This document discusses landslides, including what they are, their causes and impacts. It provides the following key points:
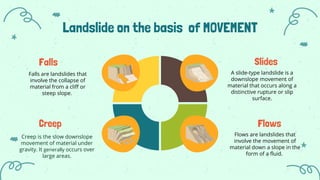
- Landslides are the downslope movement of rock, debris and soil under the influence of gravity. They are classified based on movement (falls, slides, flows, creeps) and material (rock falls, debris falls, mud flows).
- Common causes of landslides include heavy rainfall, earthquakes, deforestation, mining, urbanization.
- Impacts of landslides include loss of life, damage to infrastructure and property, impacts on river ecosystems, and changes to landscapes.
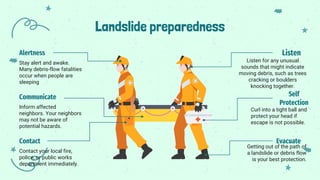
- Preventive measures include increasing forest cover, reducing urbanization activities, removing loose material from