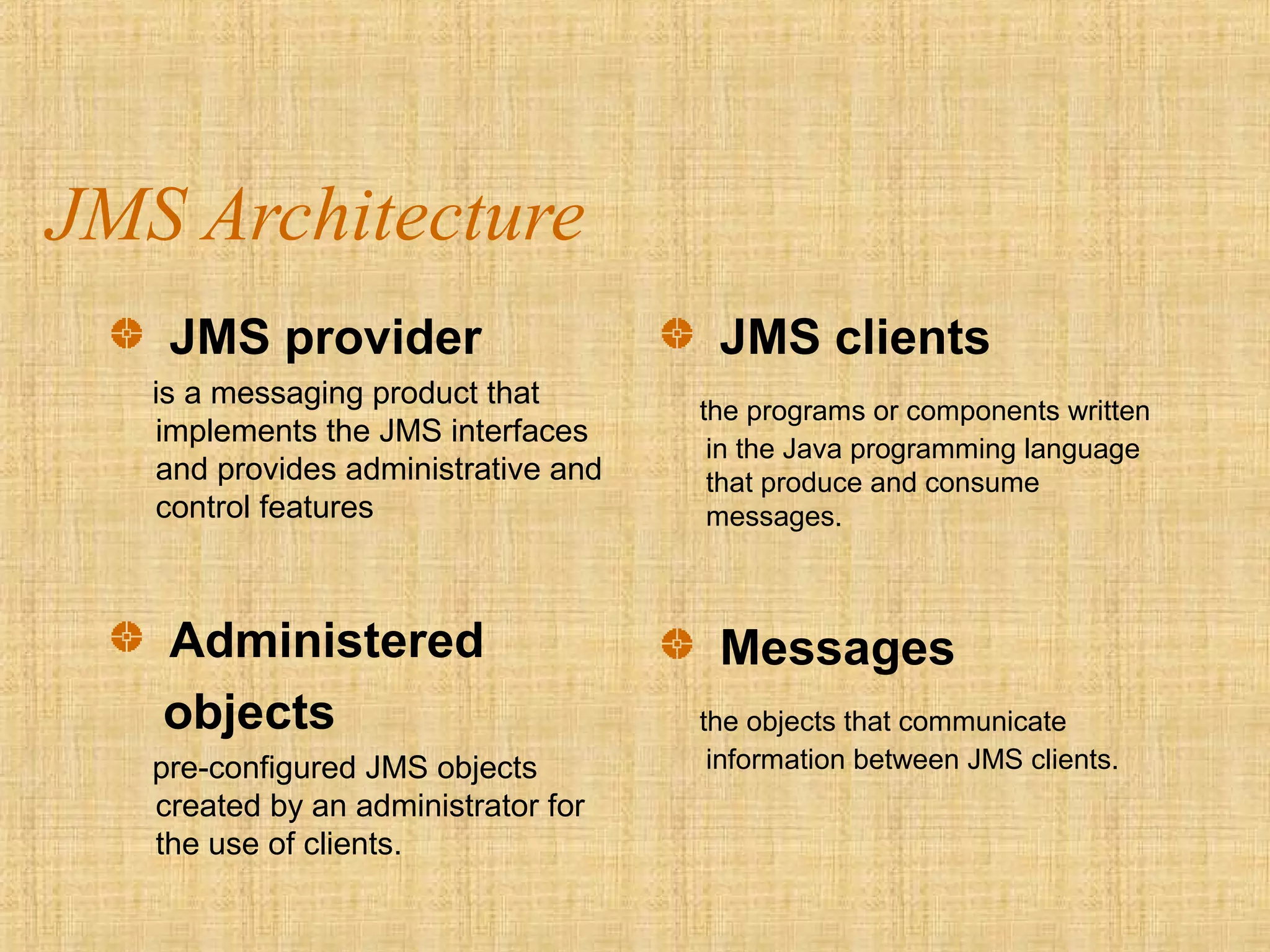
The document discusses Java Message Service (JMS), which allows Java programs to exchange messages. JMS uses three message exchange models: publish-subscribe messaging involving topics and multiple senders/receivers; point-to-point messaging using message queues with one sender and receiver; and request-reply messaging to send and receive related messages. A JMS provider implements the JMS interfaces and APIs to enable asynchronous, reliable messaging between distributed Java applications.