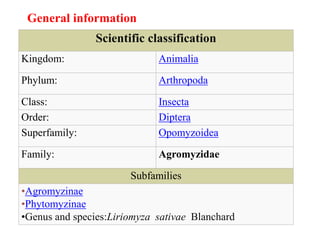
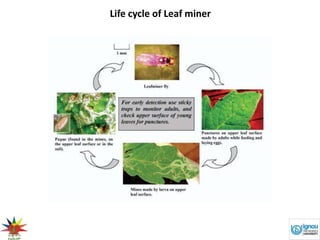
Leafminer is a pest that damages vegetable crops like tomatoes. Its larvae burrow into and feed on leaf tissue, leaving winding tunnels that can cause leaves to drop prematurely and reduce crop yields. The leafminer has a 2-week lifecycle with multiple generations per year. Management strategies focus on conservation biological control using natural enemies like parasitic wasps. Cultural practices like removing old crop residues and selecting resistant varieties can also help reduce infestations. Chemicals should be avoided if possible to protect natural enemies, as the pest has developed resistance to many insecticides.