Recommended
PPTX
Operators in java By cheena
PDF
PDF
PPTX
OOPJ_PPT2,JAVA OPERATORS TPYE WITH EXAMPLES.pptx
PPT
4_A1208223655_21789_2_2018_04. Operators.ppt
PPT
PPTX
PPT ON JAVA AND UNDERSTANDING JAVA'S PRINCIPLES
PPTX
Java Operators with Simple introduction.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Arithmetic Operators ____ java.pptx
PDF
PDF
Programming in Java-Operators in Java with examples
PDF
Programming in Java: Introduces Operators in Java
PDF
Programming in Java- on operators types and usage
PPTX
Java Operators with Simple introduction.pptx
PDF
4.Lesson Plan - Java Operators.pdf...pdf
PPTX
Computer programming 2 Lesson 7
PDF
PPTX
Lecture-02-JAVA, data type, token, variables.pptx
PPTX
dizital pods session 3.pptx
PPTX
Pj01 4-operators and control flow
PPTX
presentation on array java program operators
DOCX
PPTX
java-tokens-data-types.pptx ciiiidddidifif
PPTX
MEMORY &FORGETTING. Shilpa Hotakar.Psychology pptx
PDF
Artificial Intelligence in Research and Academic Writing, Workshop on Researc...
More Related Content
PPTX
Operators in java By cheena
PDF
PDF
PPTX
OOPJ_PPT2,JAVA OPERATORS TPYE WITH EXAMPLES.pptx
PPT
4_A1208223655_21789_2_2018_04. Operators.ppt
PPT
PPTX
PPT ON JAVA AND UNDERSTANDING JAVA'S PRINCIPLES
PPTX
Java Operators with Simple introduction.pptx
Similar to Java_Operators_and_Shift_Operations (1).pptx
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Arithmetic Operators ____ java.pptx
PDF
PDF
Programming in Java-Operators in Java with examples
PDF
Programming in Java: Introduces Operators in Java
PDF
Programming in Java- on operators types and usage
PPTX
Java Operators with Simple introduction.pptx
PDF
4.Lesson Plan - Java Operators.pdf...pdf
PPTX
Computer programming 2 Lesson 7
PDF
PPTX
Lecture-02-JAVA, data type, token, variables.pptx
PPTX
dizital pods session 3.pptx
PPTX
Pj01 4-operators and control flow
PPTX
presentation on array java program operators
DOCX
PPTX
java-tokens-data-types.pptx ciiiidddidifif
Recently uploaded
PPTX
MEMORY &FORGETTING. Shilpa Hotakar.Psychology pptx
PDF
Artificial Intelligence in Research and Academic Writing, Workshop on Researc...
PDF
Judgement Regarding Land Acquisition Act not Applicable to Encroachers.pdf
PPTX
Chapter 1: Introduction to Strategic Management.pptx
PPTX
GRADE 8_WEEK 2_QUARTER 4_ENGLISH_MATATAG.pptx
PPTX
ENGLISH-7-Quarter-4-Week-3 Matatag .pptx
PPTX
Math 8 Quarter 4 Week 4-SECONDARY DATA.pptx
PPTX
A brief introduction to Minor vegetable crops.pptx
PDF
RAJAT ARORA SIR PHYSICAL EDUCATION NOTES ALL CHAPTERS .pdf
PDF
Project Management Unit I SE OE-II SPPU Pune (2024 Pattern)
PDF
Using T-Test to Analyze Research Data.pdf
PDF
How "Raiders of the Lost Ark" and "Ordinary People" Employ Non-Verbal Acting
PPTX
WEEK 2 (2).pptx TLE COOKERY 10 QUARTER 4
PPTX
Math 8 Quarter 4 Week 3 PRIMARY DATA.pptx
PPTX
Health9_Q4 PPT_Week 1_Lesson 1 (Intentional Injuries).pptx
PPTX
How to Manage Checkout Policy & Customer Portal in Odoo 18 Website
PPTX
How to Manage Reservation Method in Odoo 18 Inventory
PDF
TỔNG HỢP 156 ĐỀ CHÍNH THỨC KỲ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI TIẾNG ANH LỚP 12 CÁC TỈN...
PPTX
Cultivation practice of Okra in Nepal.pptx
PDF
Workshop 29 Crystal Review All Students by YogiGoddess
Java_Operators_and_Shift_Operations (1).pptx 1. Operators and Expressions
Operators: Symbols used to perform operations on variables and values.
Expressions: A combination of variables, operators, and values that produce a result.
Example: int result = a + b * c;
2. 3. Relational Operators
== Equal to
!= Not equal to
> Greater than
< Less than
>= Greater than or equal to
<= Less than or equal to
Example: if (a > b)
4. 5. 6. 7. Why Arithmetic in Java?
Even with a calculator, arithmetic operations in Java are needed:
- Automate calculations
- Perform dynamic computations in code
- Useful in gaming, finance, simulations, etc.
8. Data Types That Can't Use
Arithmetic
Cannot perform arithmetic on:
- boolean (true/false)
- Objects (non-numeric unless overridden)
- Strings (except + for concatenation)
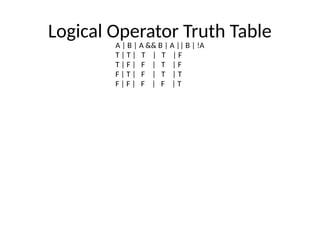
9. Logical Operator Truth Table
A | B | A && B | A || B | !A
T | T | T | T | F
T | F | F | T | F
F | T | F | T | T
F | F | F | F | T
10. Shift Operators in Java
<< Left Shift (multiply by 2ⁿ)
>> Right Shift (divide by 2ⁿ)
>>> Unsigned Right Shift (fills with 0)
Example:
int a = 5; a << 1 = 10