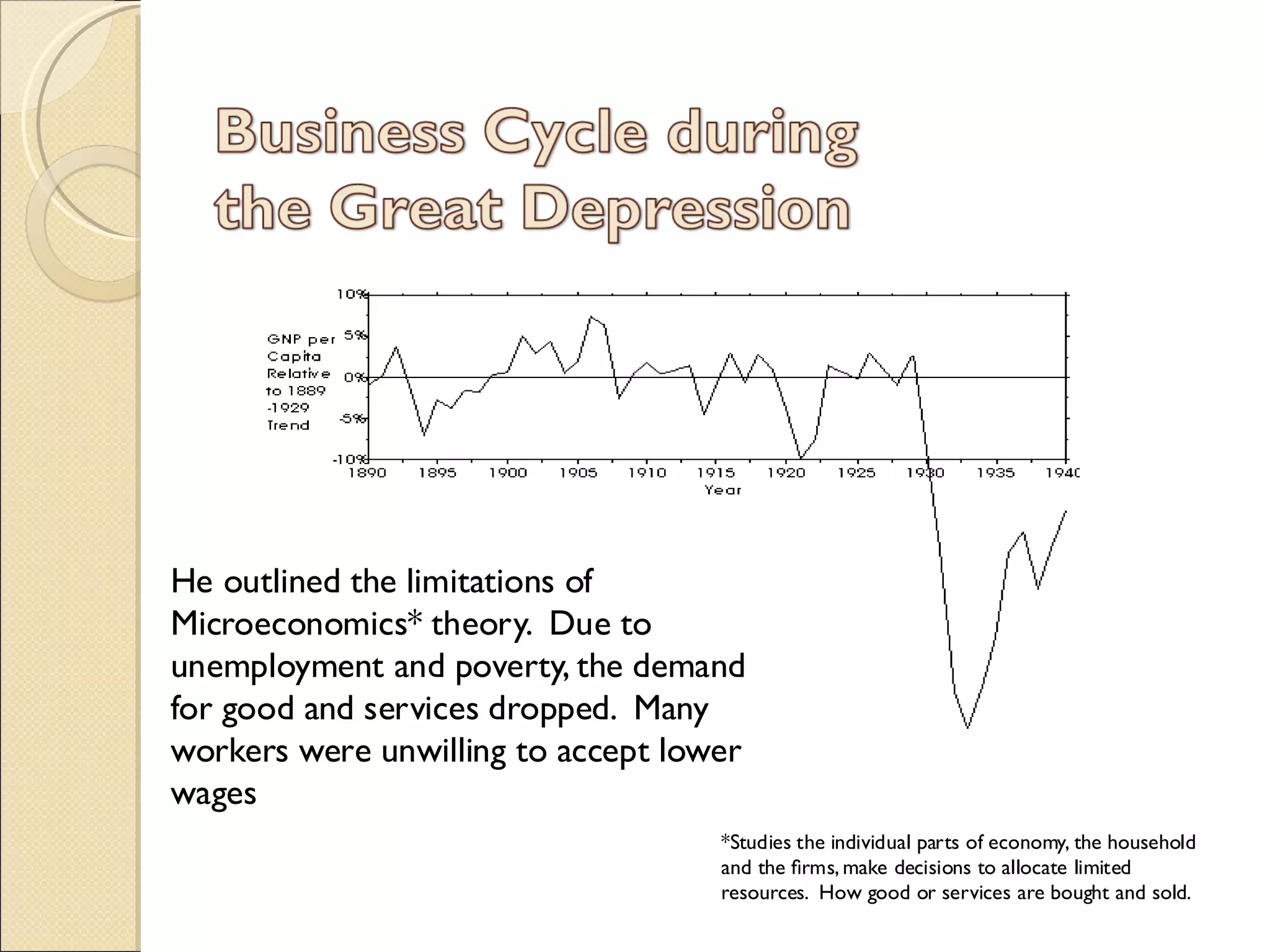
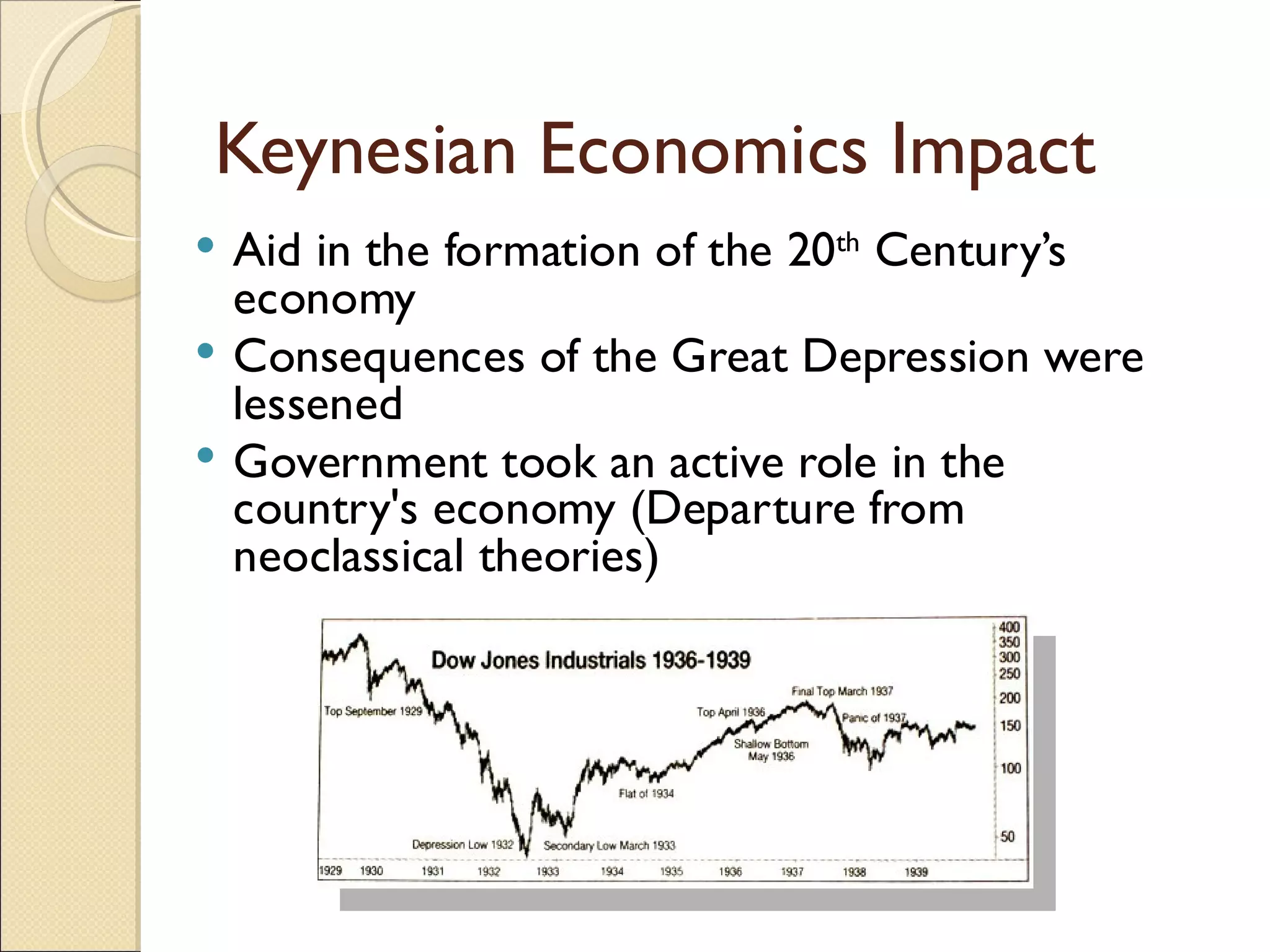
This document summarizes the life and work of John Maynard Keynes, a British economist known as the father of macroeconomics. It outlines that Keynes helped lead economies out of the Great Depression by advocating for interventionist policies like increased government spending. He challenged established neoclassical economic theories by introducing new concepts like consumption and the multiplier effect. Keynes argued the government should ensure full employment and regulate markets. His theories formed the basis of Keynesian economics and influenced economic policy for decades following World War II.