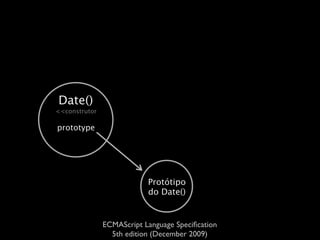
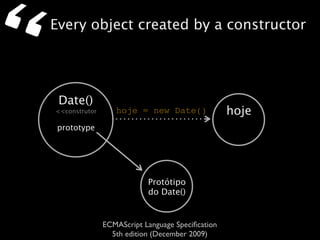
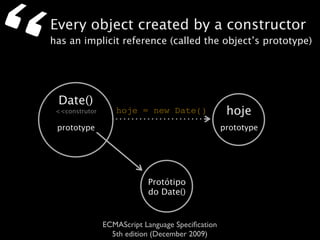
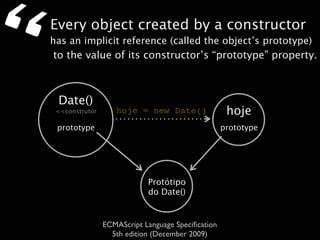
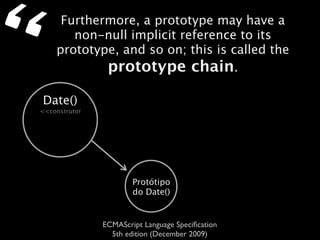
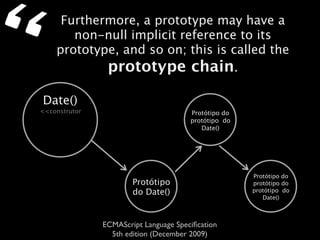
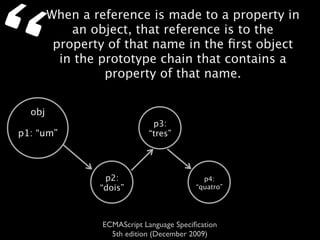
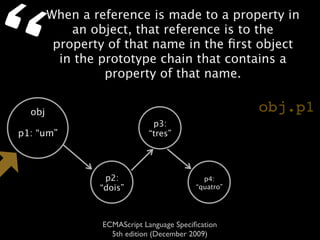
The document is a specification from ECMA International that defines the ECMAScript language. It describes ECMAScript as an object-oriented scripting language intended to be used in web browsers and web servers to perform computations and manipulate objects within a host environment provided by the browser or server. It outlines the core language types, operators, statements and provides examples of how ECMAScript scripts can interact with objects in the browser environment like windows, forms and events.




![function validateForm() {
var x = document.forms["myForm"]["fname"].value
if (x == null || x == "") {
alert("Nome obrigatório!");
return false;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-5-320.jpg)





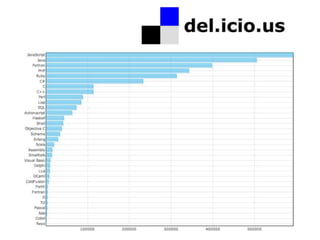
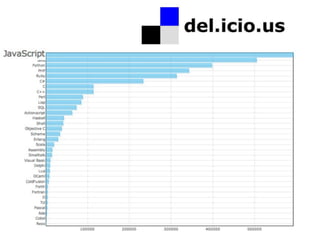






























![Estruturas
for/in
var array = [1,3,5,7,9]
for (var i in array) {
alert(array[i])
}
(...)
ECMAScript Language Specification
5th edition (December 2009)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-48-320.jpg)
![Estruturas
for/each/in
> var obj = { a: 1, b: 3, c: 5 }
> obj.a
1
> for(p in obj) {
alert(p + ": " + obj[p])
}
> for each (v in obj) {
alert(v) // v aqui igual ao obj[p] acima
}
ECMAScript Language Specification
5th edition (December 2009)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-49-320.jpg)





