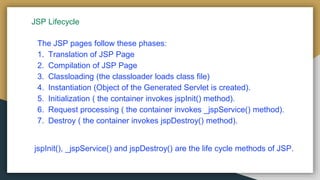
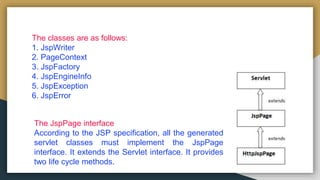
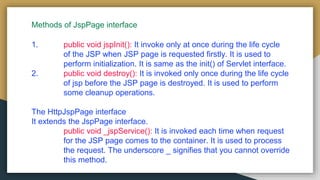
The document explains JSP (Java Server Pages) technology as an extension of servlets that enhances web application development with features like expression language and custom tags. It outlines the advantages of JSP over servlets, including easier maintenance, faster development, and reduced code complexity. Additionally, it details the JSP lifecycle phases and provides an overview of the JSP API, highlighting key interfaces and methods.