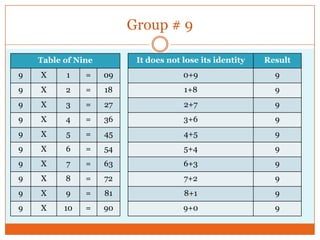
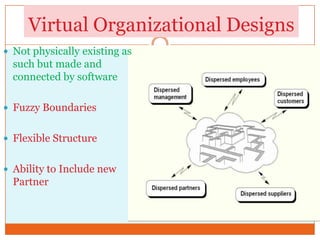
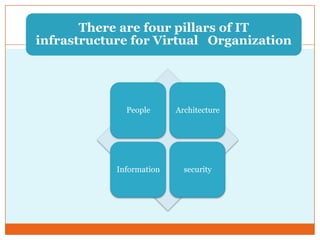
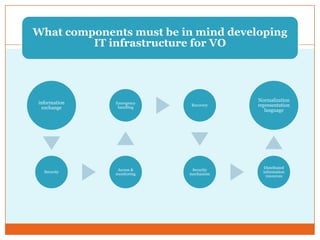
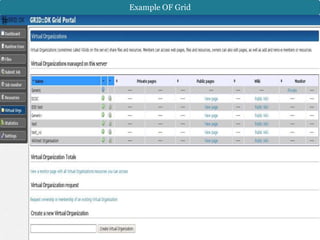
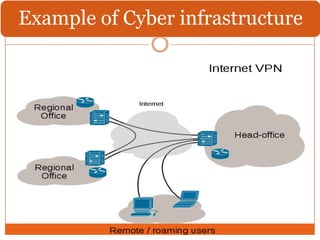
This document discusses the IT infrastructure needed to support a virtual organization. It first defines a virtual organization as a temporary or permanent coalition of dispersed individuals, groups, or organizations that pool resources to achieve common goals relying on information technology. It then outlines some key components of an IT infrastructure for a virtual organization, including networking, distributed computing, web services, security, and facilities like email, file sharing, and video conferencing. Finally, it discusses approaches to building such an infrastructure, such as grid computing, cloud computing, and virtualization, and some technical challenges around compatibility, security, and dynamic technology changes.



















![References
[1]S.E. Bleaker, The virtual organization, Futurist 28 2.2010.
[2]Infrastructures for virtual organizations – where we are Luis M.
Camarinha-Matos New University of Lisbon Quinta da Torre – 2829-516
Monte Caparica, Portugal.
[3] L. M. Camarinha-Matos, H. Afsarmanesh, “Virtual Enterprise
Modeling and Support Infrastructures:Applying Multi- Agent Systems
Approaches”, in Multi-Agent Systems and Applications, M. Luck, V. Marik,
O. Stpankova, R. Trappl (eds.), Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence
LNAI 2086, pp.335-364, Springer, ISBN 3-540-42312-5, July 2001.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itinfra4vo-140405114350-phpapp01/85/IT-infrastructure-for-Virtual-Organization-26-320.jpg)
![27
[4] The Anatomy of the Grid Enabling Scalable Virtual Organizations *
Ian Foster • Carl Kesselman § Steven Tuecke • {foster,
tuecke}@mcs.anl.gov, carl@isi.edu
[5] Virtual Teams: a Literature Review
Nader Ale Ebrahim, Shamsuddin Ahmed and Zahari Taha
Department of Engineering Design and Manufacture, Faculty of
Engineering, University of Malaya
50603, Lembah Pantai, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itinfra4vo-140405114350-phpapp01/85/IT-infrastructure-for-Virtual-Organization-27-320.jpg)
