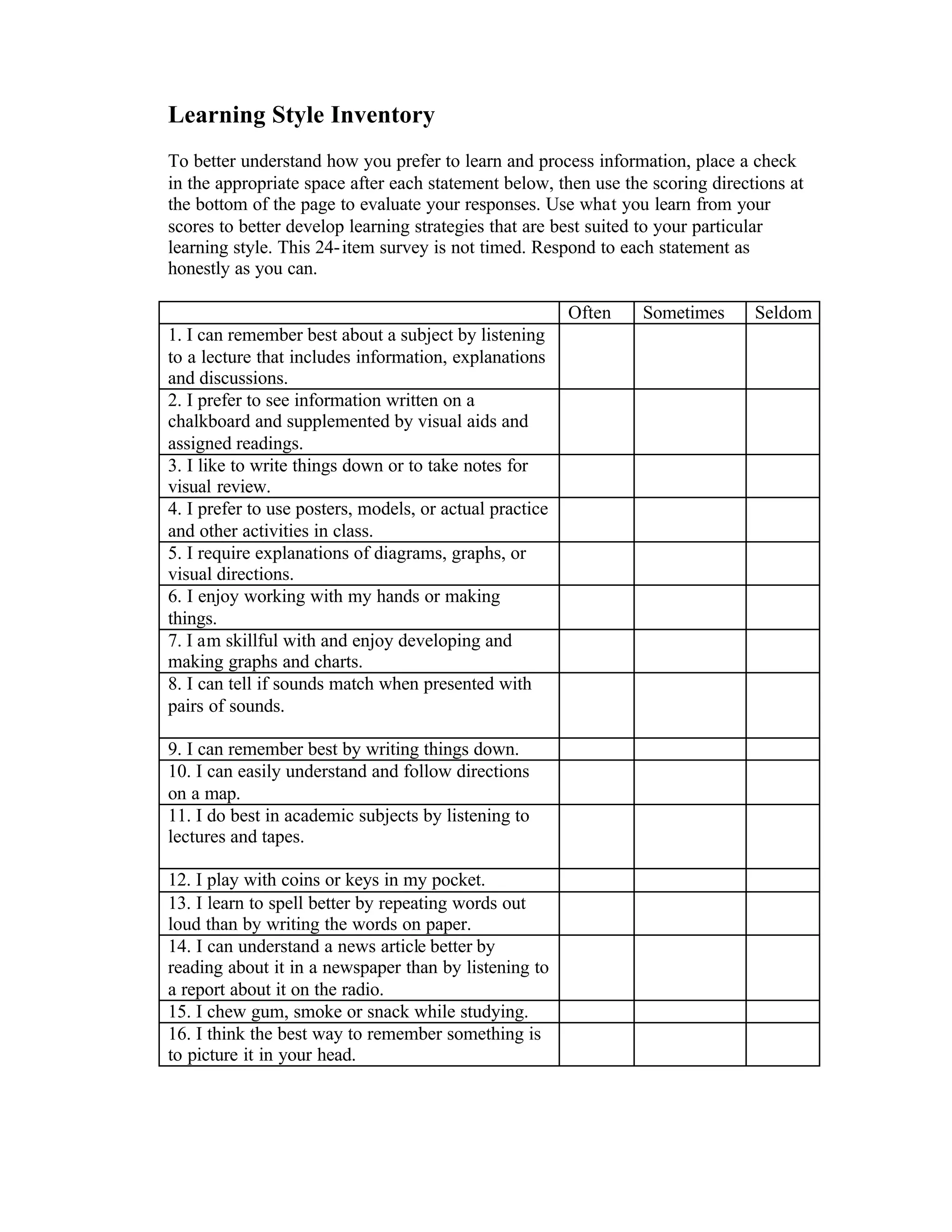
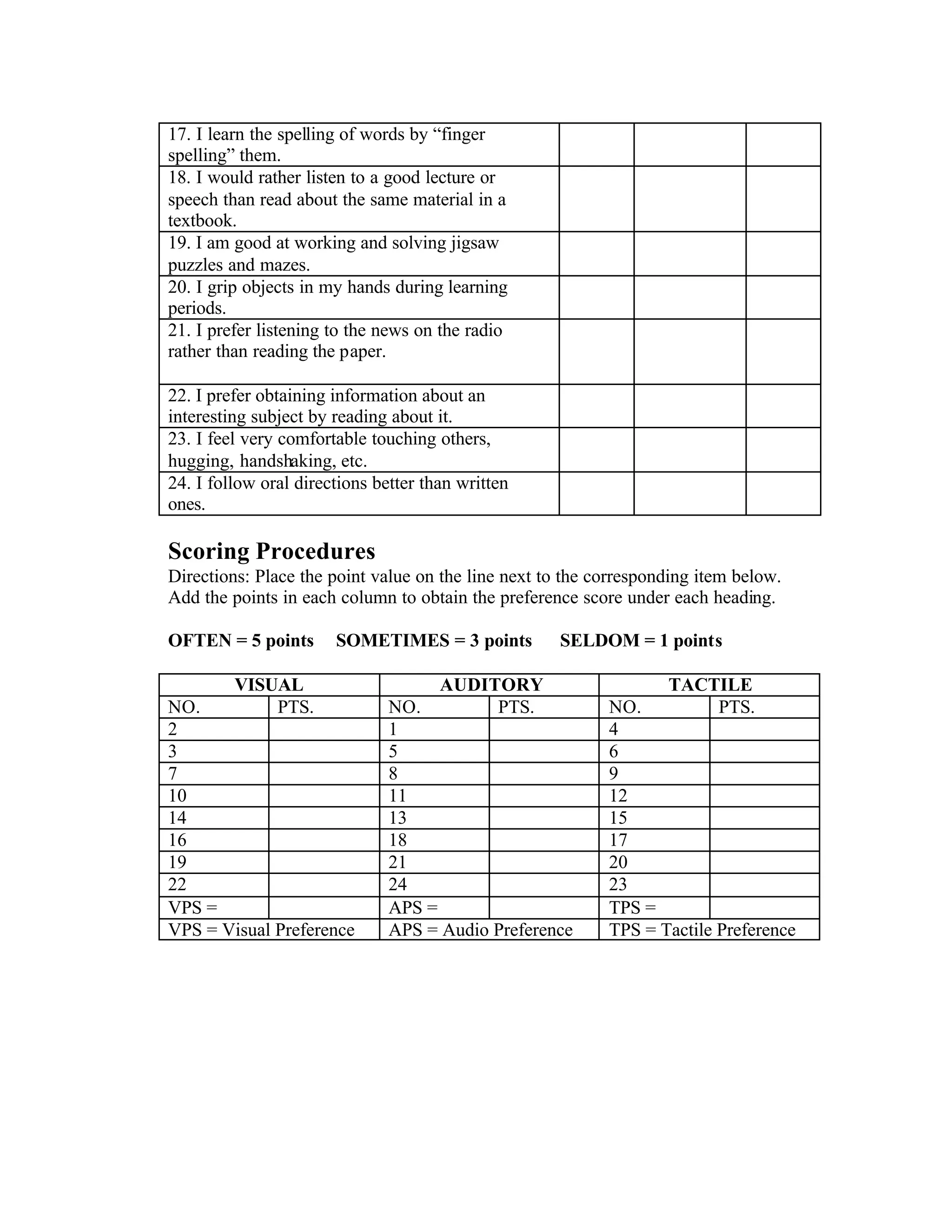
This document provides information about different learning styles and assessments to determine a learner's preferred style. It includes a 24-item learning style inventory where learners check boxes to indicate if statements apply to them often, sometimes, or seldom. Scoring is used to determine preferences for visual, auditory or tactile learning. Characteristics of each style are described. The document provides hints for visual, auditory and kinesthetic learners on how to best process and retain information according to their style.