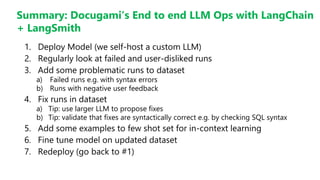
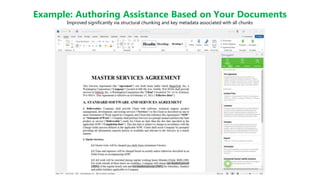
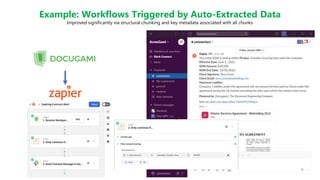
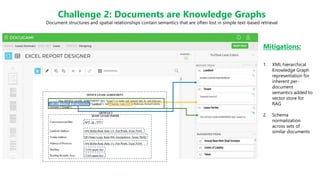
The Document Engineering Company presented a webinar on lessons learned from deploying large language models with LangSmith. They discussed challenges with using LLMs on real documents, which are more complex than flat text. Documents contain structure like headings and tables, and relationships that form a knowledge graph. They demonstrated how to represent documents as XML to preserve semantics and improve retrieval augmented generation. Complex chains in production require debugging failures from issues like syntax errors or rate limits. Their approach is to regularly analyze failures, add examples to training, and fine tune models in an end-to-end process.






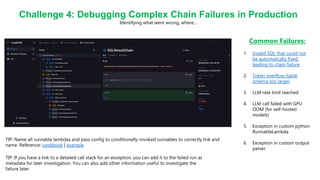
![Challenge 3: Building Complex Chains with the LangChain
Expression Language
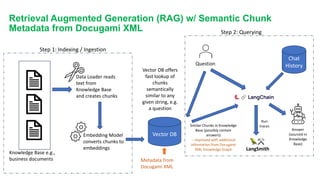
Real-world chains can get complicated with parallel branches, output parsers, few shot examples, conditional sub-chains, etc.
Question
“What were the
total midmarket
gross sales for
Mexico in
2014?”
Generate
SQL Query
SQL DB
(read-only)
Table
schema and
sample rows
Run SQL
Query
Explainers
(in parallel)
Result
Explainer
Query
Explainer
(for non-
technical
users)
SELECT SUM("Gross
Sales") FROM
financial_data WHERE
Segment = "Midmarket"
AND Country = "Mexico"
AND Year = 2014;
Syntax
Error?
(pysqlite3.dbapi2.O
perationalError) no
such table:
financial_data
Attempt
Fixup
SELECT SUM("Gross
Sales") FROM "Financial
Data" WHERE Segment =
"Midmarket" AND Country
= "Mexico" AND Year =
2014;
"[(451890.0,)]"
The total
midmarket gross
sales for Mexico
in 2014 were
$451,890.
Sum of 'Gross
Sales' for the
'Midmarket' segment
in Mexico for the
year 2014.
Sample code: https://rebrand.ly/docugami_complex_chain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docugamiwebinar-llmsinproduction-230920071519-179a639f/85/LangChain-Docugami-Webinar-9-320.jpg)