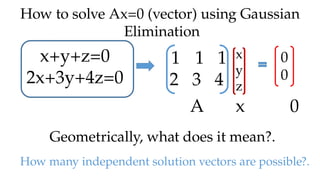
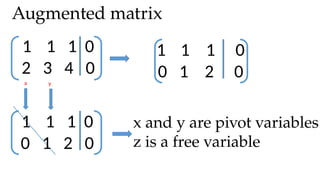
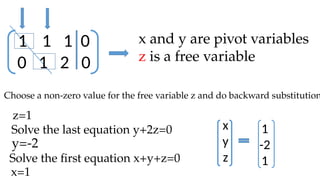
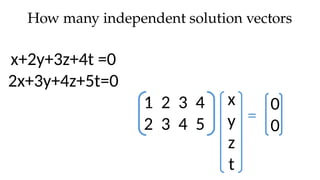
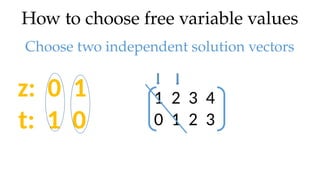
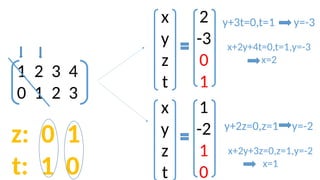
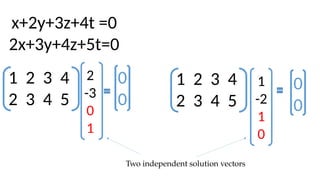
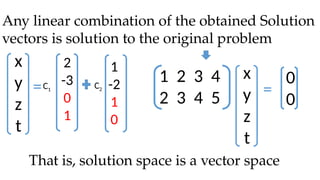
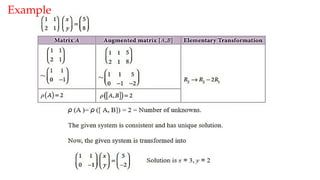
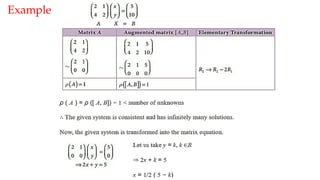
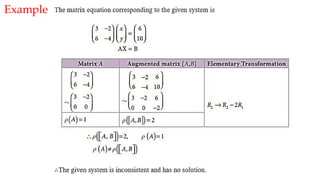
The document discusses Gaussian elimination for solving systems of linear equations, highlighting its foundational concepts such as linear combinations and vector spaces. It outlines the process of using reduced row echelon form (RREF) to determine basis sets for row and column spaces and explains the geometrical interpretation of solution vectors in homogeneous systems. Additionally, it explores determining the number of independent solution vectors based on free variables and provides examples to illustrate these concepts.





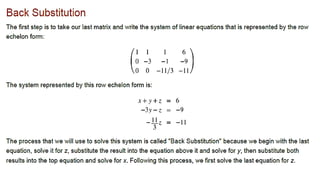

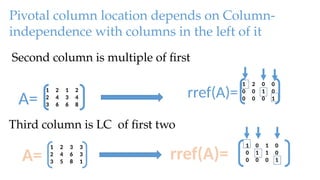
![How to use rref to get basis set for row space and
column space.
Ans:
all nonzero rows of rref(A) form basis set for row space
[a b]=rref(A)
a=reduced matrix
b=array giving index of pivotal columns
Brows=a(1:length(b),:) % Row-space basis set
Bcols=A(:,b) % column-space basis set from columns of A
Note: multiple ways to choose a basis set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l02gaussianelimination-241103140803-5334f024/85/L02_Gaussian-Elimination-for-solving-Equations-pptx-10-320.jpg)