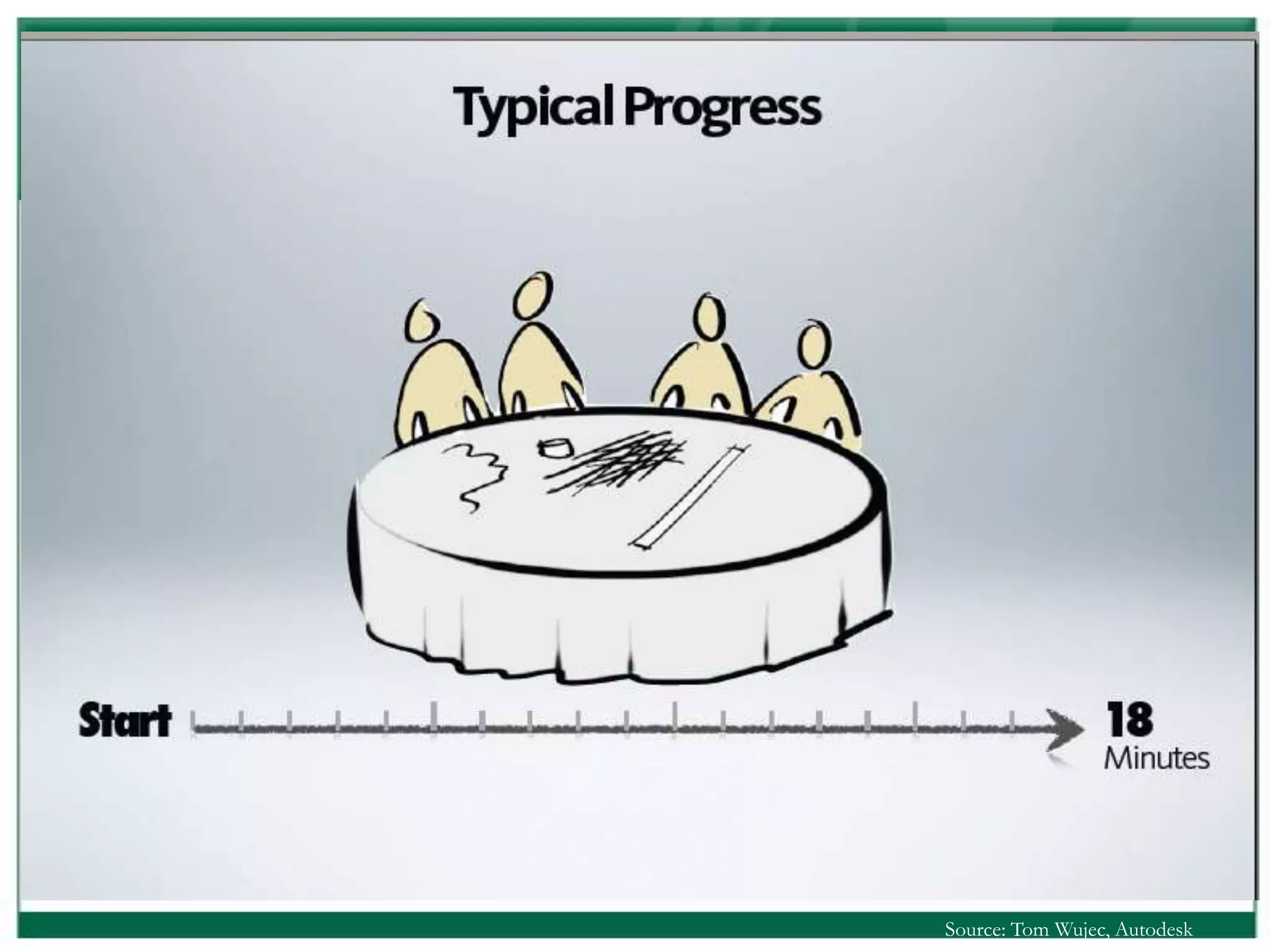
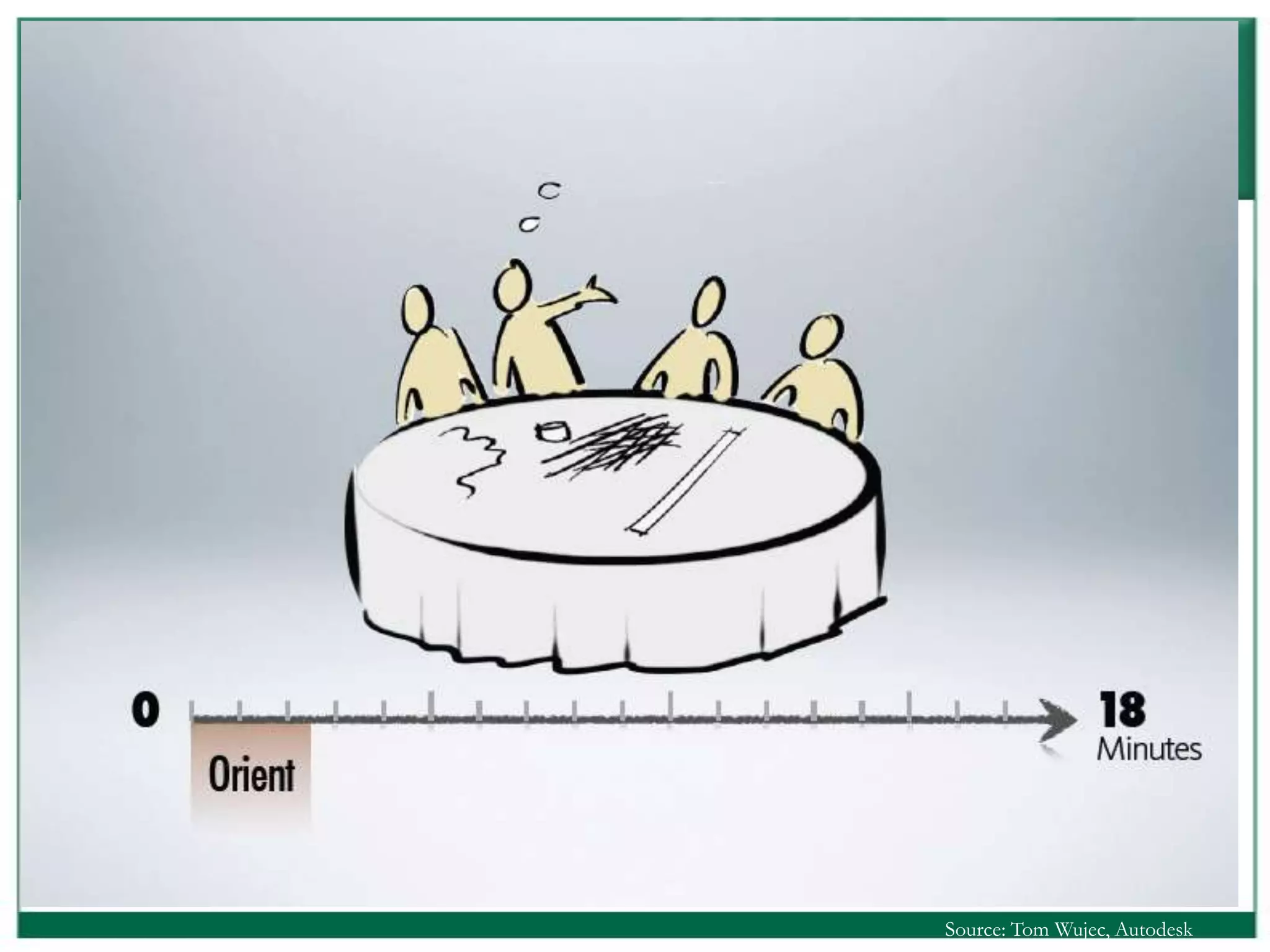
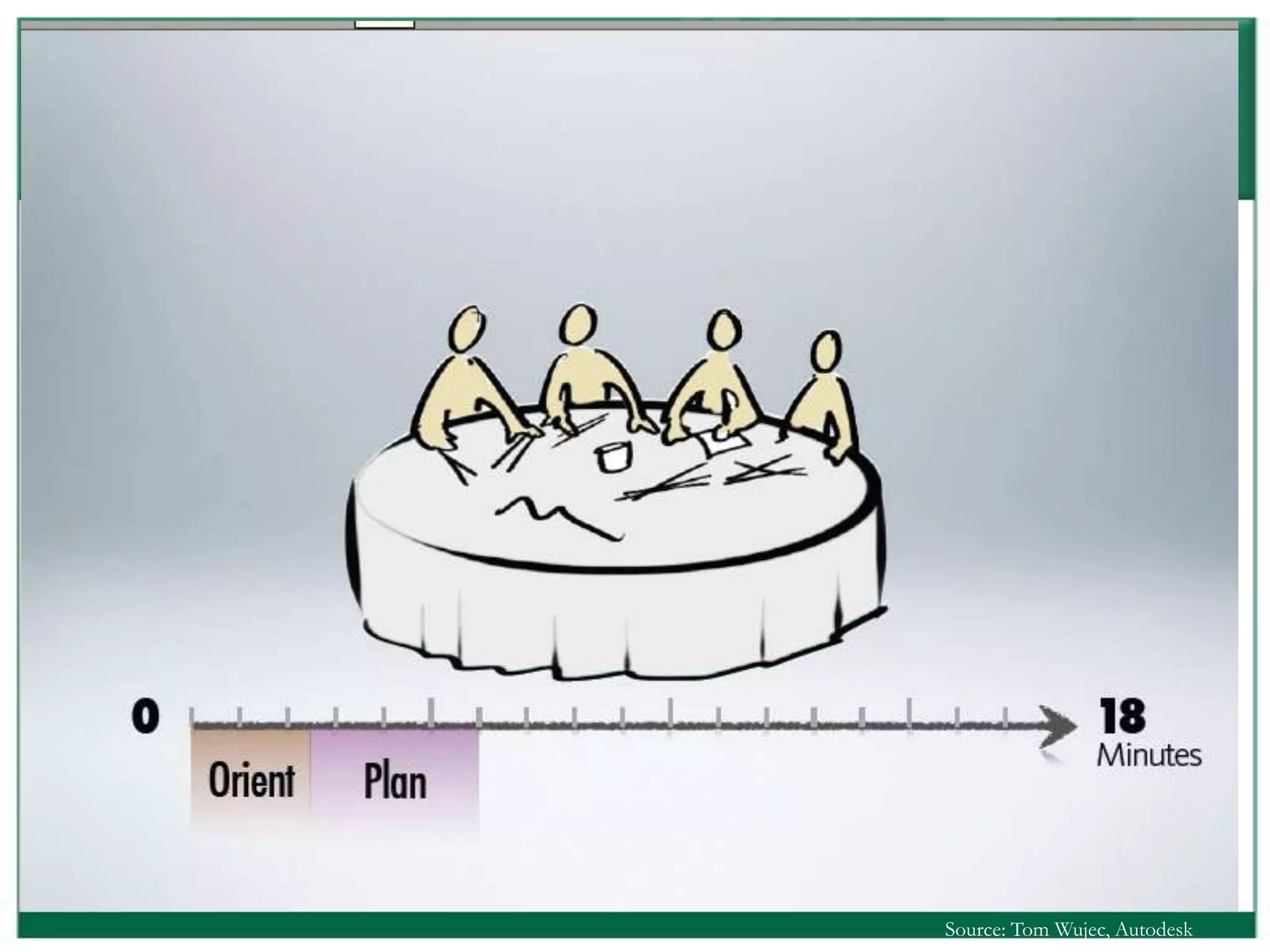
