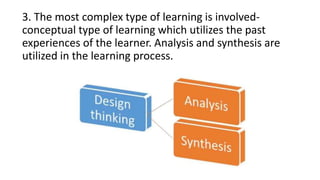
The document outlines the principles of Gestalt theory of learning and its implications for education, emphasizing that learning is a holistic process involving the integration of new experiences with prior knowledge. It describes various methods for teaching that align with Gestalt principles, such as the integration and unit methods, which focus on the learner as a whole and encourage active engagement. Additionally, the theory recognizes individual differences and promotes the overall growth of students, stressing the importance of contextual understanding in the learning process.