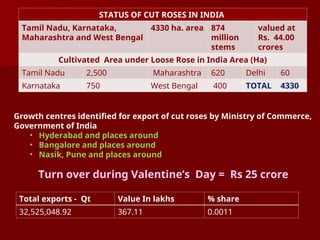
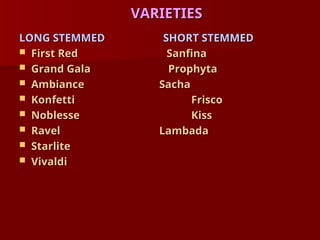
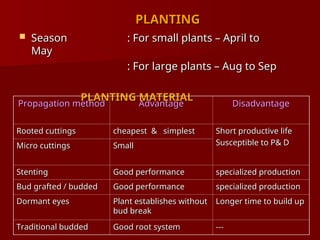
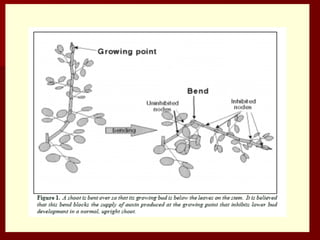
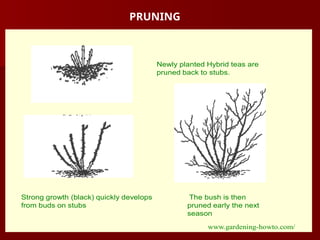
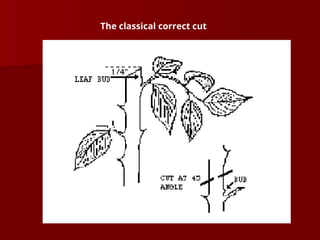
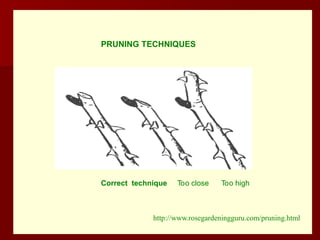
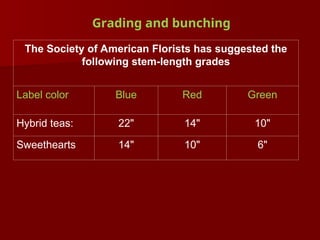
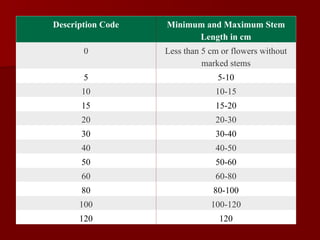
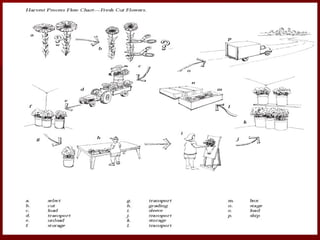
The document discusses the production technology and status of Dutch roses in the floriculture industry of India, highlighting key producing states like Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu. It details various rose types, including hybrid tea, floribunda, and spray roses, along with information on cultivation techniques, climatic requirements, and propagation methods. Additionally, it covers rose breeders and the characteristics of various rose varieties cultivated for their commercial potential.