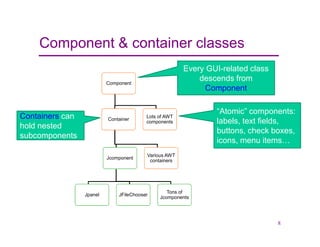
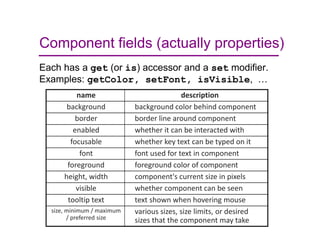
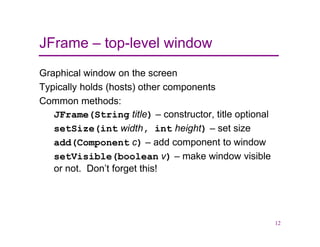
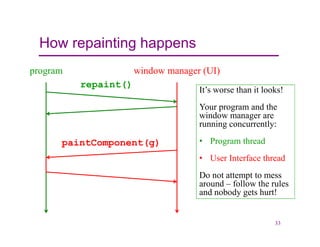
This document provides an overview of Java graphics and GUI programming using the Swing and AWT libraries. It discusses why GUIs are important to study, the key components and containers in the Swing/AWT hierarchy like JFrame and JPanel. It also covers graphics drawing, layout managers that position components, and event-driven programming. The document is intended as an introduction to working with Java GUIs and graphics.