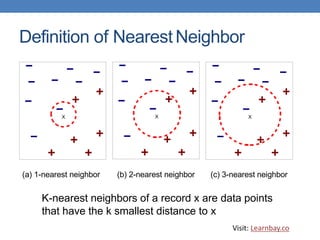
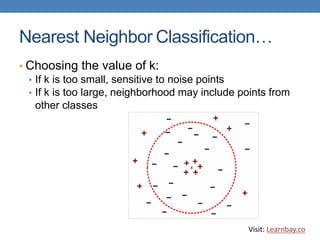
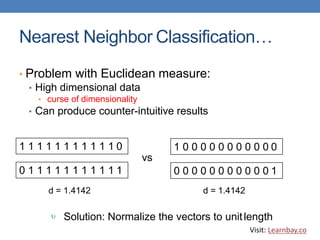
This document discusses nearest neighbor classification, which is an instance-based machine learning algorithm. It stores all training records and classifies new records based on their similarity to stored examples, by finding the k nearest neighbors and predicting the class as the most common label among those neighbors. Key aspects covered include using a distance metric like Euclidean distance to find neighbors, choosing an optimal k value, addressing scaling issues between attributes, and challenges with high-dimensional data.