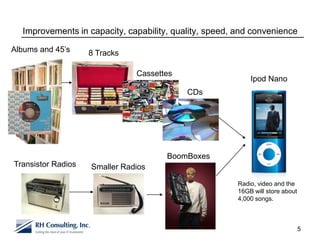
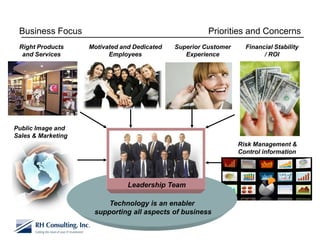
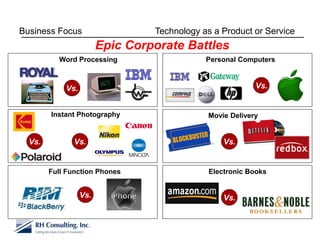
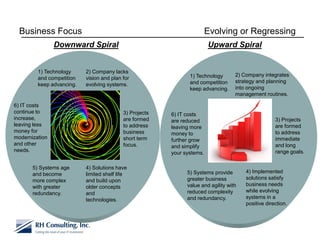
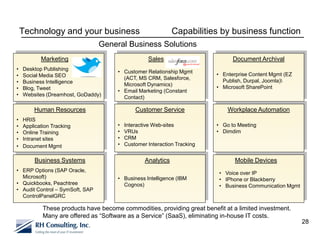
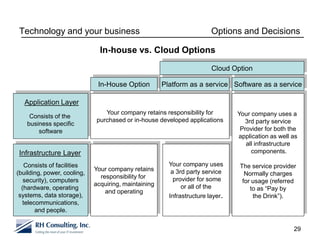
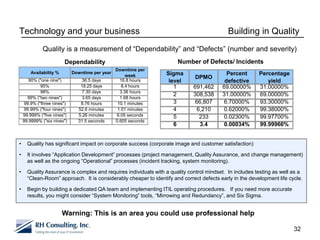
The document discusses using technology to transform business. It begins by asking business leaders about their comfort level with technology, whether they feel like they are drowning, treading water, or surfing with technology. It then covers several topics related to technology and business, including social media, cloud computing, business intelligence, and more. The document aims to highlight areas business leaders need to think about to improve conversations and decision making using technology.