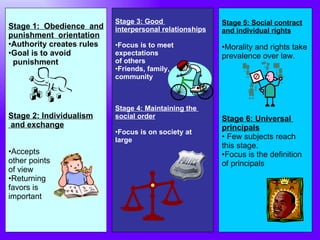
Lawrence Kohlberg was an American psychologist known for his theory of moral development. He studied under Jean Piaget and revealed his stage theory of moral development in 1958. Kohlberg proposed that moral reasoning develops through six stages grouped into three levels: pre-conventional, conventional, and post-conventional. His research involved interviewing children and presenting moral dilemmas to understand their reasoning. Kohlberg developed a method of assessing moral development that focused on how individuals think about social experiences rather than as a result of maturation alone.