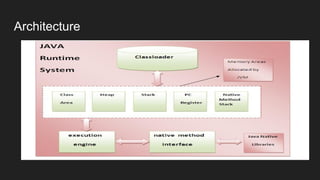
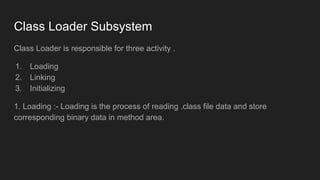
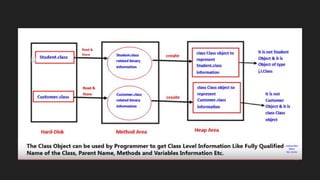
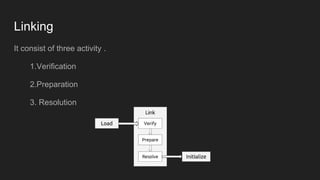
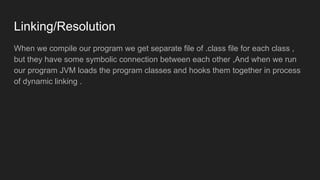
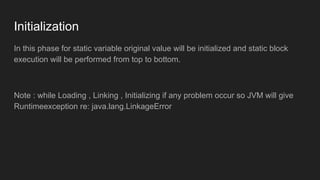
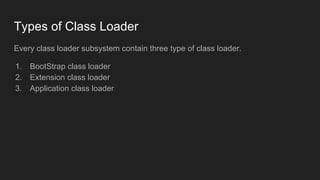
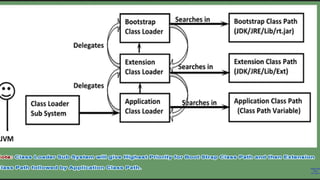
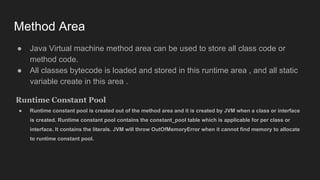
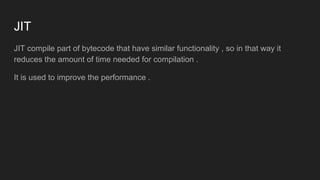
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a runtime engine that loads and runs Java applications. It is divided into three main components: the class loader subsystem, memory areas, and an execution engine. The class loader loads .class files, verifies them, and loads the binary data into the method area. The memory areas include the method area for storing class data, heap for objects, and stack for local variables. The execution engine interprets bytecode and uses just-in-time compilation to improve performance.