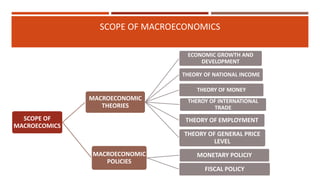
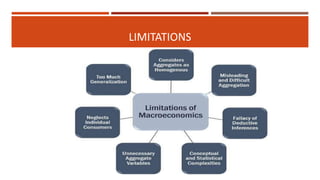
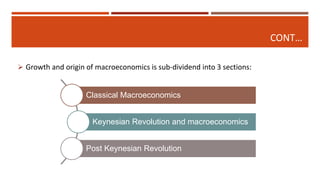
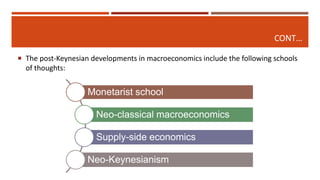
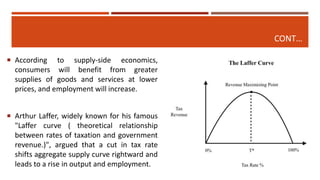
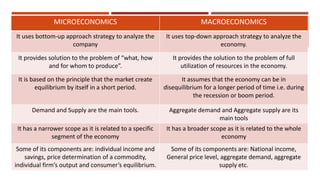
Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, examining aggregates such as national income, output, employment and price levels. It analyzes how these aggregates interact and how policies affect their behavior. Macroeconomics emerged as a separate field due to the failure of classical economics to explain the Great Depression. John Maynard Keynes developed theories emphasizing aggregate demand and the role of government in managing the economy. Later schools include monetarism, supply-side economics and new classical macroeconomics, debating the factors driving output and inflation.