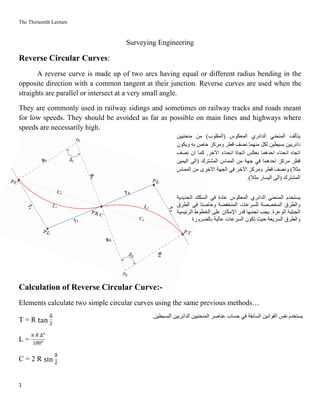
1. A reverse circular curve consists of two circular arcs bending in opposite directions that share a common tangent. They are commonly used in railway sidings and roads meant for low speeds.
2. To calculate a reverse curve, the first curve is dropped from its point of commencement (P.C.) using tables and methods. Then the second curve is dropped from the point of reverse curvature (P.R.C.).
3. An example problem calculates the main stations of a horizontal reverse circular curve given the elements of the two curves and their radii, central angles, and stations of points of curvature, reverse curvature, and tangency.