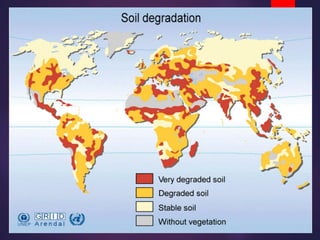
Land degradation refers to the reduction in soil quality and fertility due to various human and environmental factors. It is a major challenge for sustainable development. The causes of land degradation include deforestation, soil erosion, mining, unsustainable agricultural practices, and urban expansion. These activities can lead to declines in soil quality, water availability, biodiversity, and agricultural productivity. Conservation measures to prevent land degradation involve practices like strip farming, crop rotation, contour farming, and construction of bunds and ridges to reduce soil erosion. Sustainable land management aims to utilize land resources for production without reducing long-term productivity through practices informed by climate information.