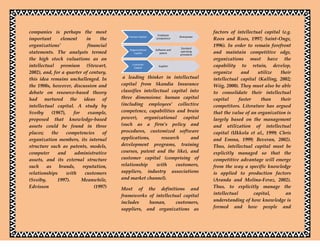
This document discusses intellectual capital and its importance to organizations. It defines intellectual capital as comprising of knowledge embedded assets such as employee skills, relationships, innovations, and machines. Intellectual capital theorists view these knowledge assets as more important than traditional financial and physical assets. The document also describes the different components of intellectual capital, including human capital, organizational capital, and customer capital. Finally, it discusses the levels of knowledge within intellectual capital - explicit knowledge that is documented, and tacit knowledge based on experiences and interactions. Intellectual capital management is needed to access and utilize these knowledge assets for competitive advantage.