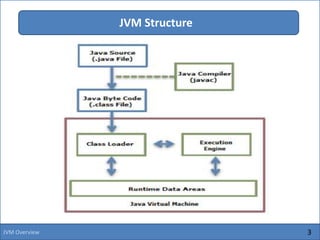
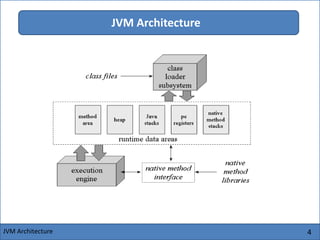
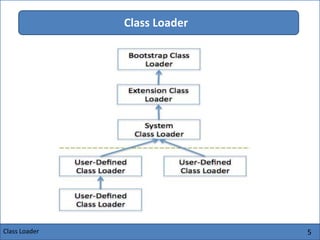
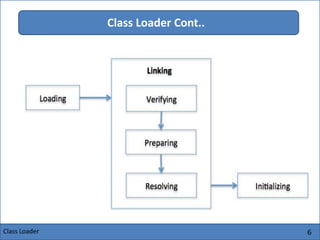
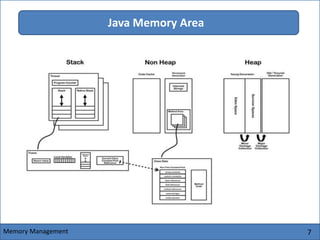
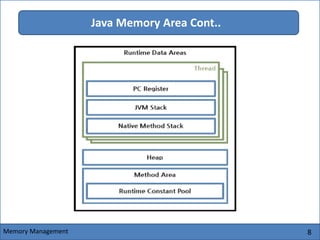
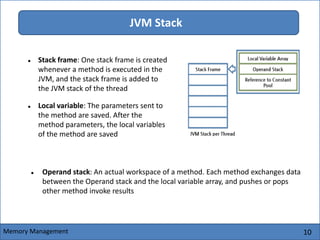
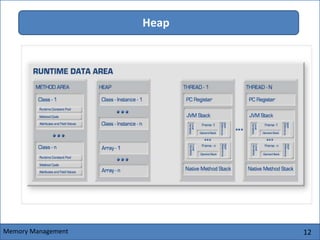
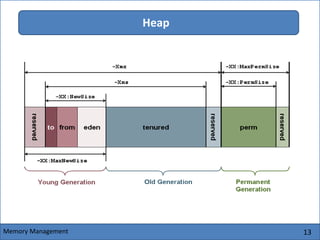
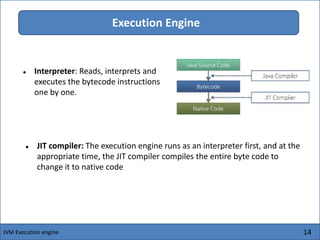
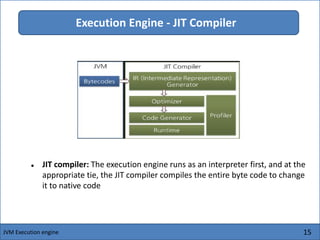
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is an abstract computing machine that executes Java bytecode. It has several core components including a class loader, memory areas like the heap and stack, and an execution engine. The execution engine initially interprets bytecode instructions but can optimize performance by just-in-time compiling frequently used bytecode into native machine code. The JVM provides a layer of abstraction between Java applications and the underlying hardware or operating system.