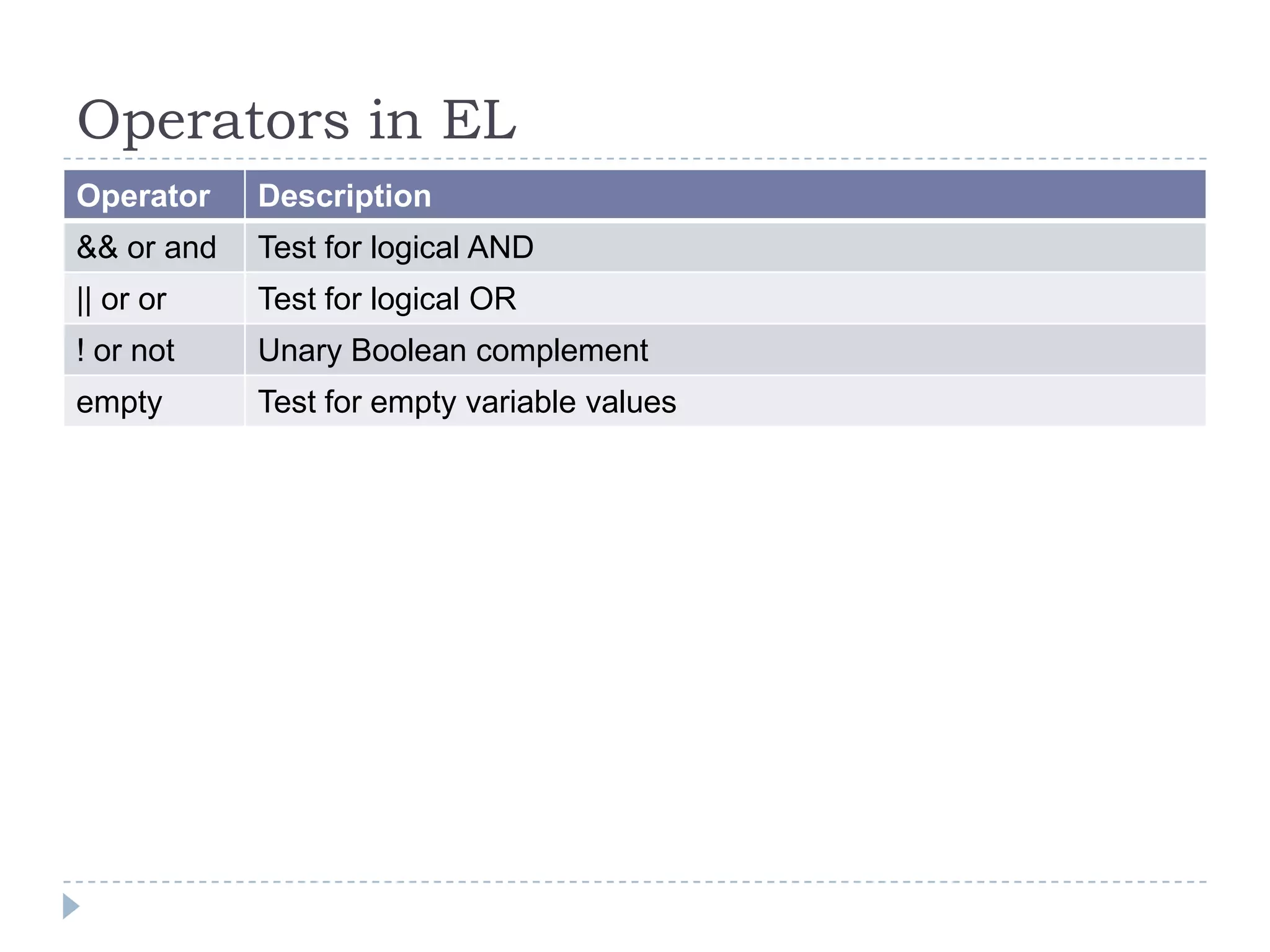
JavaBeans are Java classes that follow certain conventions to allow their properties and methods to be accessed easily. A JavaBean must have a no-argument constructor, implement Serializable, and have getter and setter methods for any properties. Expression Language allows easy access to JavaBean properties through operators like . and [] and is evaluated by the container unless isELIgnored is set to true. Common operators in EL include arithmetic, logical, comparison, and empty.




![Expression Language (EL)
Here expr specifies the expression itself. The most
common operators in JSP EL are . and []. These two
operators allow you to access various attributes of Java
Beans and built-in JSP objects.
For example above syntax <jsp:setProperty> tag can be
written with an expression like:
<jsp:setProperty name="box" property="perimeter"
value="${2*box.width+2*box.height}"/>
When the JSP compiler sees the ${} form in an attribute,
it generates code to evaluate the expression and
substitutes the value of expression.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabeans-131114005559-phpapp01/75/Java-beans-5-2048.jpg)

![Operators in EL
Operator
Description
.
Access a bean property or Map entry
[]
Access an array or List element
()
Group a sub-expression to change the evaluation order
+
Addition
-
Subtraction or negation of a value
*
Multiplication
/ or div
Division
%
Modulo (remainder)
== or eq
Test for equality
!= or ne
Test for inequality
< or lt
Test for less than
> or gt
Test for greater than
<= or le
Test for less than or equal
>= or gt
Test for greater than or equal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabeans-131114005559-phpapp01/75/Java-beans-7-2048.jpg)