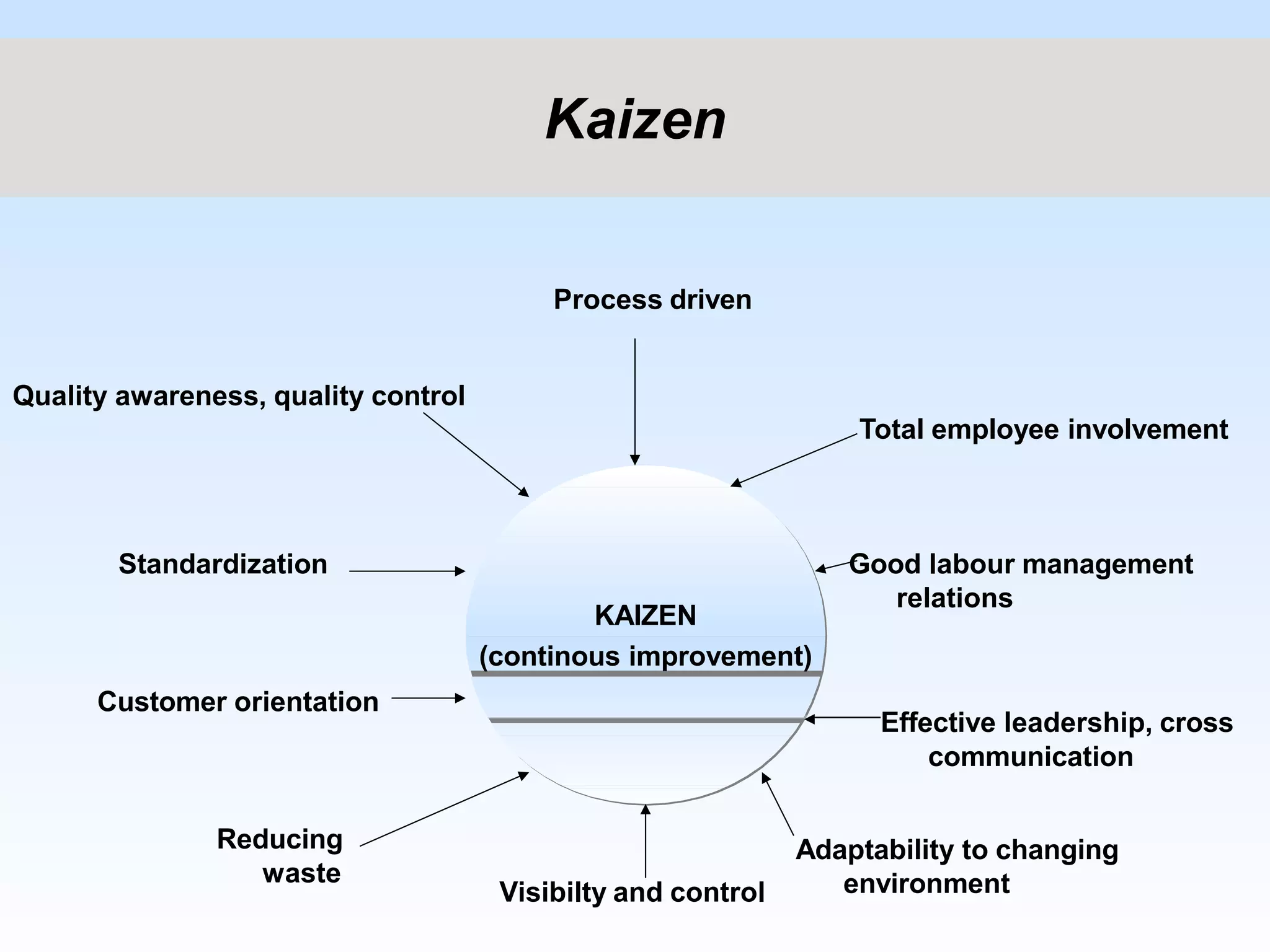
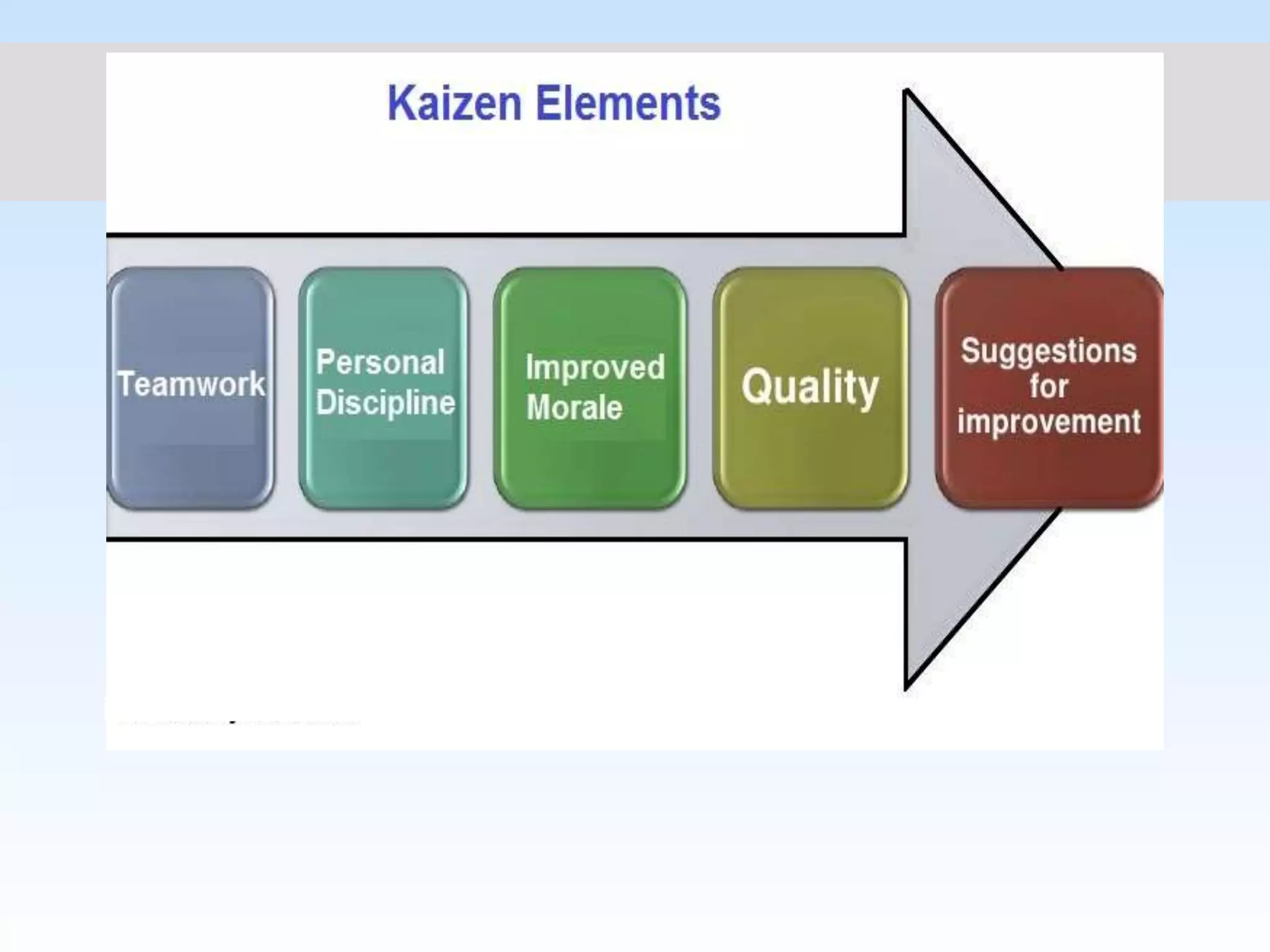
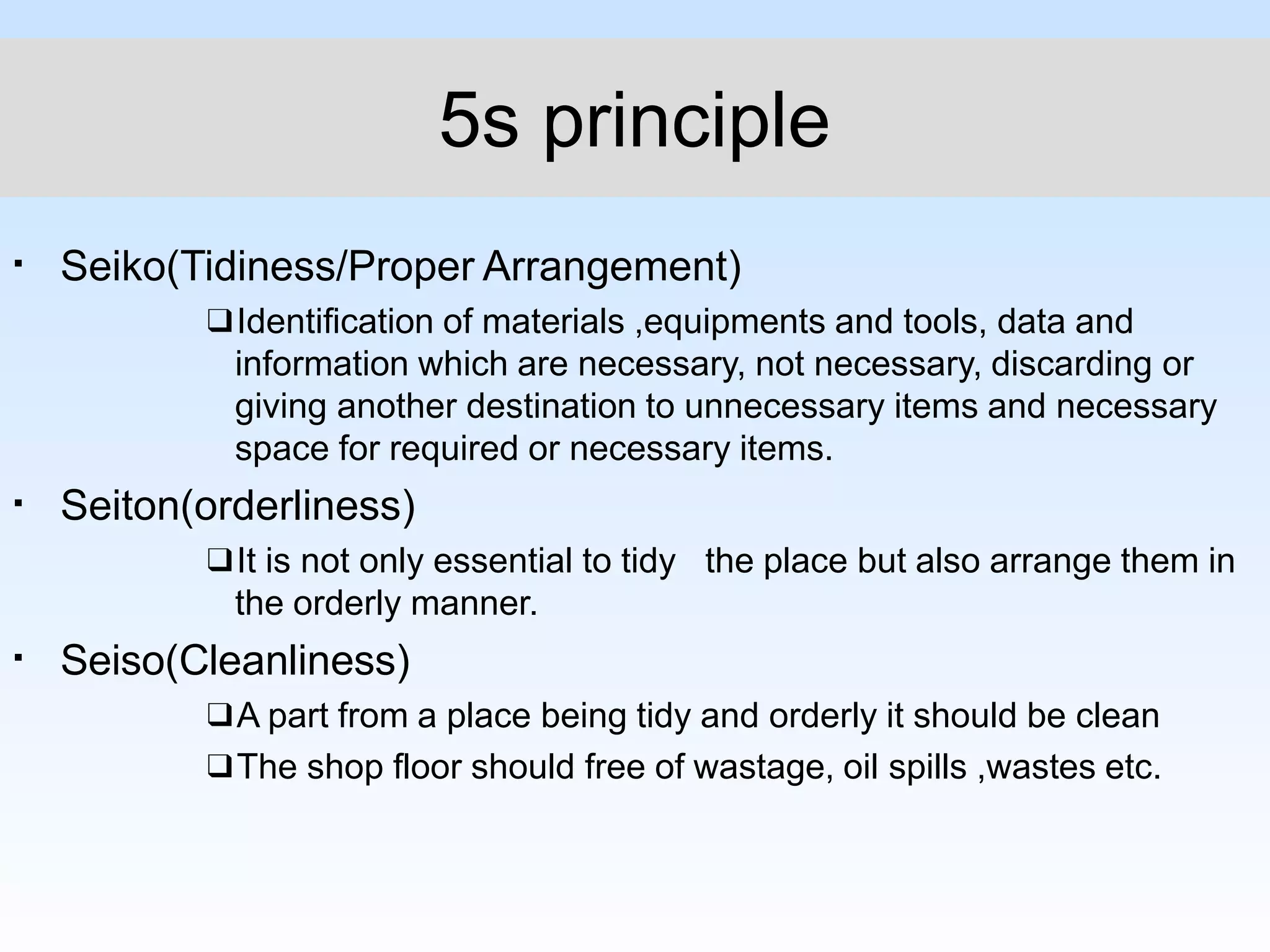
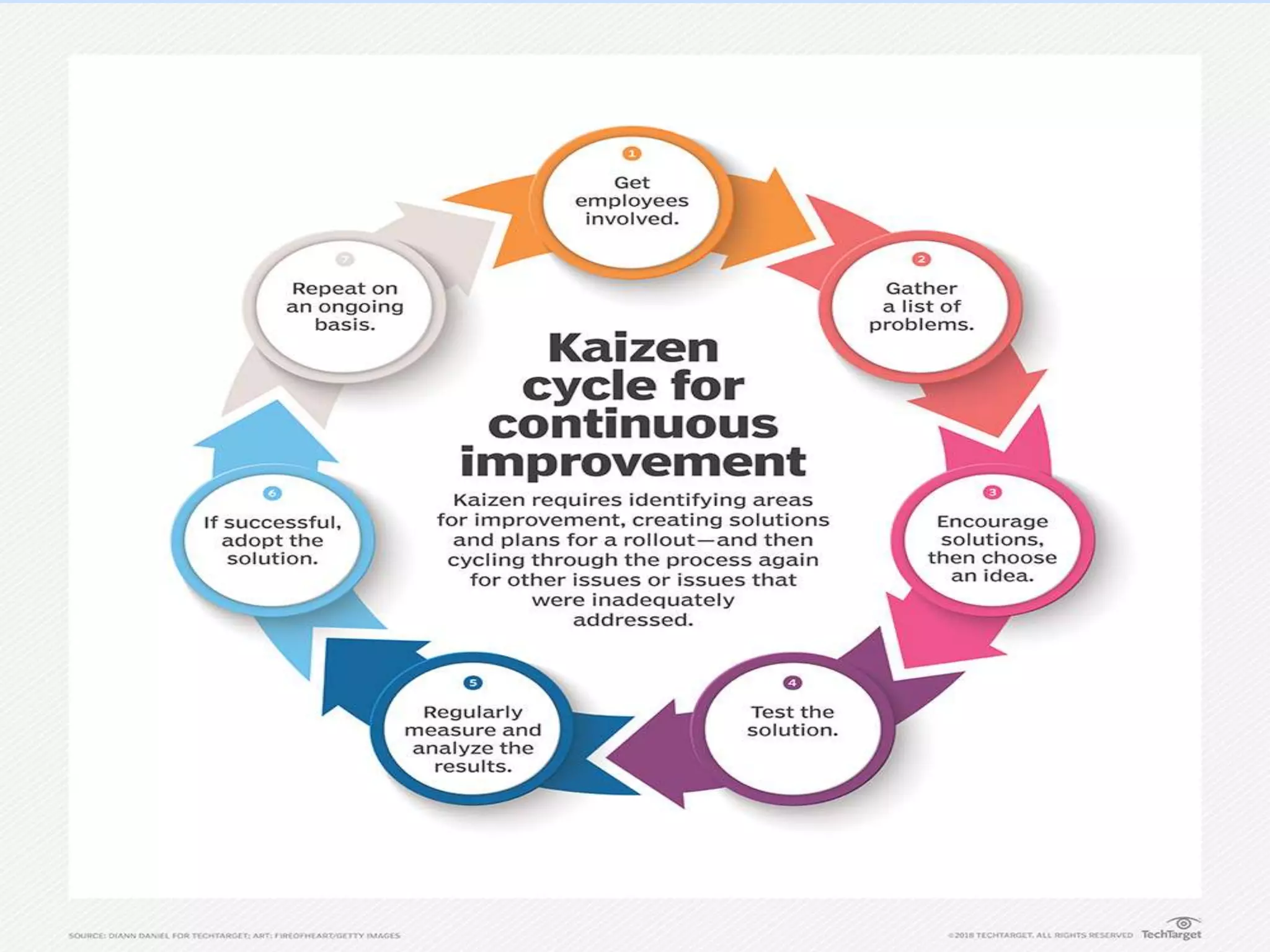
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy of continuous improvement involving small, incremental changes to processes. It has been applied in healthcare, government, and other industries to make processes more effective, efficient, and adequate with little to no expense. The main objectives of Kaizen include good labor relations, communication, adaptability, reducing waste, and customer orientation. The three basic principles are workplace effectiveness using 5S tools, eliminating waste, strain and discrepancy, and standardization of processes, materials, and machinery.