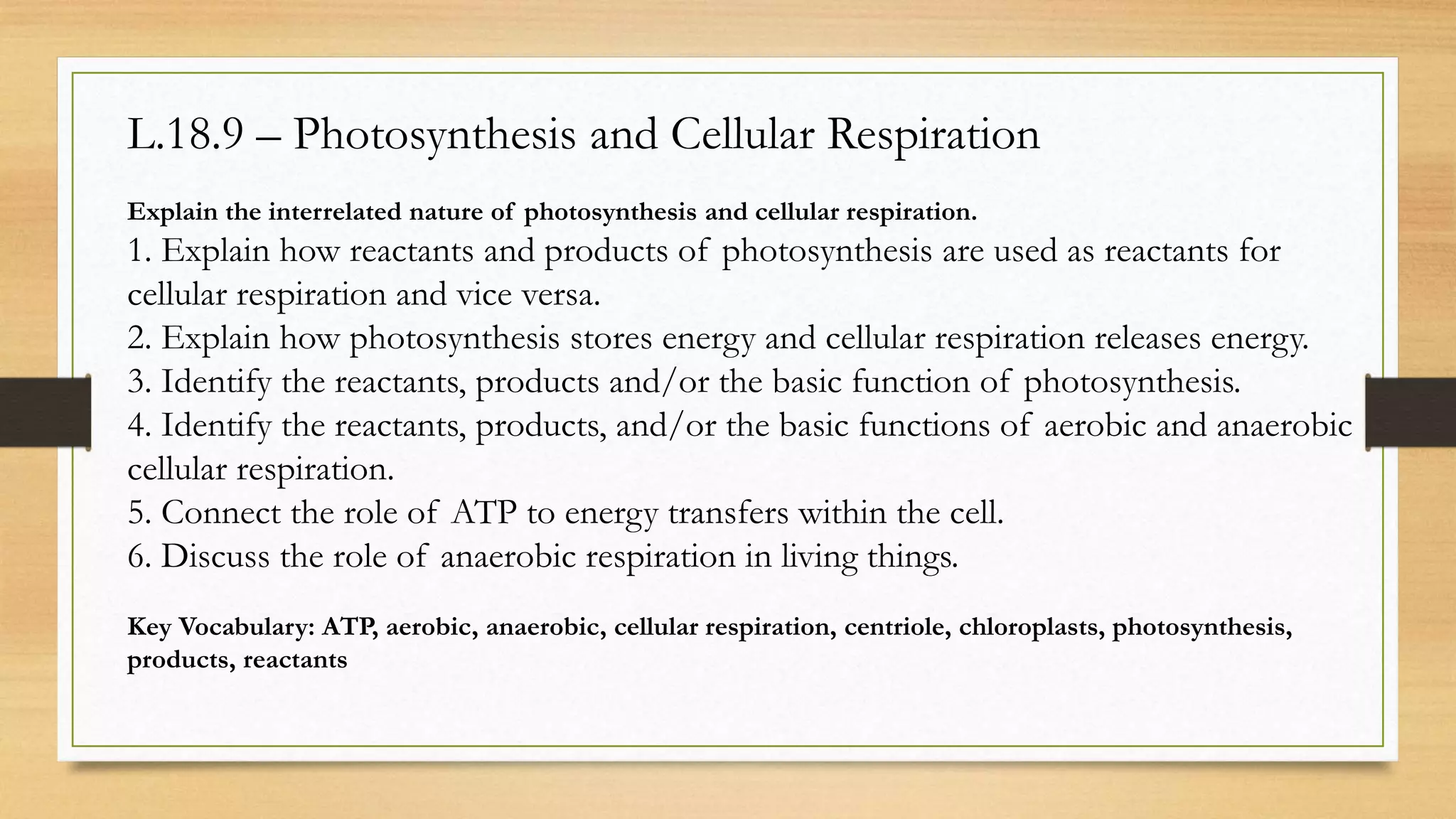
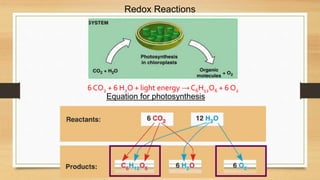
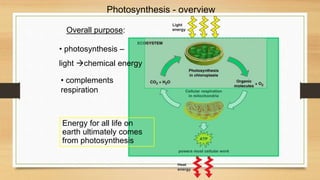
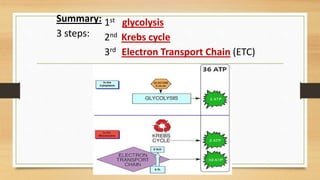
The document discusses photosynthesis and cellular respiration. It explains that:
1) Photosynthesis uses light energy, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. The products of photosynthesis are then used as reactants in cellular respiration.
2) Photosynthesis stores energy in chemical bonds, while cellular respiration releases energy by breaking those bonds.
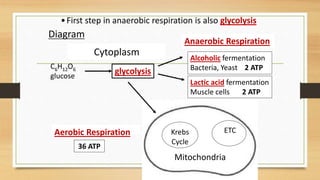
3) There are two types of cellular respiration - aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen and produces much more ATP, and anaerobic respiration which occurs without oxygen and produces less ATP.