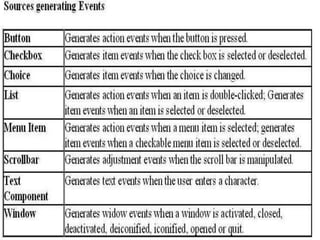
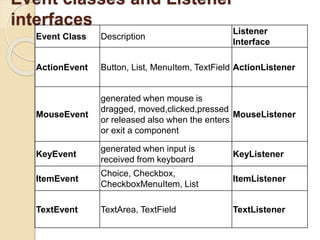
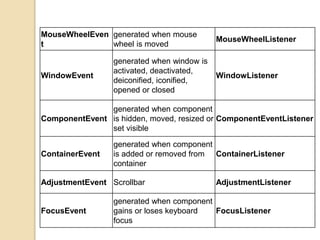
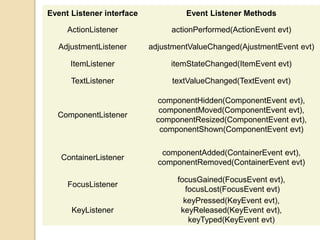
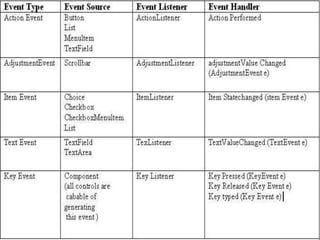
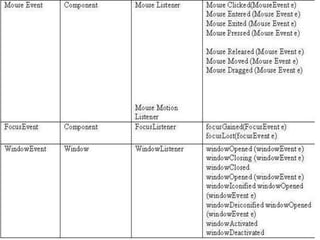
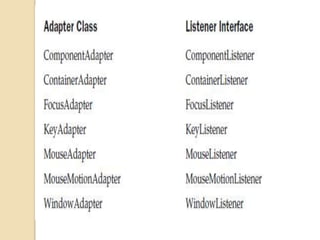
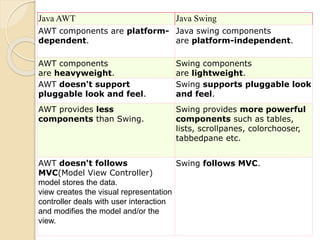
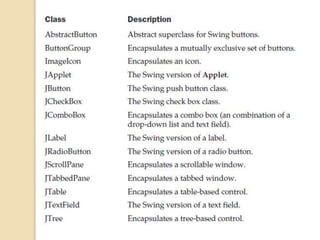
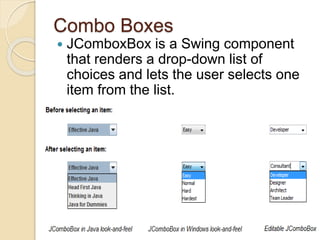
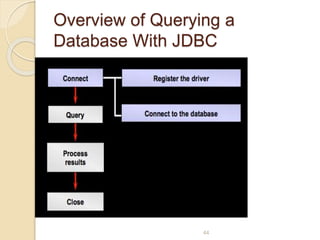
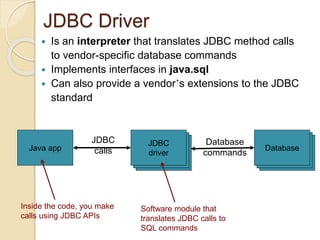
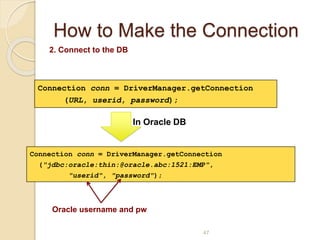
The document discusses event handling in Java. It describes what events are, how event handling works using the delegation event model. It lists common event classes and their corresponding listener interfaces. It provides examples of using events and listeners to handle button clicks and key presses. It also discusses adapter classes that simplify creating event handlers.


