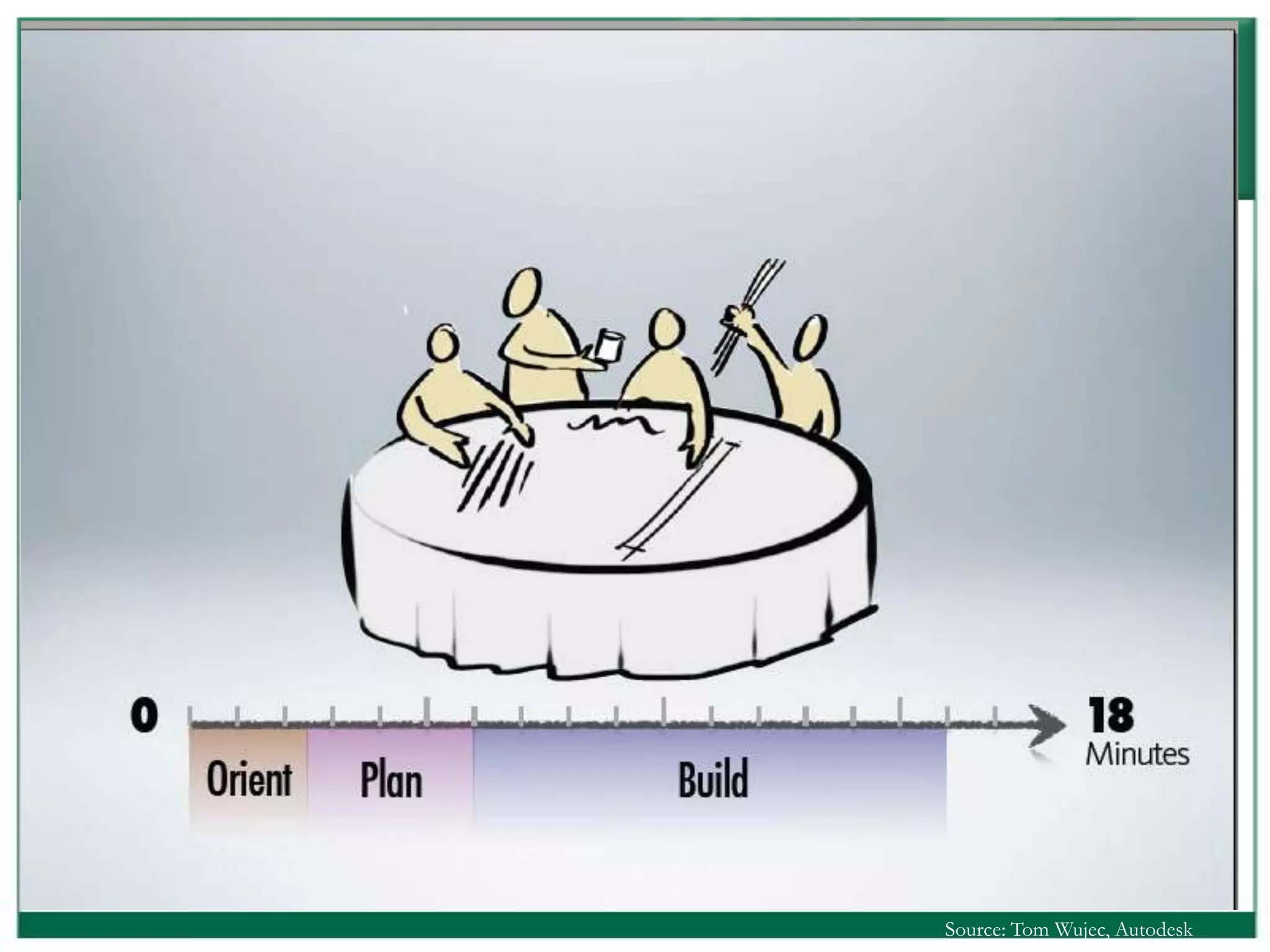
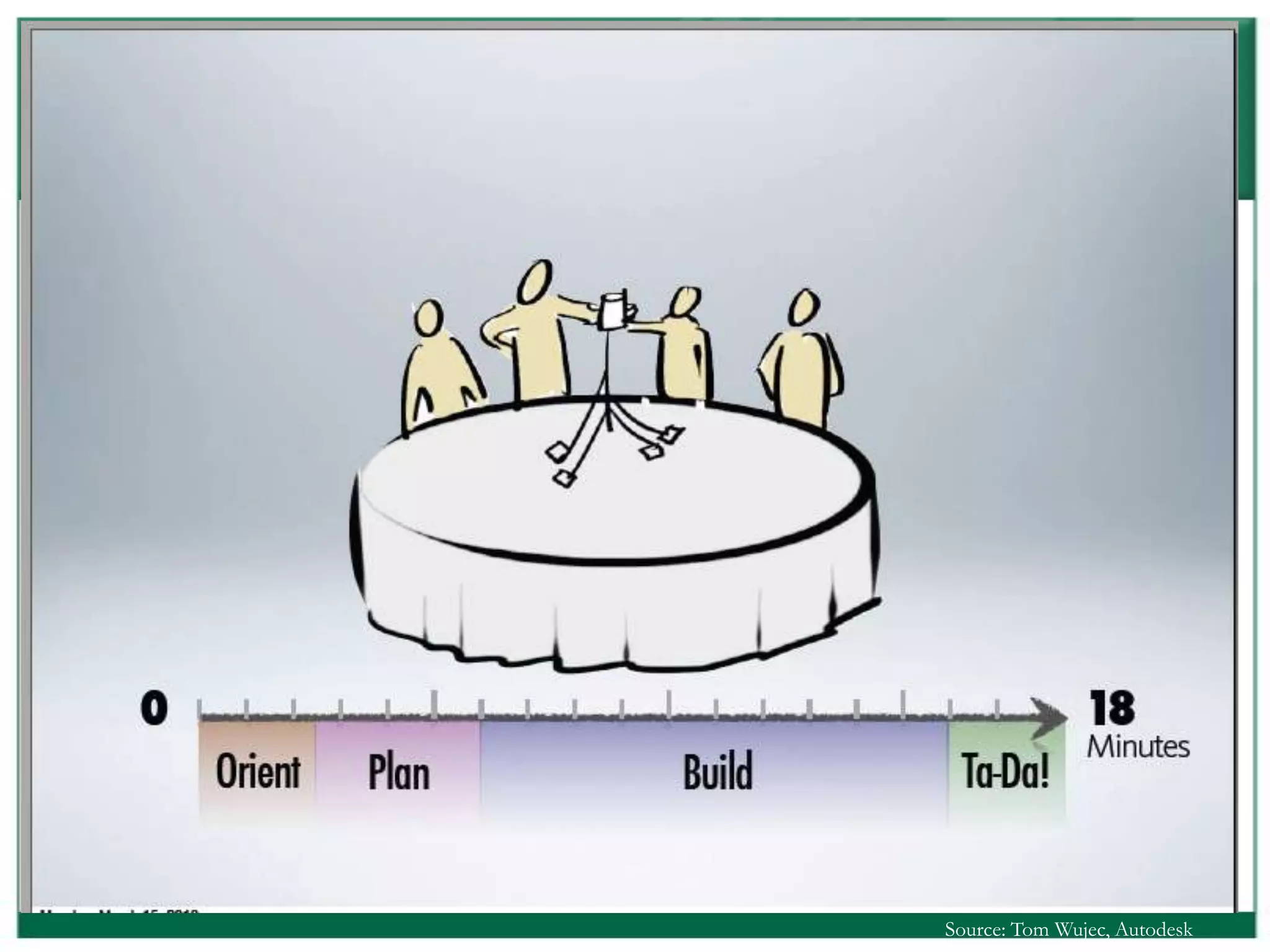
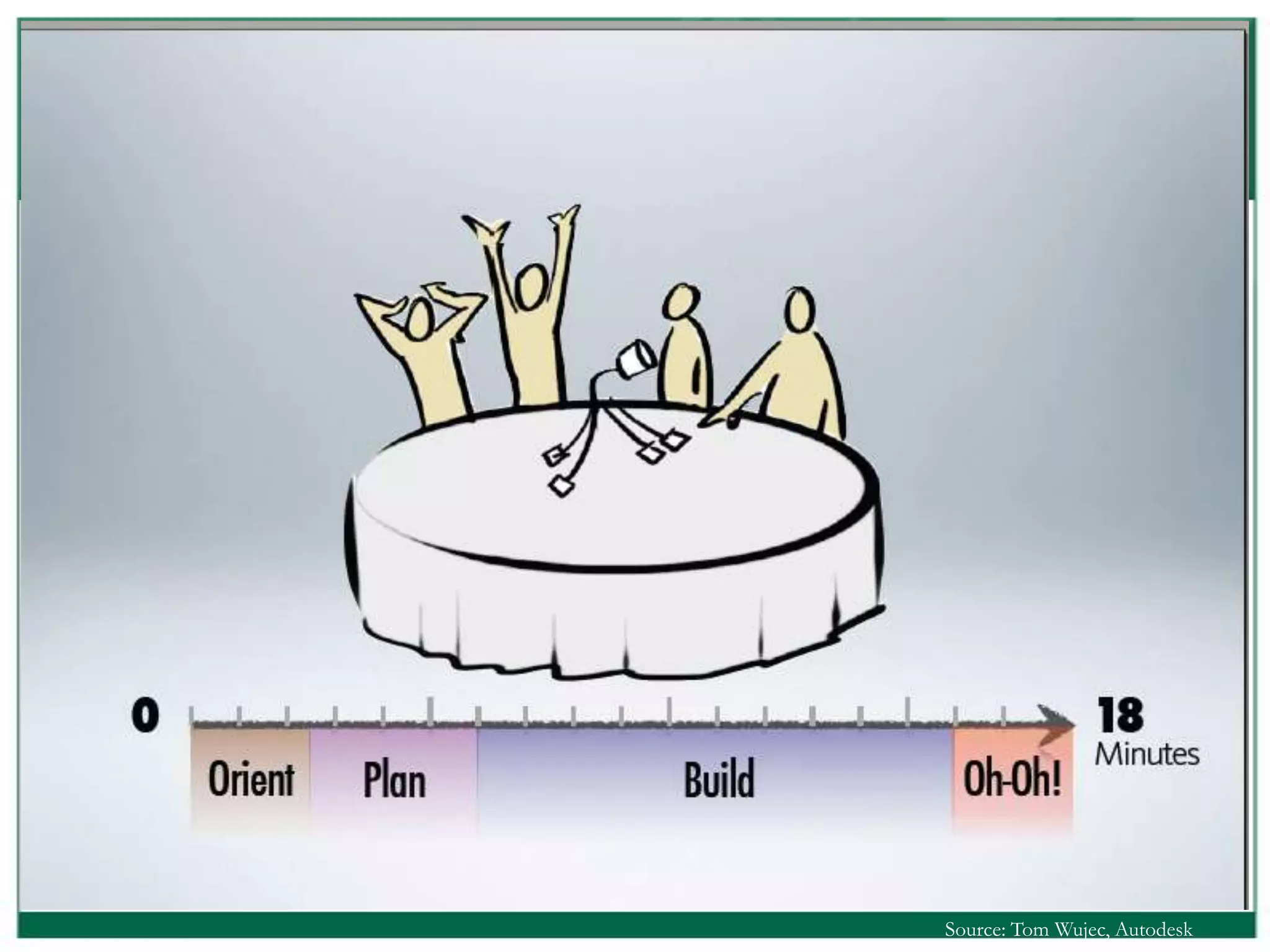
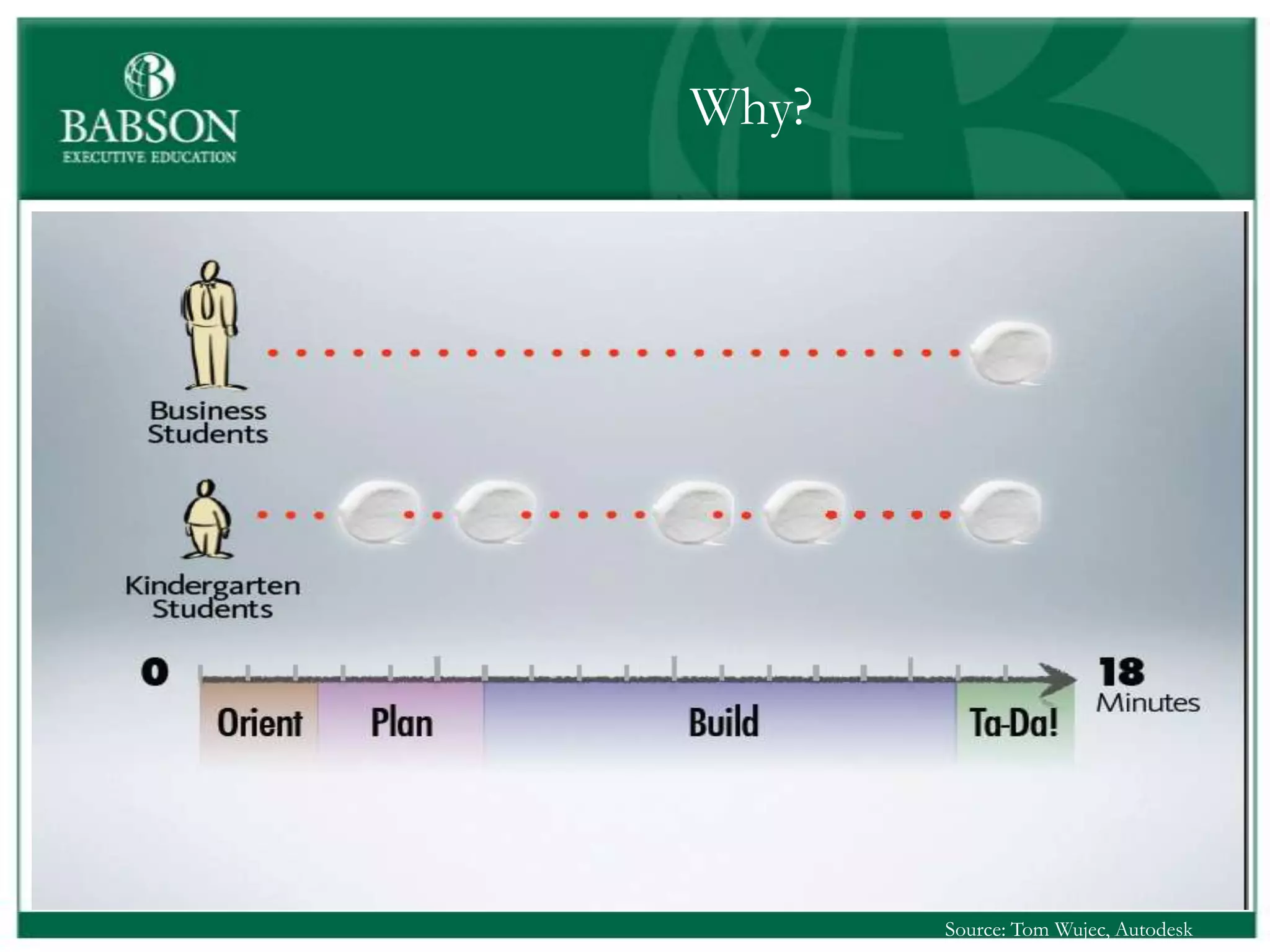
