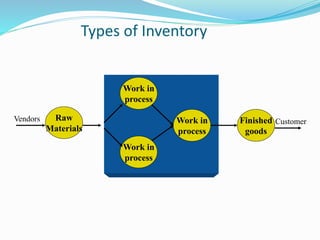
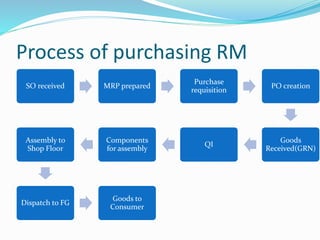
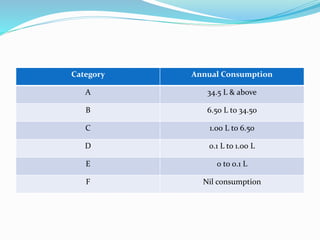
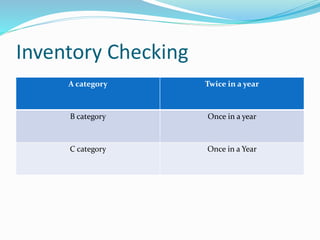
Inventory includes raw materials, work in process, and finished goods. It is managed to meet future demand and resale goals. There are different inventory control methods like ABC analysis that categorizes items by importance. The economic order quantity model determines the optimal amount to purchase to minimize ordering and holding costs. Last in first out and first in first out are methods for issuing inventory. Periodic and perpetual systems exist for inventory counting, and ABC analysis determines the frequency of counting for each category. Efficient inventory management involves proper planning of purchasing, handling, and storage of materials.