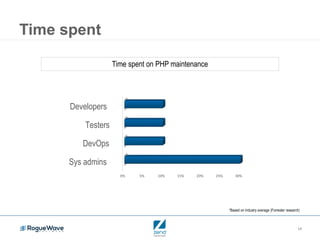
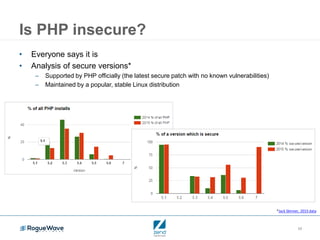
This document outlines the key elements of building a perfect PHP application for enterprise use, emphasizing the importance of security, performance, and scalability. It discusses best practices for maintaining an up-to-date PHP stack, application security measures, and the costs associated with system failures. Overall, it serves as an introduction to a series focused on developing enterprise PHP applications and optimizing performance.