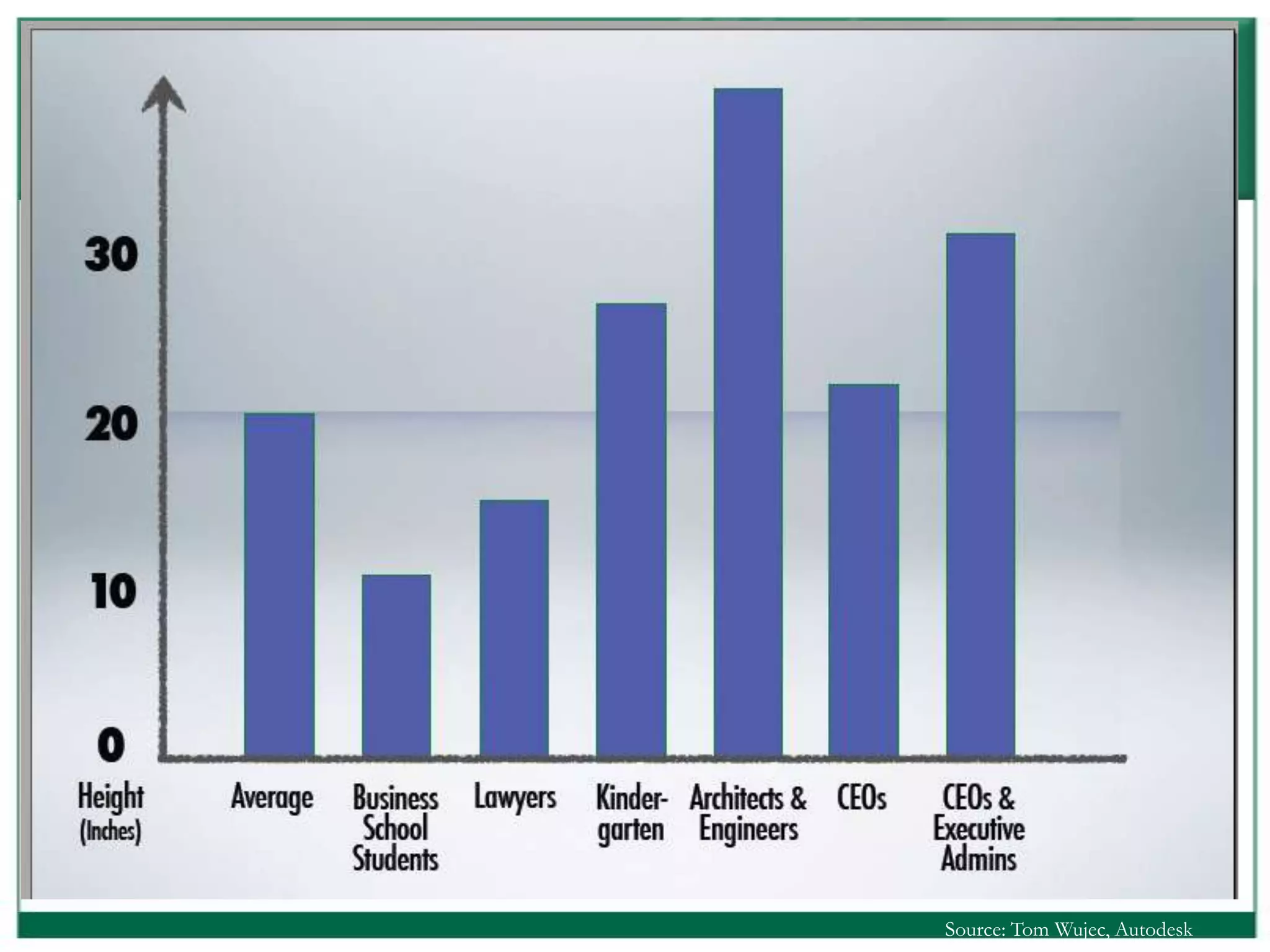
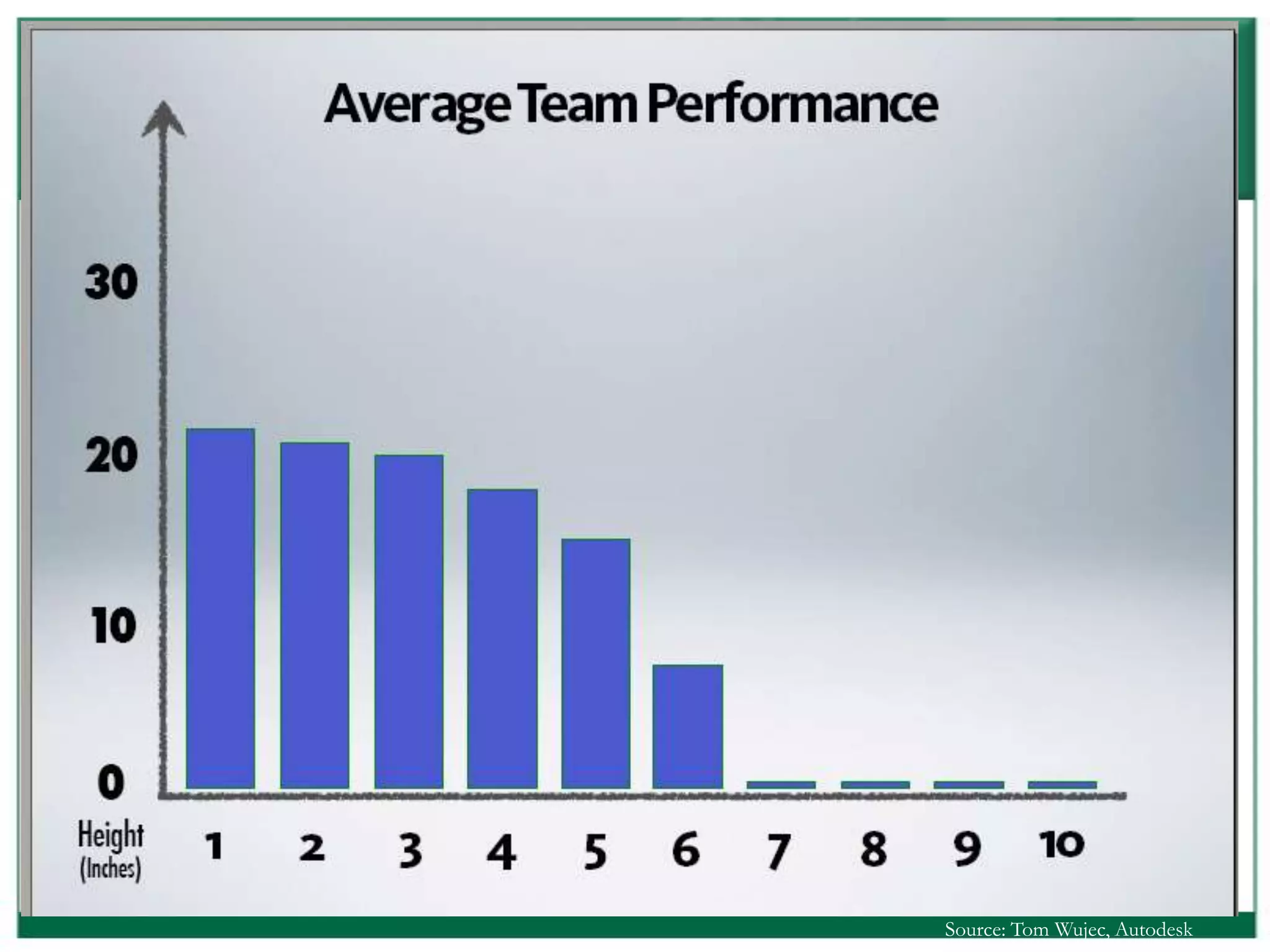
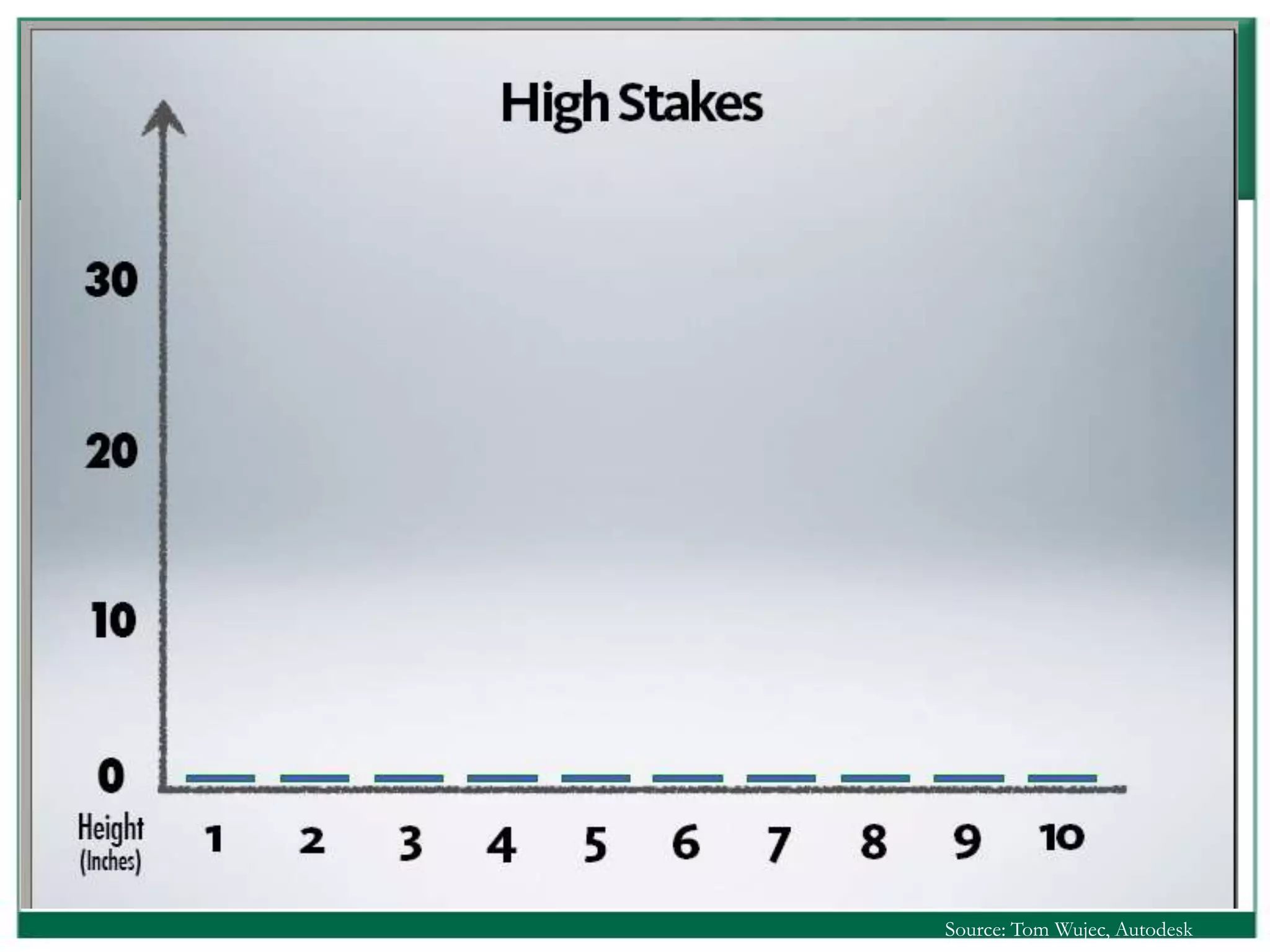
