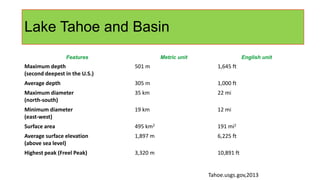
The document summarizes Kalie Ceglia's geology field assignment at Lake Tahoe, which involved studying the geologic evolution of the Tahoe Basin, collecting rock and plant samples, and taking photos of glacial features. Key findings include: the Basin was formed by faulting 400 million years ago; samples collected included quartz, agate, granite, and a snow plant; photos documented evidence of glacial scraping and movement in locations like Emerald Bay and Eagle Falls.