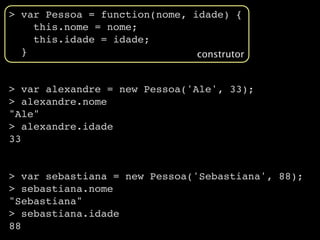
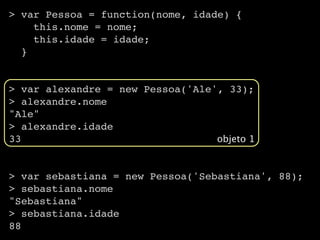
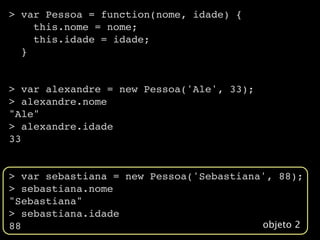
![> var ale = new Object()
> ale.nome = "Alexandre Gomes"
"Alexandre Gomes"
> ale.nascimento = new Date(1977,8,8)
Thu Sep 08 1977 00:00:00 GMT-0300 (BRT)
> ale.nome
"Alexandre Gomes"
> ale.nascimento
Thu Sep 08 1977 00:00:00 GMT-0300 (BRT)
> ale[‘nome’]
"Alexandre Gomes"
> ale[‘nascimento’]
Thu Sep 08 1977 00:00:00 GMT-0300 (BRT)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-56-320.jpg)


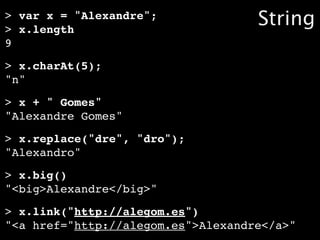

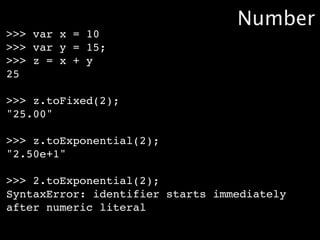
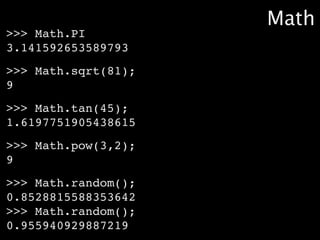
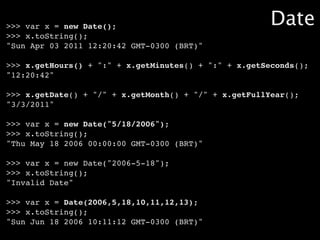
![>>> var texto = "O gato roeu a roupa do rei de roma";
>>> var regex = new RegExp("gato", “”);
>>> texto.match(regex);
["gato"]
Regex
>>> regex.exec(texto);
["gato"]
>>> texto.match(/gato/);
["gato"]
>>> texto.match(/O gato/);
["O gato"]
>>> texto.match(/o gato/);
null
>>> texto.match(/o gato/i);
["O gato"]
>>> texto.match(/o gato.*/i);
["O gato roeu a roupa do rei de roma"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-65-320.jpg)
![var x = new Array();
>>> [] Array
x[0] = "laranja"
>>> ["laranja"]
x[2] = "maçã"
>>> ["laranja", undefined, "maçã"]
x.length
>>> 3
x.sort();
>>> ["laranja", "maçã", undefined]
x.reverse();
>>> [undefined, "maçã", "laranja"]
x = ["pera", "uva", new Date()]
x.toString();
>>> "pera,uva,Sun Apr 03 2011 11:53:18 GMT-0300 (BRT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-67-320.jpg)

















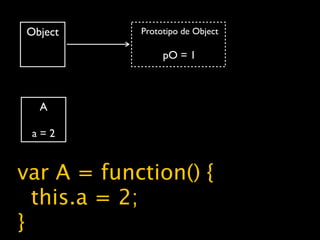
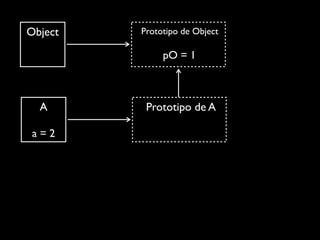
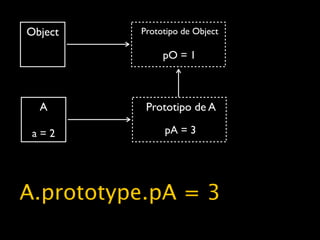
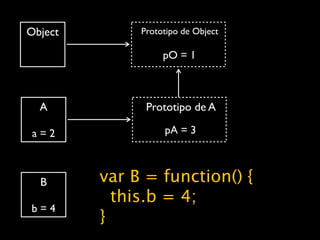













![cubes = (function() {
var _i, _len, _results;
_results = [];
for (_i = 0, _len = list.length; _i < _len; _i++) {
num = list[_i];
_results.push(math.cube(num));
}
return _results;
})();
cubes = (math.cube num for num in list)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptdojeitocerto-110413232207-phpapp01/85/Javascript-do-jeito-certo-172-320.jpg)