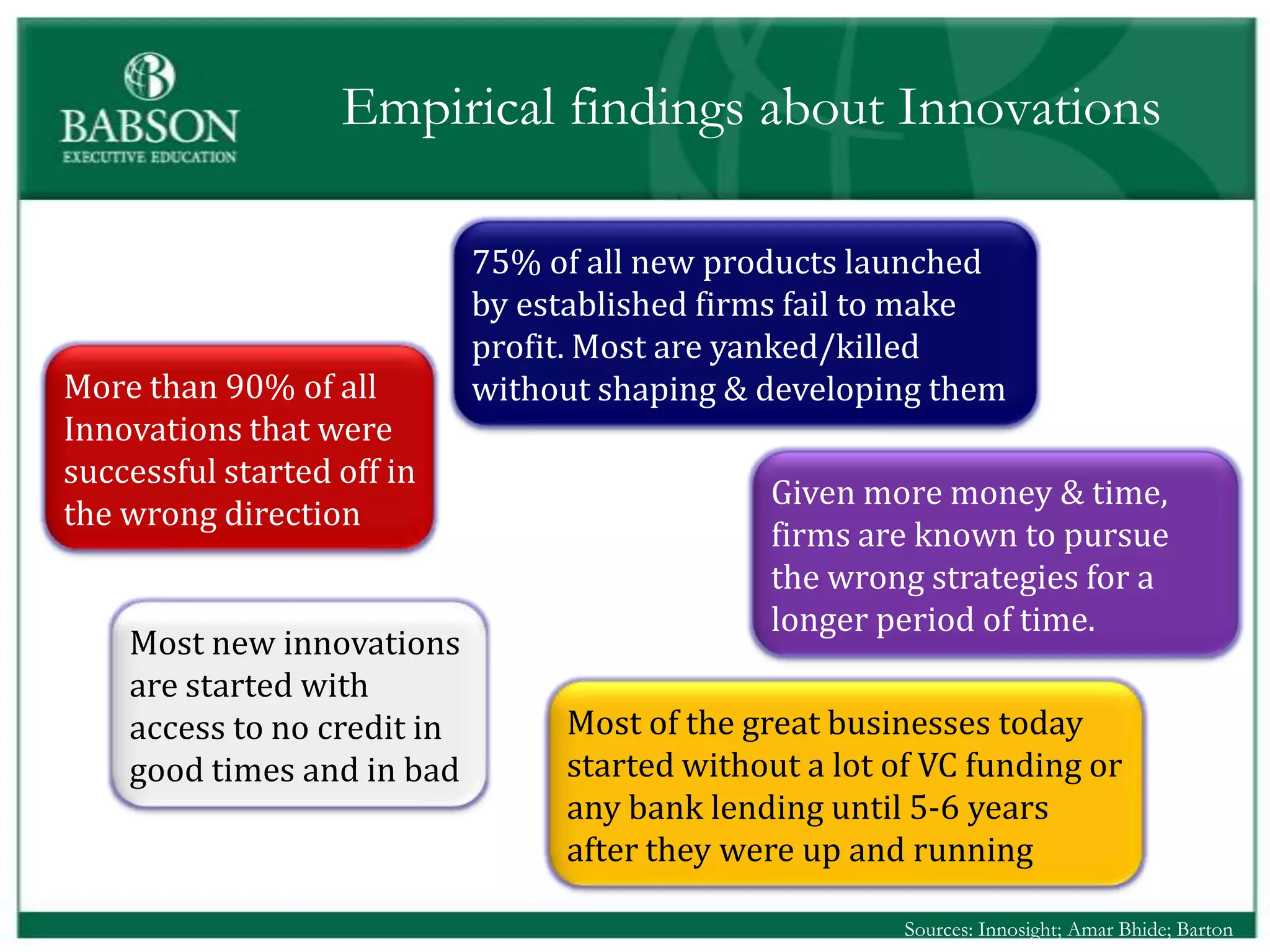
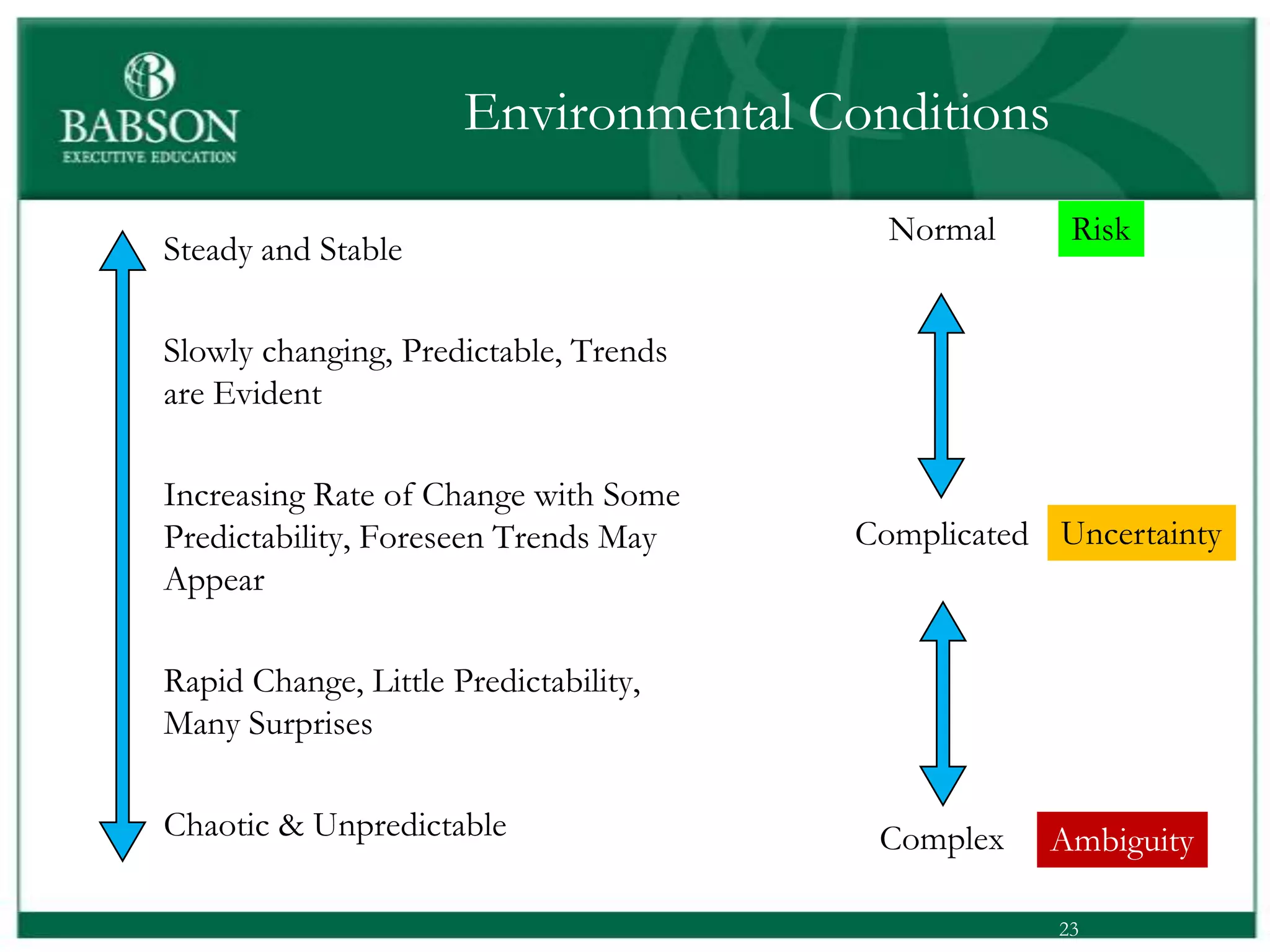
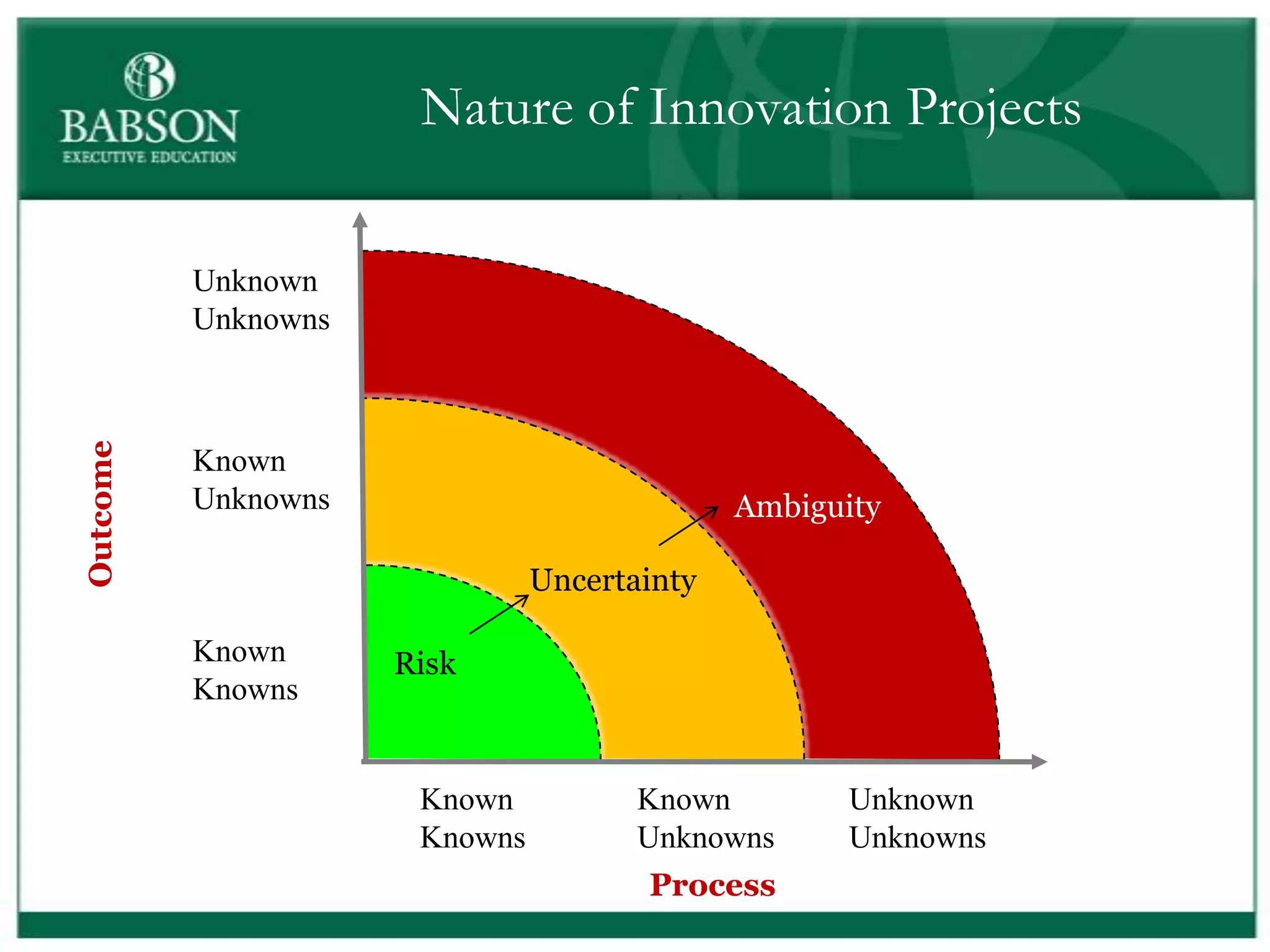
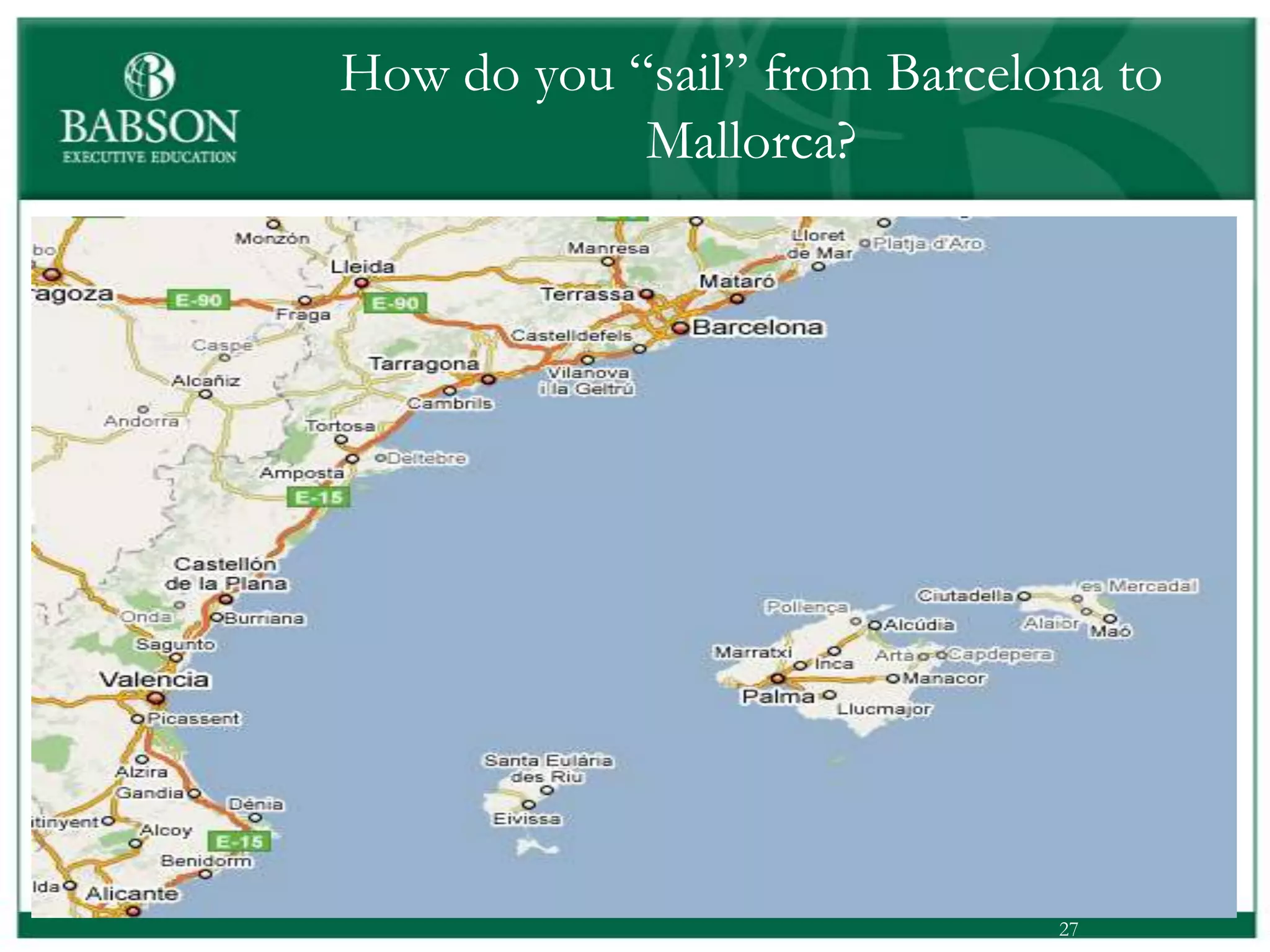
