1. Jet Airways acquired Air Sahara in 2007 for Rs. 1450 crore, after initial negotiations to purchase it for Rs. 2300 crore fell through.
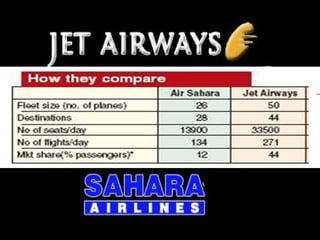
2. The acquisition provided Jet Airways with Air Sahara's fleet of 27 aircraft, infrastructure, and presence in markets it previously did not serve. It also increased Jet's domestic market share.
3. Integration efforts included absorbing Air Sahara employees through training, converting Air Sahara to the Jet Lite brand, merging similar aircraft fleets, reducing costs through steps like eliminating unused facilities, and discontinuing loss-making routes.