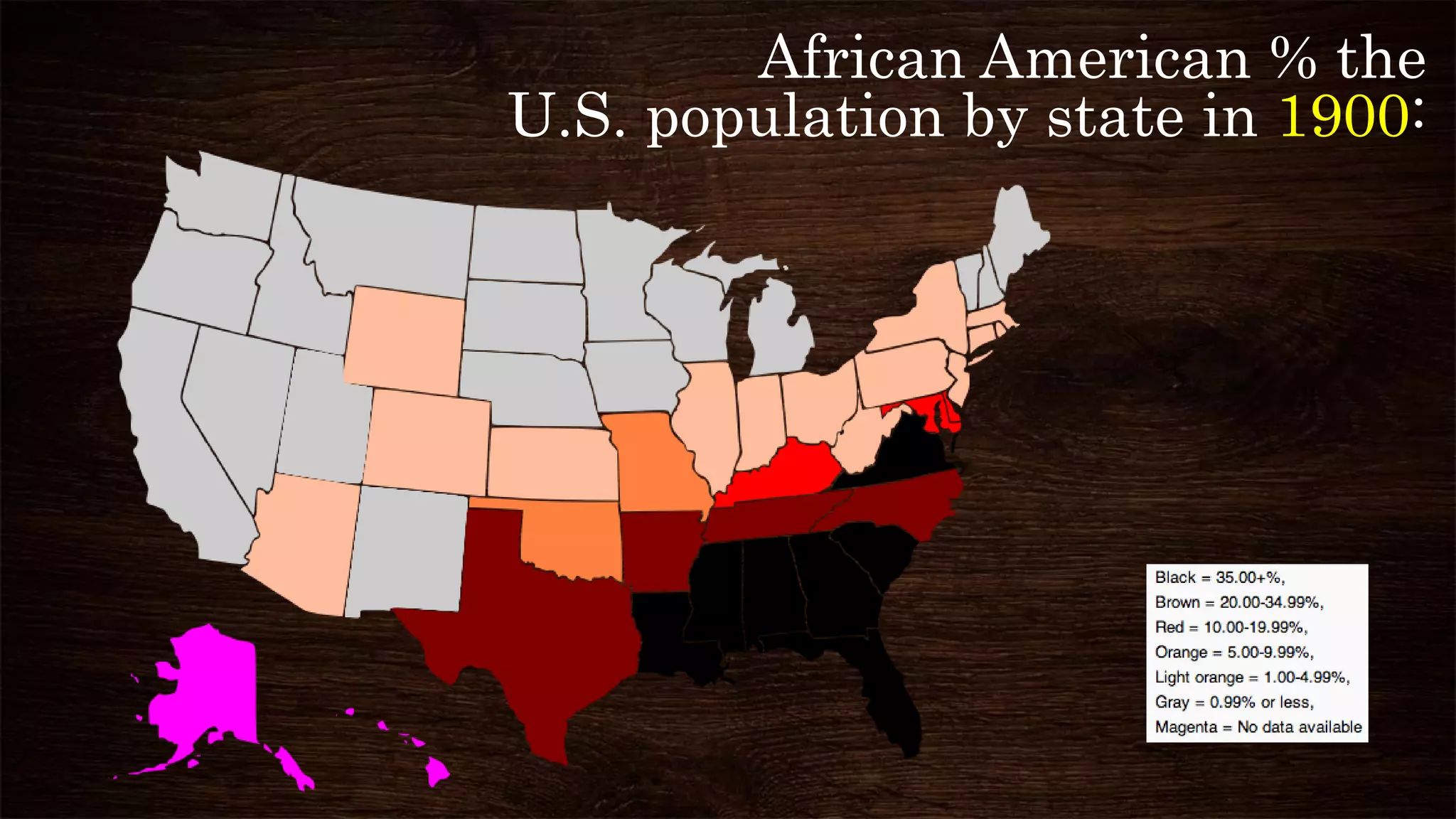
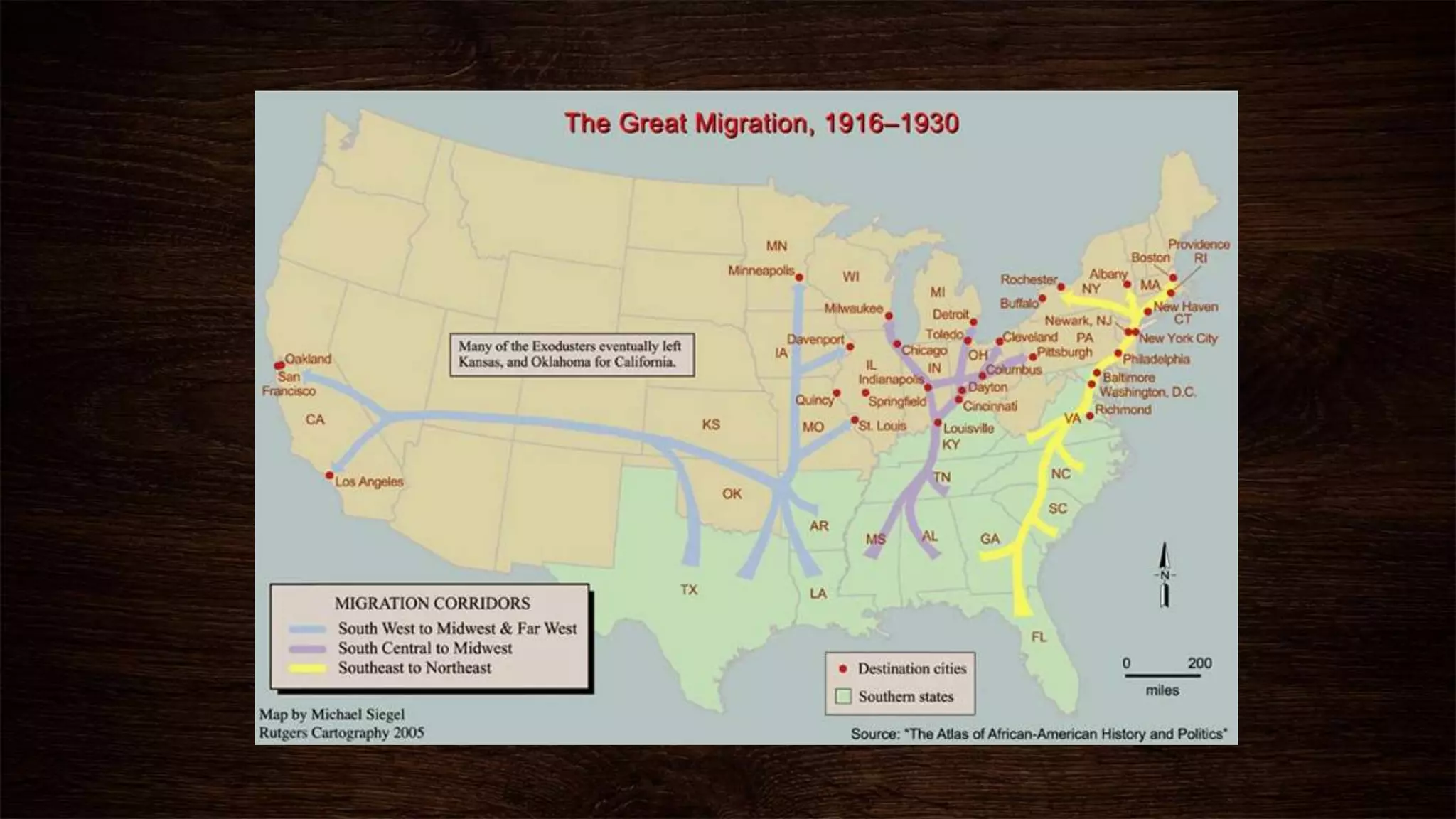
The Jim Crow Era spanned from 1876 to 1965 in the United States. After the end of Reconstruction in 1877 and the withdrawal of federal troops from the South, Southern states imposed Jim Crow laws to legislate racial segregation and disenfranchise African Americans. During this time, African Americans faced widespread discrimination in areas like jobs, housing, education, and legal rights. In response, some African Americans migrated north in the Great Migration from 1910 to 1930 to escape harsh racial conditions and seek better employment opportunities in northern and midwestern cities, though they still faced discrimination there as well.