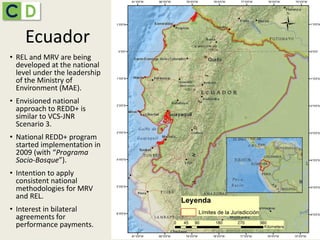
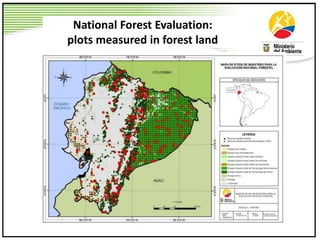
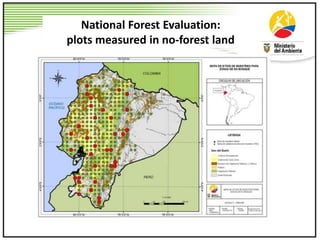
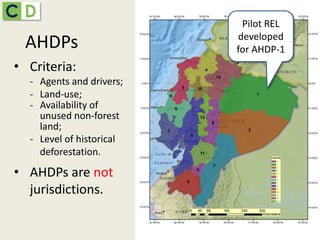
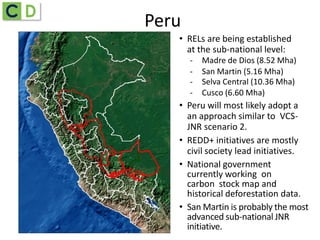
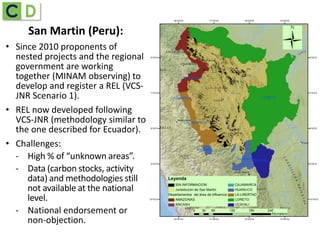
This document summarizes lessons learned from Ecuador and Peru's efforts to establish REDD+ baselines and monitoring systems at the national and sub-national levels. It discusses some of the common challenges faced, such as developing institutional capacity, generating carbon stock and activity data, and meeting various international requirements. It also identifies opportunities to take a stepwise approach and test jurisdictional REDD+ methods to help align key players and adjust approaches over time based on experiences on the ground.