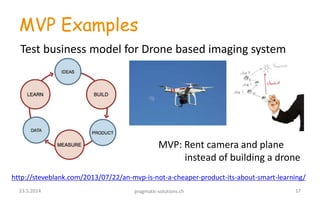
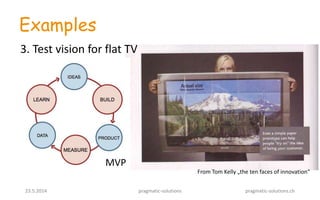
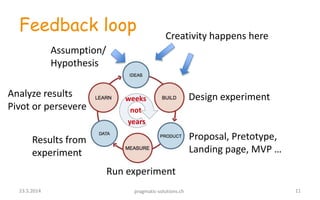
1) The document discusses the Lean Startup methodology for improving the success rate of startups. It emphasizes building the minimum viable product and getting early customer feedback through experimentation to validate assumptions and pivot if needed, rather than spending years developing the wrong product.
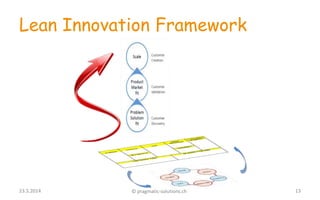
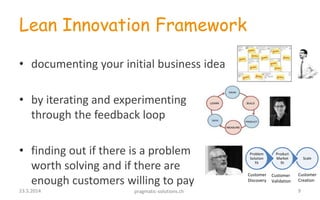
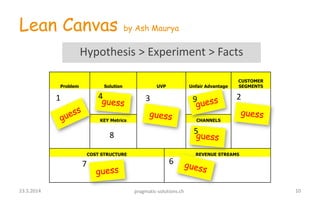
2) The Lean Canvas tool is presented as a way to document the initial business idea and iterate through customer discovery, validation, and creation phases to find a scalable and repeatable business model.
3) Traditional startup approaches are contrasted with lean approaches, with lean emphasizing problem validation over predefined solutions, minimum viable products over complete features, and continuous customer input over secrecy during development.








![Experiment report
23.5.2014 pragmatic-solutions.ch 12
Experiment report Title Author: created:
FromLeanstackbySpark59
Background:
what are you trying tio achieve?
why is it relevant?
Falsifiable Hypothesis:
declare your expected outcome
[Specific repeatable action] will [expected measurable outcome]
Set scope and time box
Details:
How do you set up the experiment
results:
qualitative or quantitative results
next action:
What is the next experiment
validated learning:
Sumarize your learning from the experiment. (Validated, invalidated,
inconclusive.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leaninnovationintroduction-startupweekend-140603234357-phpapp01/85/Lean-Innovation-introduction-12-320.jpg)