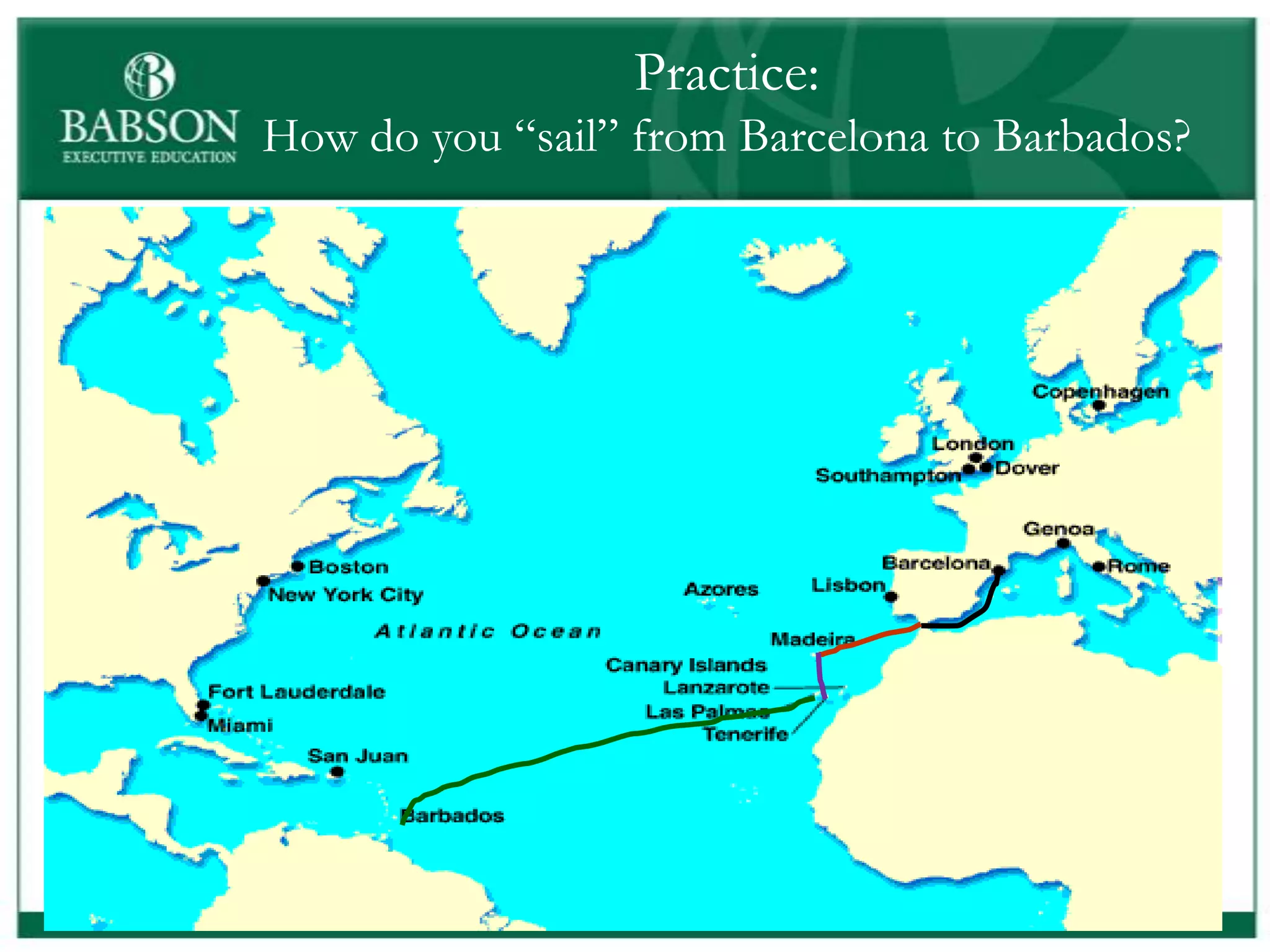
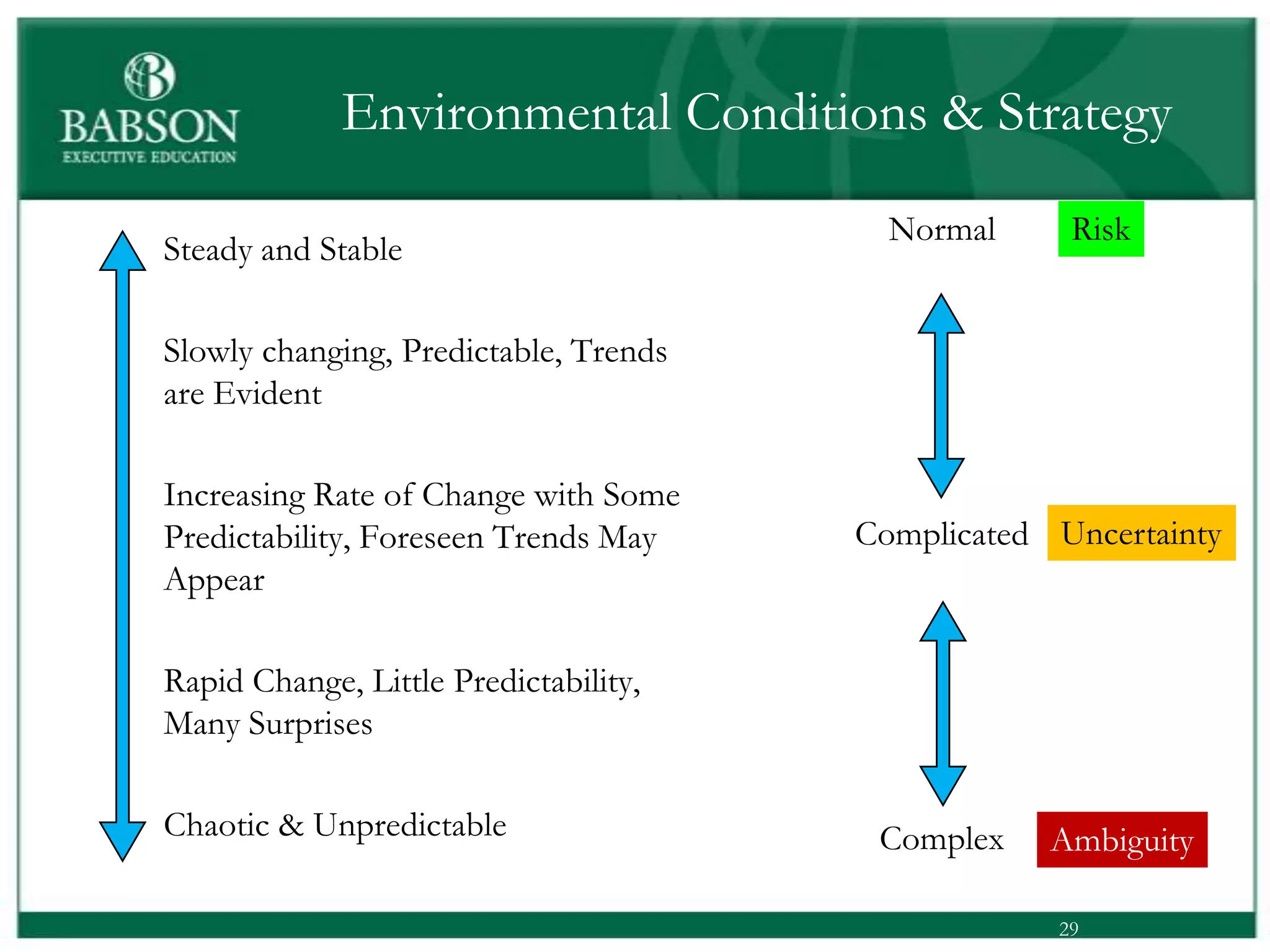
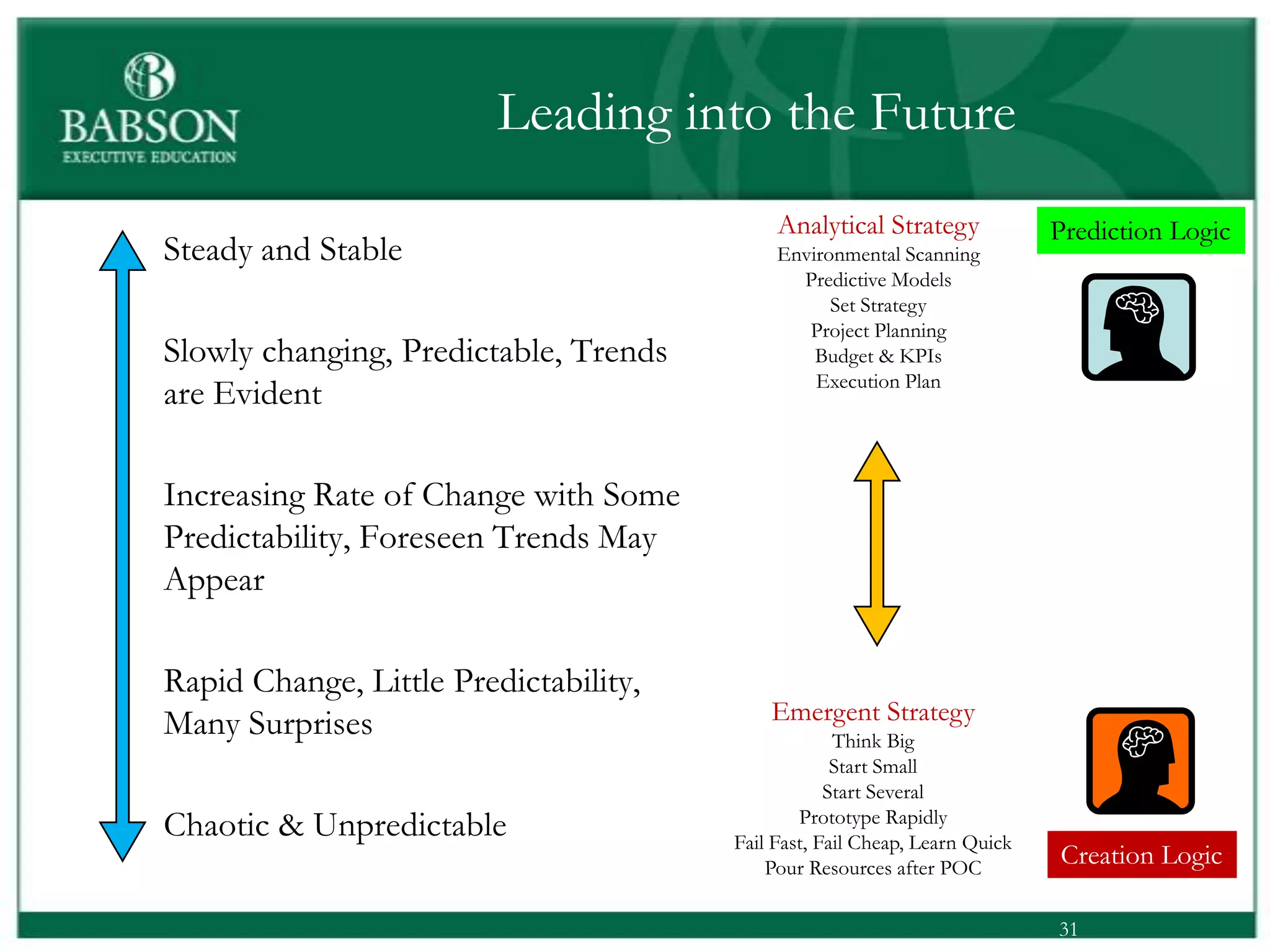
The document outlines the rules and lessons from the Marshmallow Tower game, emphasizing teamwork and rapid prototyping. It discusses broader findings related to innovation, highlighting the high failure rate of new products and the ineffectiveness of current innovation strategies. Key insights include the importance of diverse skills, the need for emergent strategies, and learning through action to foster effective innovation processes.