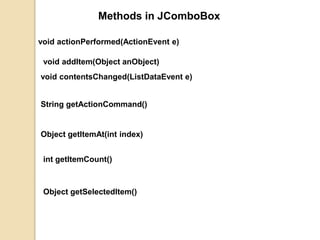
![JComboBox Constructors
JComboBox()Creates a JComboBox with a default data
model.
JComboBox(ComboBoxModel aModel)Creates a
JComboBox that takes its items from an existing
ComboBoxModel.
JComboBox(Object[] items)Creates a JComboBox that
contains the elements in the specified array.
JComboBox(Vector<?> items)Creates a JComboBox
that contains the elements in the specified Vector.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpnotes-160315042250/85/Jp-notes-29-320.jpg)
![Creating a new JComboBox component
JComboBox<String> comboLanguage = new JComboBox<String>();
comboLanguage.addItem("English");
comboLanguage.addItem(“Telugu");
comboLanguage.addItem(“Hindi");
comboLanguage.addItem(“Tamil");
comboLanguage.addItem(“Kannada");
String[] languages = new String[] {"English", “Telugu", “Hindi", “Tamil", “Kannada"};
JComboBox<String> comboLanguage = new JComboBox<String>(languages);
Vector<String> languages = new Vector<String>();
languages.addElement("English");
languages.addElement(“Telugu");
languages.addElement(“Hindi");
languages.addElement(“Tamil");
languages.addElement(“Kannada");
JComboBox<String> comboLanguage = new JComboBox<String>(languages);
myComboBox.setEditable(true);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpnotes-160315042250/85/Jp-notes-31-320.jpg)


![protected JPanel createInnerPanel(String text) {
JPanel jplPanel = new JPanel();
JLabel jlbDisplay = new JLabel(text);
jlbDisplay.setHorizontalAlignment(JLabel.CENTER);
jplPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 1));
jplPanel.add(jlbDisplay);
return jplPanel;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("TabbedPane Source
Demo");
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
frame.getContentPane().add(new
JTabbedPaneDemo(),BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(400, 125);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpnotes-160315042250/85/Jp-notes-34-320.jpg)


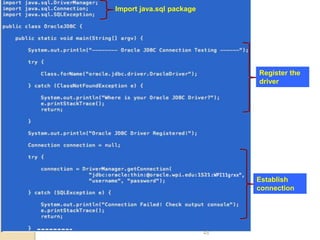
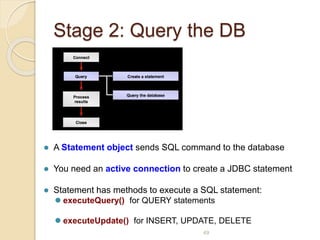
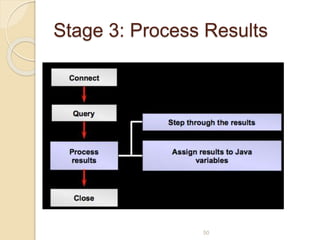
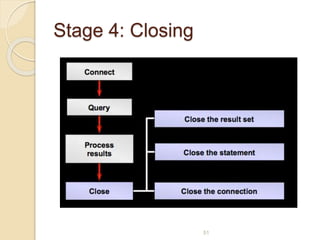

![Example: Connect to Microsoft
SQL Server via JDBC
System contains Microsoft JDBC Driver.
JDBC database URL for SQL Server
◦ The syntax of database URL for SQL Server
is as follows:
◦ jdbc:sqlserver://[serverName[instanceNa
me]
[:portNumber]][;property=value[;property=val
ue]]
Where:
serverName: host name or IP address of machine on which SQL server is
running.
instanceName: name of the instance to connect to on serverName. The default
instance is used if this parameter is not specified.
portNumber: port number of SQL server, default is 1433.
property=value: specify one or more additional connection properties.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpnotes-160315042250/85/Jp-notes-46-320.jpg)

![import java.sql.*;
public class Sqlselection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class.forName("com.microsoft.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver");
String userName = “user4";
String password = “pwd";
String url = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhostsqlexpress";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, password);
Statement s1 = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = s1.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM EMP");
String[ ] result = new String[20];
if(rs!=null) {
while (rs.next()) {
for(int i = 0; i <result.length ;i++) {
for(int j = 0; j <result.length;j++) { result[j]=rs.getString(i);
System.out.println(result[j]);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpnotes-160315042250/85/Jp-notes-48-320.jpg)