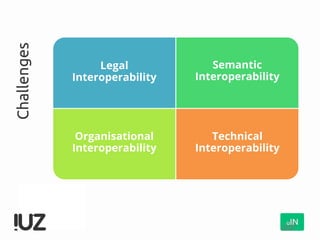
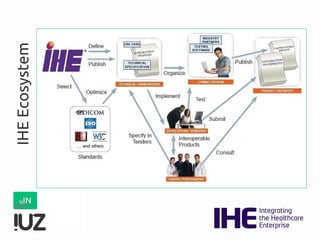
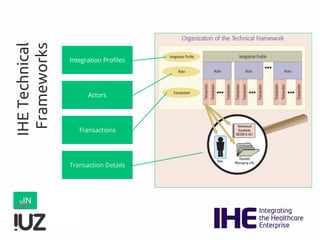
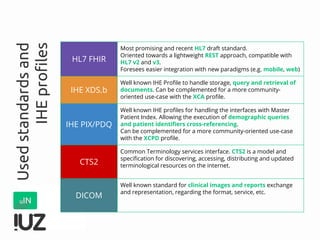
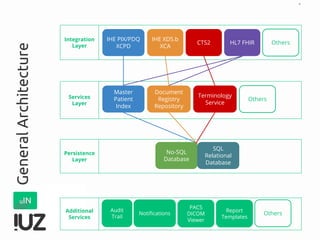
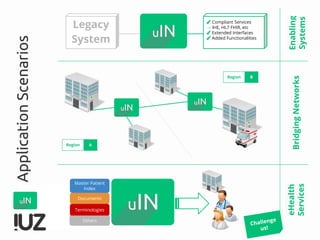
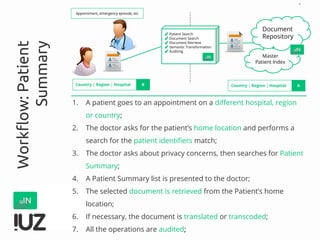
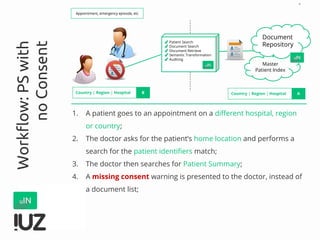
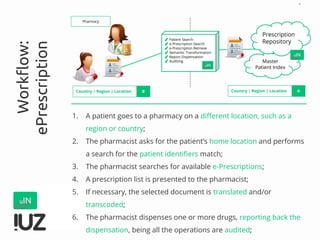
The document outlines the concept of cross-border interoperability in healthcare, emphasizing the ability to exchange health information across countries while addressing various challenges, including legal, semantic, and technical interoperability. It highlights the roles of initiatives like IHE and HL7 in promoting standards for better information exchange and patient care, as well as providing examples of workflows and use cases for effective implementation. Additionally, it discusses the integration of systems, services, and different actors to enhance healthcare cooperation and improve patient outcomes.