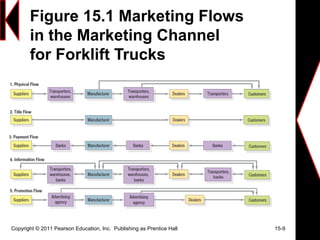
This document discusses marketing channels and channel management. It begins by defining a marketing channel system as the set of organizations involved in making a product available to consumers. It then discusses how companies design channel systems, manage channel members, integrate channels, and address channel conflicts. The document also covers the rise of e-commerce and m-commerce channels and the issues companies face with these new channels.