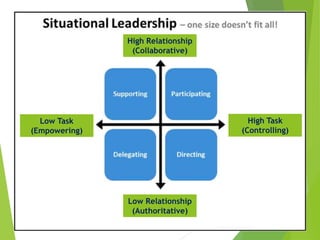
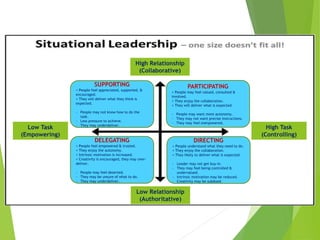
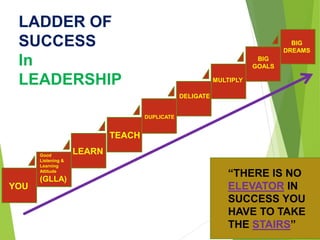
The document discusses the significance of leadership in management, defining key characteristics and contrasting leaders with managers. It outlines various leadership styles, including autocratic, democratic, paternalistic, and laissez-faire, highlighting their effects on team dynamics and performance. The text emphasizes the responsibilities of effective leaders in motivating, guiding, and fostering a productive environment for their teams.