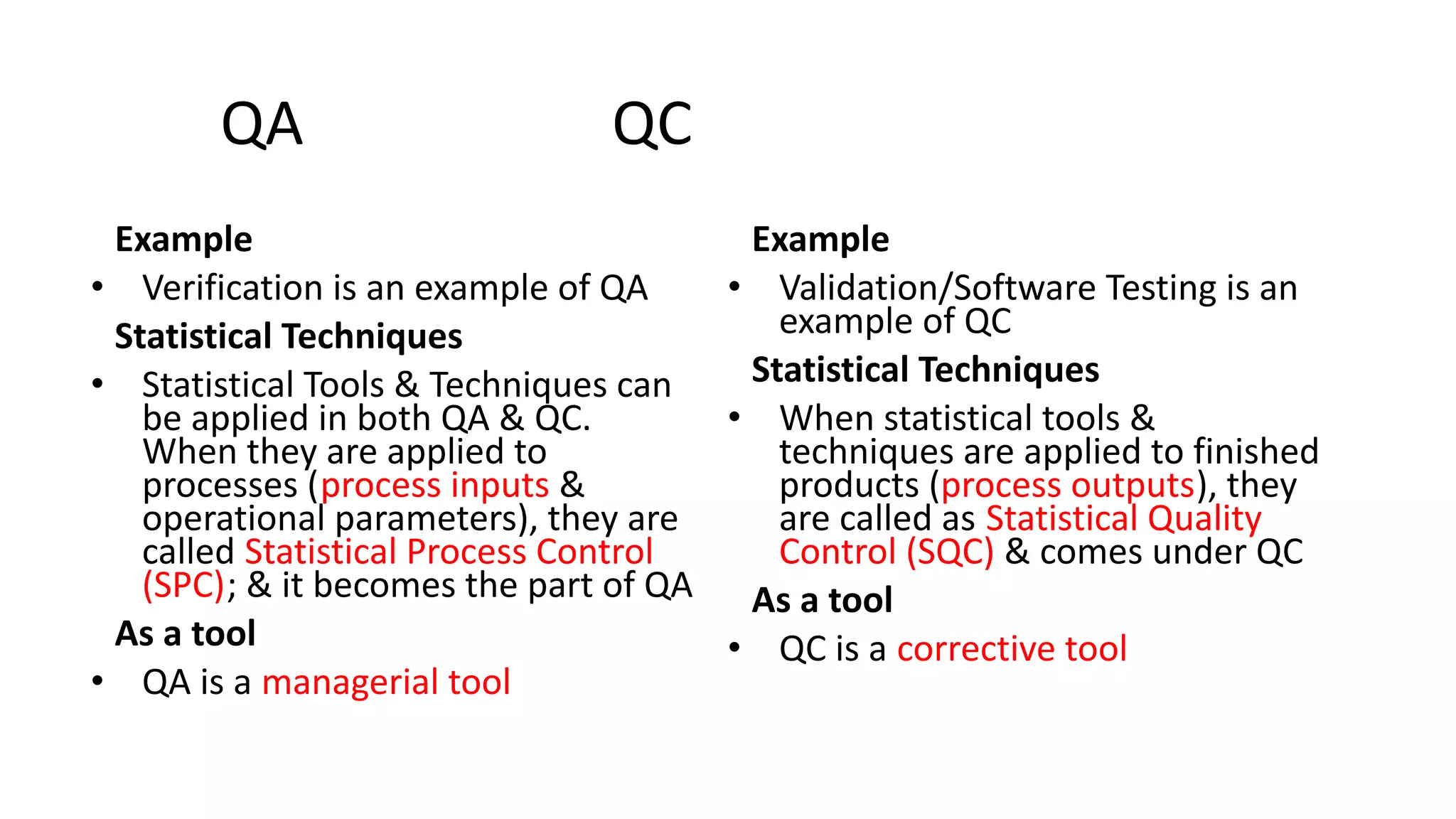
The document outlines the principles and practices of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) in various fields, emphasizing the importance of maintaining high standards in products and services to satisfy customer needs. It details the components of QA and QC systems, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), error prevention, and continuous quality improvement, while also discussing statistical tools used in these processes. Additionally, it highlights the role of organizations like ISO in promoting quality management standards globally.