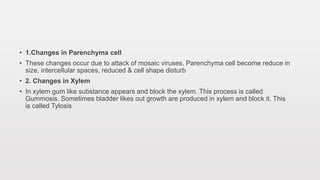
Viruses can cause a variety of symptoms in infected plants. External symptoms include chlorosis, mosaic patterns, mottleing, vein clearing or chlorosis, necrosis, ring spots, enations, stunted growth, and premature leaf shedding. Internal symptoms involve changes to parenchyma cells, xylem, phloem, and cell organelles. Symptoms can be localized to infection sites or systemic throughout the plant. Some viruses may cause latent, asymptomatic infections or symptoms can be masked for periods of time.