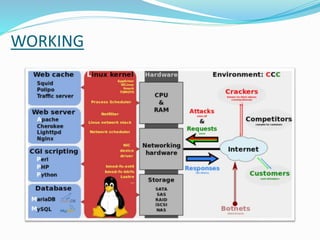
The document outlines the components and workings of the LAMP web development stack, including Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP. It discusses how Linux provides the base operating system, Apache is the web server, MySQL stores and retrieves data, and PHP is used to manipulate and display information. The document also covers advantages like cost-effectiveness, limitations for transient data loads, and how to secure each component of the LAMP stack.