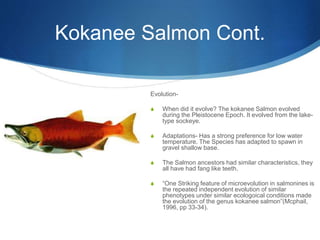
This document summarizes Jake Dawson's geology project on Lake Tahoe. It discusses the evolution of Kokanee salmon in Lake Tahoe, adapting from sockeye salmon during the Pleistocene epoch. It also describes the glacial formation of Emerald Bay through processes like U-shaped valleys and lateral moraines. Finally, it examines the igneous granite, metamorphic slate rock, and metasedimentary Tallac rocks found in the Lake Tahoe region.