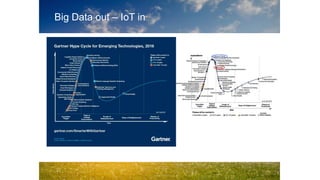
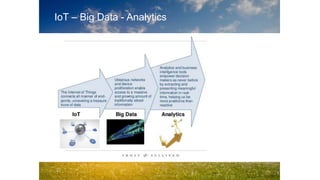
1. Digitization is changing everything from how we access media to new forms of transportation like ride sharing.
2. The Digital Single Market strategy aims to improve access to digital goods and services, support digital networks and services, and make digitization a driver for economic growth.
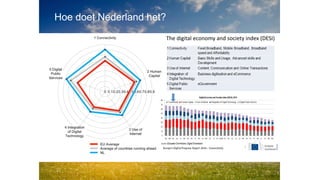
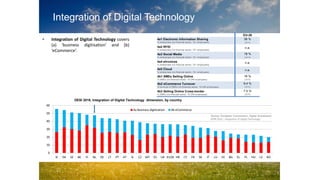
3. The Netherlands currently has a good starting position in Europe according to the DESI index, but further digitization of the economy is a focus of the Dutch Digital Agenda.