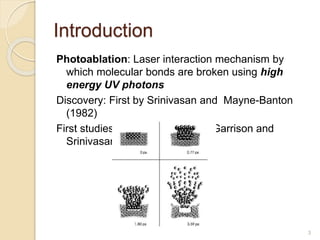
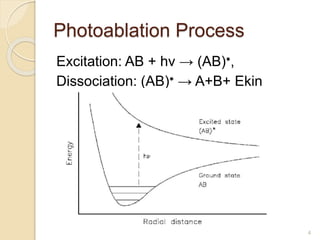
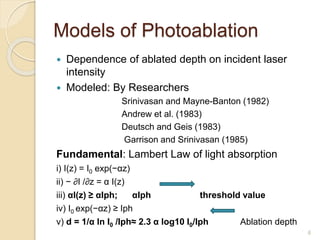
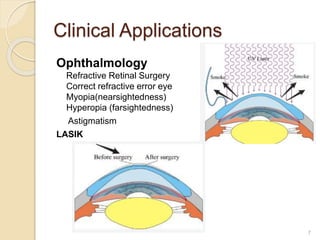
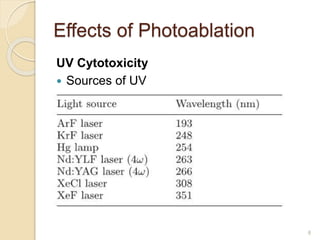
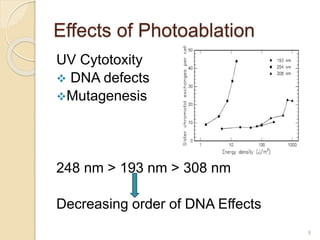
The document discusses laser photoablation, a process that uses high energy UV photons to break molecular bonds, with its discovery credited to Srinivasan and Mayne-Banton in 1982. Key applications include refractive eye surgeries such as LASIK, while also highlighting the potential cytotoxic effects of UV lasers, including DNA damage. The document concludes by reaffirming the importance of photoablation in ophthalmology and the associated risks from UV exposure.