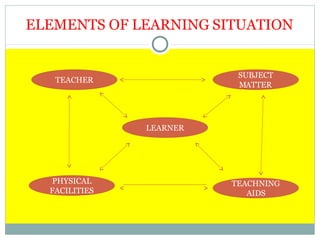
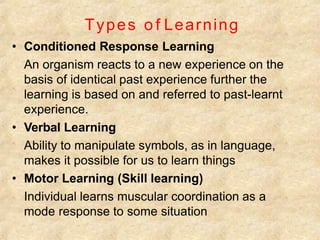
This document discusses learning and the elements that make up an effective learning situation. It defines learning as a process through which behavior changes as a result of experience. An effective learning situation includes a knowledgeable teacher, interested learners, relevant subject matter, adequate teaching aids and facilities, and principles of adult learning. Senses like sight have a strong impact on learning retention, with learners retaining about 83% of visual information. Different types of learning are discussed, like conditioned response learning, verbal learning, motor learning, and attitude learning. Thorndike's laws of learning and various theories of learning like behavioral and cognitive theories are also summarized.