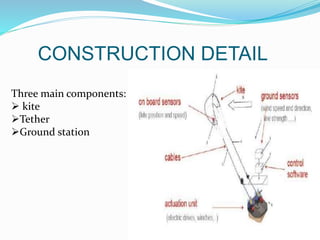
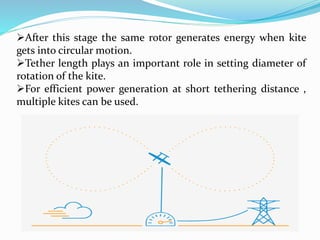
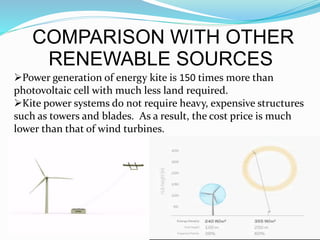
The document discusses energy kites as an innovative approach to renewable wind energy, highlighting their advantages over traditional wind turbines such as lower costs and increased efficiency. Crosswind kite systems utilize kites tethered to the ground to harvest high-altitude winds, with significant potential for electricity generation. Implementing energy kite technology on a large scale could reduce reliance on conventional power sources and help combat global warming.