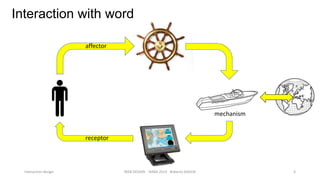
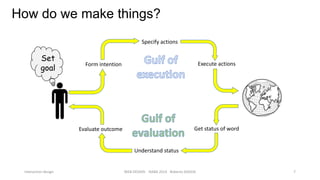
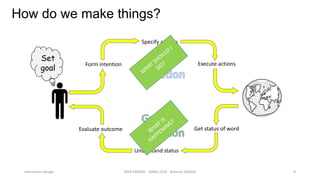
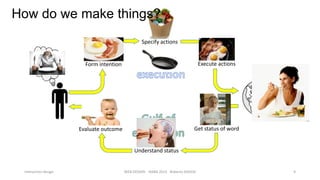
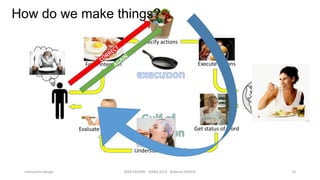
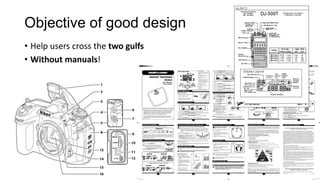
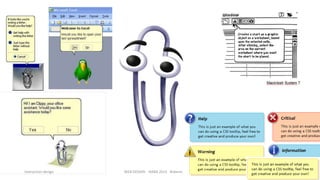
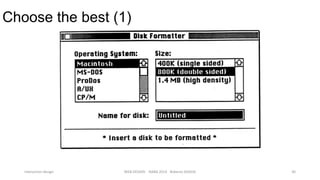
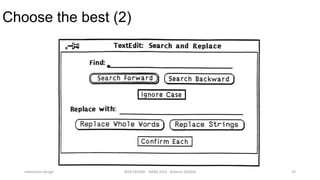
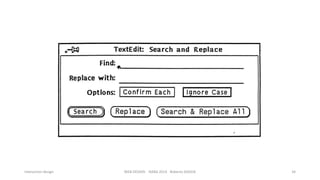
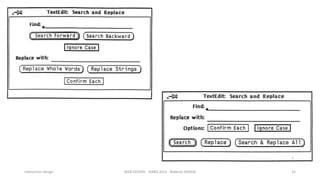
This document discusses interaction design and principles for user-centered design. It covers several topics: the seven stages of human action with goals, intentions, actions, feedback, and evaluation; crossing the gulfs of execution and evaluation in design; affordances and how objects provide clues about their use; the ISO principles of suitability, self-descriptiveness, controllability, conformity, error tolerance, individualization and learning; and tradeoffs in design decisions. The document emphasizes designing intuitive interfaces that guide users without the need for manuals.